|
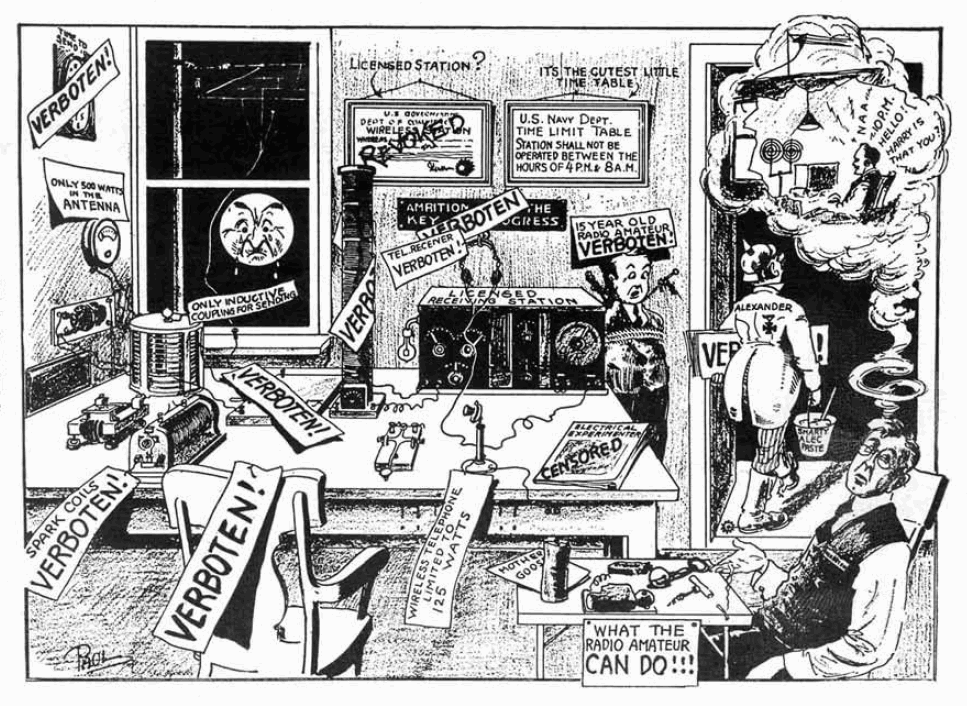
General Power Of Competence
"Everything which is not forbidden is allowed" is a legal maxim. It is the concept that any action can be taken unless there is a law against it. It is also known in some situations as the "general power of competence" whereby the body or person being regulated is acknowledged to have competent judgement of their scope of action. The opposite principle "everything which is not allowed is forbidden" states that an action can only be taken if it is specifically allowed. A senior English judge, Sir John Laws, stated the principles as: "For the individual citizen, everything which is not forbidden is allowed; but for public bodies, and notably government, everything which is not allowed is forbidden." Legal philosopher Ota Weinberger put it this way: "In a closed system in which all obligations are stated explicitly the following inference rules are valid: (XI) Everything which is not forbidden is allowed". Domestic law Czech Republic The Czech constitution, Article 2, paragrap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coronavirus Act 2020
The Coronavirus Act 2020 (c. 7) is an act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom that granted the government emergency powers to handle the COVID-19 pandemic. The act allowed the government the discretionary power to limit or suspend public gatherings, to detain individuals suspected to be infected by COVID-19, and to intervene or relax regulations in a range of sectors to limit transmission of the disease, ease the burden on public health services, and assist healthcare workers and the economically affected. Areas covered by the act included the National Health Service, social care, schools, police, Border Force, local councils, funerals and courts. The act was introduced to Parliament on 19 March 2020, and passed the House of Commons without a vote on 23 March, and the House of Lords on 25 March. The act received royal assent on 25 March 2020. The act specified a two-year time limit that could be shortened or lengthened by six months at ministerial discretion. Several of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exception That Proves The Rule
"The exception that proves the rule" is a saying whose meaning is contested. Henry Watson Fowler's ''Modern English Usage'' identifies five ways in which the phrase has been used, and each use makes some sort of reference to the role that a particular case or event takes in relation to a more general rule. Two original meanings of the phrase are usually cited. The first, preferred by Fowler, is that the presence of an exception applying to a ''specific'' case establishes ("proves") that a ''general'' rule exists. A more explicit phrasing might be "the exception that proves ''the existence of'' the rule." Most contemporary uses of the phrase emerge from this origin, although often in a way which is closer to the idea that all rules have their exceptions. The alternative origin given is that the word "prove" is used in the archaic sense of "test", a reading advocated, for example, by a 1918 ''Detroit News'' style guide:''The exception proves the rule'' is a phrase that arises from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Entick V Carrington
''Entick v Carrington'' 765EWHC KB J98is a leading case in English law and UK constitutional law establishing the civil liberties of individuals and limiting the scope of executive (government), executive power. The case has also been influential in other common law jurisdictions and was an important motivation for the Fourth Amendment to the United States Constitution. It is famous for the dictum of Lord Camden: "If it is law, it will be found in our books." Facts On 11 November 1762, the King's Chief Messenger, Nathan Carrington, and three other King's messengers, James Watson, Thomas Ardran, and Robert Blackmore, broke into the home of the Grub Street writer John Entick (c. 1703 – 1773) in the parish of St Dunstan, Stepney "with force and arms". Over the course of four hours, they broke open locks and doors and searched all of the rooms before taking away 100 charts and 100 pamphlets, causing £2,000 of damage (). The King's messengers were acting on the orders of L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ace Trade
Ace Books is a publisher of science fiction (SF) and fantasy books founded in New York City in 1952 by A. A. Wyn, Aaron A. Wyn. It began as a genre publisher of mystery fiction, mysteries and western (genre), westerns, and soon branched out into other genres, publishing its first science fiction title in 1953. This was successful, and science fiction titles outnumbered both mysteries and westerns within a few years. Other genres also made an appearance, including nonfiction, Gothic fiction, gothic novels, media tie-in novelizations, and romance novel, romances. Ace became known for the ''dos-à-dos binding#Tête-bêche, tête-bêche'' binding format used for many of its early books, although it did not originate the format. Most of the early titles were published in this "Ace Double" format, and Ace continued to issue books in varied genres, bound ''tête-bêche'', until 1973. Ace, along with Ballantine Books, was one of the leading science fiction publishers for its first ten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Once And Future King
''The Once and Future King'' is a collection of fantasy novels by T. H. White about the legend of King Arthur. It is loosely based upon the 1485 work ''Le Morte d'Arthur'' by Sir Thomas Malory. It was first published in 1958 as a collection of shorter novels that were published from 1938 to 1940, with some new or amended material. The title refers to a legend that Arthur will one day return as king. Plot Most of the book takes place in Gramarye, the name that White gives to Britain, and chronicles the youth and education of King Arthur, his rule as a king, and the romance between Sir Lancelot and Queen Guinevere. The story starts in the final years of the rule of King Uther Pendragon. '' The Sword in the Stone'' The first part, "The Sword in the Stone" (first published 1938), chronicles Arthur's upbringing by his foster father Sir Ector, his rivalry and friendship with his foster brother Kay, and his initial training by Merlyn, a wizard who lives through time backwards. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
State (polity)
A state is a politics, political entity that regulates society and the population within a definite territory. Government is considered to form the fundamental apparatus of contemporary states. A country often has a single state, with various administrative divisions. A state may be a unitary state or some type of federation, federal union; in the latter type, the term "state" is sometimes used to refer to the federated state, federated polities that make up the federation, and they may have some of the attributes of a sovereign state, except being under their federation and without the same capacity to act internationally. (Other terms that are used in such federal systems may include "province", "Region#Administrative regions, region" or other terms.) For most of prehistory, people lived in stateless societies. The earliest forms of states arose about 5,500 years ago. Over time societies became more Social stratification, stratified and developed institutions leading to Centra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Heinlein
Robert Anson Heinlein ( ; July 7, 1907 – May 8, 1988) was an American science fiction author, aeronautical engineer, and naval officer. Sometimes called the "dean of science fiction writers", he was among the first to emphasize scientific accuracy in his fiction, and was thus a pioneer of the subgenre of hard science fiction. His published works, both fiction and non-fiction, express admiration for competence and emphasize the value of critical thinking. His plots often posed provocative situations which challenged conventional social mores. His work continues to have an influence on the science-fiction genre, and on modern culture more generally. Heinlein became one of the first American science-fiction writers to break into mainstream magazines such as ''The Saturday Evening Post'' in the late 1940s. He was one of the best-selling science-fiction novelists for many decades, and he, Isaac Asimov, and Arthur C. Clarke are often considered the "Big Three" of English-language ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Totalitarian Principle
In quantum mechanics, the totalitarian principle states: "Everything not forbidden is compulsory." Physicists including Murray Gell-Mann borrowed this expression, and its satirical reference to totalitarianism, from the popular culture of the early twentieth century. The statement refers to a surprising feature of particle interactions: that any interaction that is not forbidden by a small number of simple conservation laws is not only allowed, but ''must'' be included in the sum over all " paths" that contribute to the outcome of the interaction. Hence if it is not forbidden, there is some probability amplitude for it to happen. In the many-worlds interpretation of quantum mechanics, the principle has a more literal meaning: that every possibility at every interaction that is not forbidden by such a conservation law will actually happen (in some branch of the wave function). Origin of the phrase Neither the phrase nor its application to quantum physics originated with Gell-Ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sovereign State
A sovereign state is a State (polity), state that has the highest authority over a territory. It is commonly understood that Sovereignty#Sovereignty and independence, a sovereign state is independent. When referring to a specific polity, the term "country" may also refer to a constituent country, or a dependent territory. A sovereign state (polity), state is required to have a permanent population, defined territory, a government not under another, and the capacity to International relations, interact with other sovereign states. In actual practice, recognition or non-recognition by other states plays an important role in determining the status of a country. List of states with limited recognition, Unrecognized states often have difficulty engaging in Diplomacy, diplomatic relations with other sovereign states. History Since the end of the 19th century, almost the entire globe has been divided into sections (countries) with more or less defined borders assigned to different sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lotus Case
The ''Lotus'' case was an international legal case involving French Third Republic, France and Turkey in front of the Permanent Court of International Justice. The case is known for establishing the so-called "''Lotus'' principle" in international law. The case Background On 2 August 1926 the S.S. ''Lotus'', a French steamship, steamer, collided with the S.S. ''Bozkourt'', a Turkish steamer, in a region just north of Mytilene (Greece). As a result of the accident, eight Turkish nationals aboard the ''Bozkourt'' drowned when the vessel was torn apart by the ''Lotus''. Turkey proceeded to arrest the ''Lotus'''s captain, Mr. Demons; he was subsequently charged and condemned by the Turkish Courts for the damage and the deaths caused by the accident. Appeal to the PCIJ France protested against Turkish actions, claiming that, since the crime was committed in International waters, high seas, any charge against Mr. Demons belonged to the Flag state, flag State jurisdiction, i.e. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Law
International law, also known as public international law and the law of nations, is the set of Rule of law, rules, norms, Customary law, legal customs and standards that State (polity), states and other actors feel an obligation to, and generally do, obey in their mutual relations. In international relations, actors are simply the individuals and collective entities, such as states, International organization, international organizations, and non-state groups, which can make behavioral choices, whether lawful or unlawful. Rules are formal, typically written expectations that outline required behavior, while norms are informal, often unwritten guidelines about appropriate behavior that are shaped by custom and social practice. It establishes norms for states across a broad range of domains, including war and diplomacy, Trade, economic relations, and human rights. International law differs from state-based List of national legal systems, domestic legal systems in that it operates ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |