|
Gemstone Irradiation
Gemstone irradiation is a process in which a gemstone is intentionally exposed to large amounts of ionizing radiation in order to enhance its optical properties. Large amounts of ionizing radiation can rearrange the gemstone's crystal structure, altering its optical properties. This can significantly alter the gemstone's color or lessen the visibility of its inclusions. The process, widely practiced in jewelry industry, is done in either a particle accelerator for electron bombardment, a gamma ray facility using the radioactive isotope cobalt-60, or a nuclear reactor for neutron bombardment. Irradiation treatment has enabled the creation of gemstone colors that do not exist or are extremely rare in nature. However, the process, particularly when done in a nuclear reactor, can make the gemstones radioactive. Health risks related to the residual radioactivity in the irradiated gemstones have led to government regulations in many countries. Radioactivity and regulations The te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gemstone
A gemstone (also called a fine gem, jewel, precious stone, semiprecious stone, or simply gem) is a piece of mineral crystal which, when cut or polished, is used to make jewellery, jewelry or other adornments. Certain Rock (geology), rocks (such as lapis lazuli, opal, and obsidian) and occasionally organic chemistry, organic materials that are not minerals (such as amber, Jet (gemstone), jet, and pearl) may also be used for jewelry and are therefore often considered to be gemstones as well. Most gemstones are hard, but some softer minerals such as brazilianite may be used in jewelry because of their color or Lustre (mineralogy), luster or other physical properties that have aesthetic value. However, generally speaking, soft minerals are not typically used as gemstones by virtue of their brittleness and lack of durability. Found all over the world, the industry of coloured gemstones (i.e. anything other than diamonds) is currently estimated at US$1.55billion and is projected to s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infrared
Infrared (IR; sometimes called infrared light) is electromagnetic radiation (EMR) with wavelengths longer than that of visible light but shorter than microwaves. The infrared spectral band begins with the waves that are just longer than those of red light (the longest waves in the visible spectrum), so IR is invisible to the human eye. IR is generally (according to ISO, CIE) understood to include wavelengths from around to . IR is commonly divided between longer-wavelength thermal IR, emitted from terrestrial sources, and shorter-wavelength IR or near-IR, part of the solar spectrum. Longer IR wavelengths (30–100 μm) are sometimes included as part of the terahertz radiation band. Almost all black-body radiation from objects near room temperature is in the IR band. As a form of EMR, IR carries energy and momentum, exerts radiation pressure, and has properties corresponding to both those of a wave and of a particle, the photon. It was long known that fires e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geiger Counter
A Geiger counter (, ; also known as a Geiger–Müller counter or G-M counter) is an electronic instrument for detecting and measuring ionizing radiation with the use of a Geiger–Müller tube. It is widely used in applications such as radiation dosimetry, radiological protection, experimental physics and the nuclear industry. "Geiger counter" is often used generically to refer to any form of dosimeter (or, ''radiation-measuring device''), but scientifically, a Geiger counter is only one specific type of dosimeter. It detects ionizing radiation such as alpha particles, beta particles, and gamma rays using the ionization effect produced in a Geiger–Müller tube, which gives its name to the instrument. In wide and prominent use as a hand-held radiation survey instrument, it is perhaps one of the world's best-known radiation detection instruments. The original detection principle was realized in 1908 at the University of Manchester, but it was not until the development ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
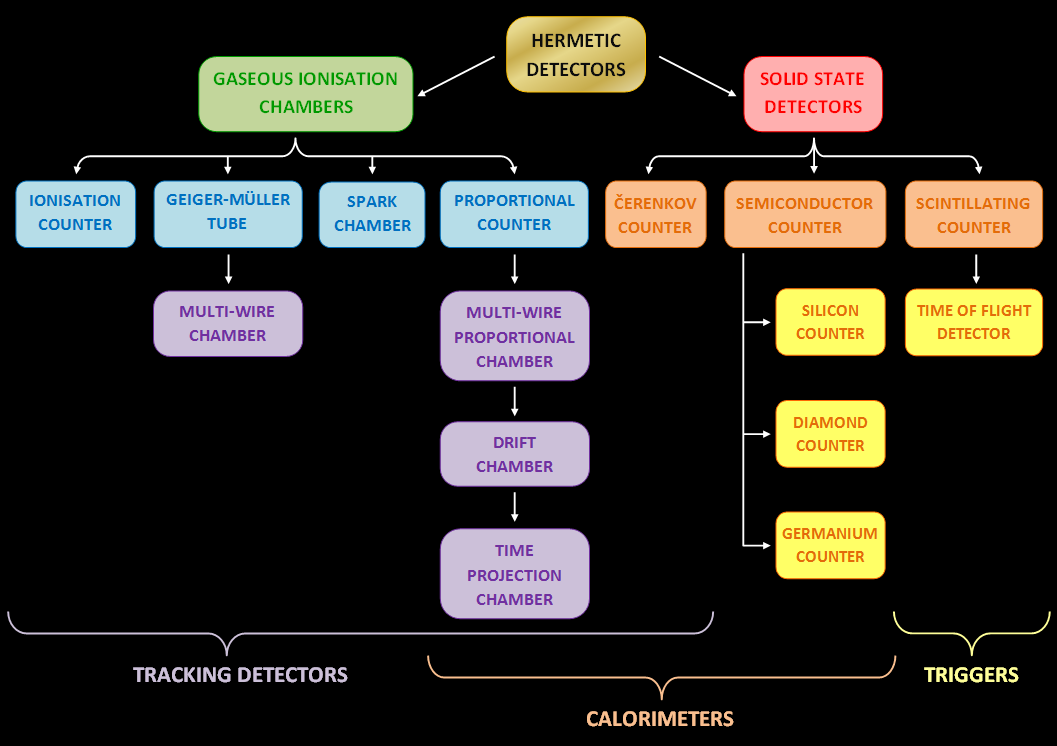
Particle Detector
In experimental and applied particle physics, nuclear physics, and nuclear engineering, a particle detector, also known as a radiation detector, is a device used to detect, track, and/or identify ionizing elementary particle, particles, such as those produced by nuclear decay, cosmic radiation, or reactions in a particle accelerator. Detectors can measure the particle energy and other attributes such as momentum, spin, charge, particle type, in addition to merely registering the presence of the particle. The operating of a nuclear radiation detector The operating principle of a nuclear radiation detector can be summarized as follows: The detector identifies high-energy particles or photons—such as alpha, beta, gamma radiation, or neutrons—through their interactions with the atoms of the detector material. These interactions generate a primary signal, which may involve ionization of gas, the creation of electron-hole pairs in semiconductors, or the emission of light in scint ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radium Bromide
Radium bromide is the bromide salt of radium, with the formula RaBr2. It is produced during the process of separating radium from uranium ore. This inorganic compound was discovered by Pierre and Marie Curie in 1898, and the discovery sparked a huge interest in radiochemistry and radiotherapy. Since elemental radium oxidizes readily in air and water, radium salts are the preferred chemical form of radium to work with.Babcock, A.B., Jr. Survey of Processes for Radium Recovery from Pitchblende Ores. ''AEC Research and Development Report''. 23 Feb 1950. No. NYO—112 Even though it is more stable than elemental radium, radium bromide is still extremely toxic, and can explode under certain conditions.Kirby, H.W; Salutsky, Murrell L. The Radiochemistry of Radium. ''Energy Citations Database'' Dec 1964''/ref> History After the Curies discovered radium (in the form of radium chloride) in 1898, scientists began to isolate radium on an industrial scale, with the intent of using it for r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Crookes
Sir William Crookes (; 17 June 1832 – 4 April 1919) was an English chemist and physicist who attended the Royal College of Chemistry, now part of Imperial College London, and worked on spectroscopy. He was a pioneer of vacuum tubes, inventing the Crookes tube, which was made in 1875. This was a foundational discovery that eventually changed the whole of chemistry and physics. He is credited with discovering the element thallium, announced in 1861, with the help of spectroscopy. He was also the first to describe the spectrum of terrestrial helium, in 1865. Crookes was the inventor of the Crookes radiometer but did not discern the true explanation of the phenomenon he detected. Crookes also invented a 100% ultraviolet blocking sunglass lens. For a time, he was interested in Spiritualism (movement), spiritualism and became president of the Society for Psychical Research. Biography Crookes's life was one of unbroken scientific activity that extended over sixty-seven years. He wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radioactive Decay
Radioactive decay (also known as nuclear decay, radioactivity, radioactive disintegration, or nuclear disintegration) is the process by which an unstable atomic nucleus loses energy by radiation. A material containing unstable nuclei is considered ''radioactive''. Three of the most common types of decay are Alpha decay, alpha, Beta decay, beta, and Gamma ray, gamma decay. The weak force is the Fundamental interactions, mechanism that is responsible for beta decay, while the other two are governed by the electromagnetic force, electromagnetic and nuclear forces. Radioactive decay is a randomness, random process at the level of single atoms. According to quantum mechanics, quantum theory, it is impossible to predict when a particular atom will decay, regardless of how long the atom has existed. However, for a significant number of identical atoms, the overall decay rate can be expressed as a decay constant or as a half-life. The half-lives of radioactive atoms have a huge range: f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Excited State
In quantum mechanics Quantum mechanics is the fundamental physical Scientific theory, theory that describes the behavior of matter and of light; its unusual characteristics typically occur at and below the scale of atoms. Reprinted, Addison-Wesley, 1989, It is ..., an excited state of a system (such as an atom, molecule or Atomic nucleus, nucleus) is any quantum state of the system that has a higher energy than the ground state (that is, more energy than the absolute minimum). Excitation refers to an increase in energy level above a chosen starting point, usually the ground state, but sometimes an already excited state. The temperature of a group of particles is indicative of the level of excitation (with the notable exception of systems that exhibit negative temperature). The lifetime of a system in an excited state is usually short: Spontaneous emission, spontaneous or stimulated emission, induced emission of a quantum of energy (such as a photon or a phonon) usually ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atomic Nucleus
The atomic nucleus is the small, dense region consisting of protons and neutrons at the center of an atom, discovered in 1911 by Ernest Rutherford at the Department_of_Physics_and_Astronomy,_University_of_Manchester , University of Manchester based on the 1909 Geiger–Marsden experiments, Geiger–Marsden gold foil experiment. After the discovery of the neutron in 1932, models for a nucleus composed of protons and neutrons were quickly developed by Dmitri Ivanenko and Werner Heisenberg. An atom is composed of a positively charged nucleus, with a cloud of negatively charged electrons surrounding it, bound together by electrostatic force. Almost all of the mass of an atom is located in the nucleus, with a very small contribution from the electron cloud. Protons and neutrons are bound together to form a nucleus by the nuclear force. The diameter of the nucleus is in the range of () for hydrogen (the diameter of a single proton) to about for uranium. These dimensions are much ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beta Particle
A beta particle, also called beta ray or beta radiation (symbol β), is a high-energy, high-speed electron or positron emitted by the radioactive decay of an atomic nucleus, known as beta decay. There are two forms of beta decay, β− decay and β+ decay, which produce electrons and positrons, respectively. Beta particles with an energy of 0.5 MeV have a range of about one metre in the air; the distance is dependent on the particle's energy and the air's density and composition. Beta particles are a type of ionizing radiation, and for radiation protection purposes, they are regarded as being more ionising than gamma rays, but less ionising than alpha particles. The higher the ionising effect, the greater the damage to living tissue, but also the lower the penetrating power of the radiation through matter. Beta decay modes β− decay (electron emission) An unstable atomic nucleus with an excess of neutrons may undergo β− decay, where a neutron is converted into a proto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alpha Particle
Alpha particles, also called alpha rays or alpha radiation, consist of two protons and two neutrons bound together into a particle identical to a helium-4 nucleus. They are generally produced in the process of alpha decay but may also be produced in different ways. Alpha particles are named after the first letter in the Greek alphabet, α. The symbol for the alpha particle is α or α2+. Because they are identical to helium nuclei, they are also sometimes written as He2+ or 2+ indicating a helium ion with a +2 charge (missing its two electrons). Once the ion gains electrons from its environment, the alpha particle becomes a normal (electrically neutral) helium atom . Alpha particles have a net spin of zero. When produced in standard alpha radioactive decay, alpha particles generally have a kinetic energy of about 5 MeV and a velocity in the vicinity of 4% of the speed of light. They are a highly ionizing form of particle radiation, with low penetration depth (stopped b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zircon
Zircon () is a mineral belonging to the group of nesosilicates and is a source of the metal zirconium. Its chemical name is zirconium(IV) silicate, and its corresponding chemical formula is Zr SiO4. An empirical formula showing some of the range of substitution in zircon is (Zr1–y, REEy)(SiO4)1–x(OH)4x–y. Zircon precipitates from silicate melts and has relatively high concentrations of high field strength incompatible elements. For example, hafnium is almost always present in quantities ranging from 1 to 4%. The crystal structure of zircon is tetragonal crystal system. The natural color of zircon varies between colorless, yellow-golden, red, brown, blue, and green. The name derives from the Persian ''zargun'', meaning "gold-hued". This word is changed into " jargoon", a term applied to light-colored zircons. The English word "zircon" is derived from ''Zirkon'', which is the German adaptation of this word. Yellow, orange, and red zircon is also known as " hyacint ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |