|
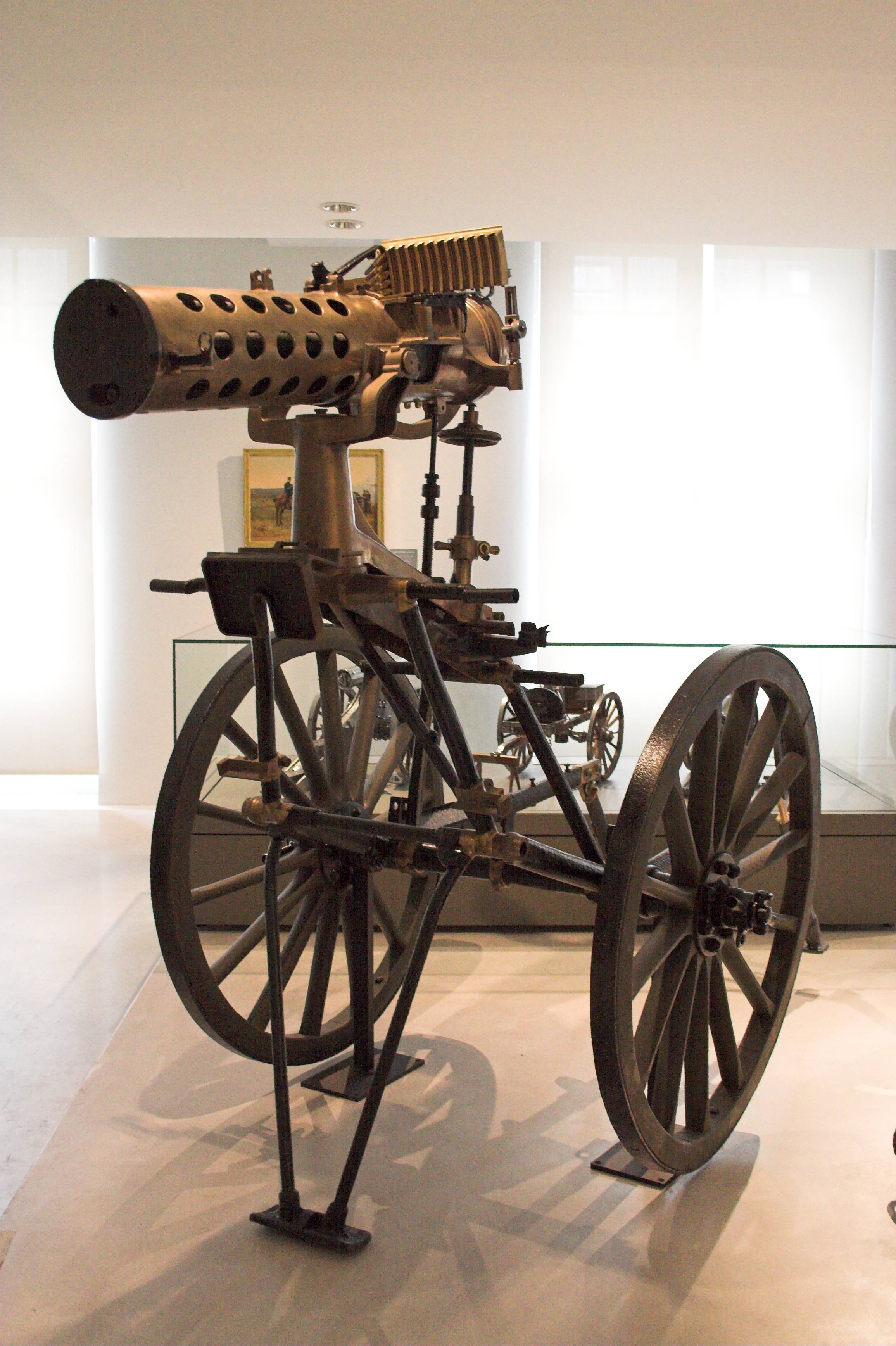
Gattling Gun
The Gatling gun is a rapid-firing multiple-barrel firearm invented in 1861 by Richard Jordan Gatling of North Carolina. It is an early machine gun and a forerunner of the modern electric motor-driven rotary cannon. The Gatling gun's operation centered on a cyclic multi-barrel design which facilitated cooling and synchronized the firing-reloading sequence. As the handwheel is cranked, the barrels rotate, and each barrel sequentially loads a single cartridge (firearms), cartridge from a top-mounted magazine (firearms), magazine, fires off the shot when it reaches a set position (usually at clock position, 4 o'clock), then ejects the spent casing out of the left side at the bottom, after which the barrel is empty and allowed to cool until rotated back to the top position and gravity-fed another new round. This configuration eliminated the need for a single reciprocating motion, reciprocating bolt (firearms), bolt design and allowed higher rates of fire to be achieved without the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
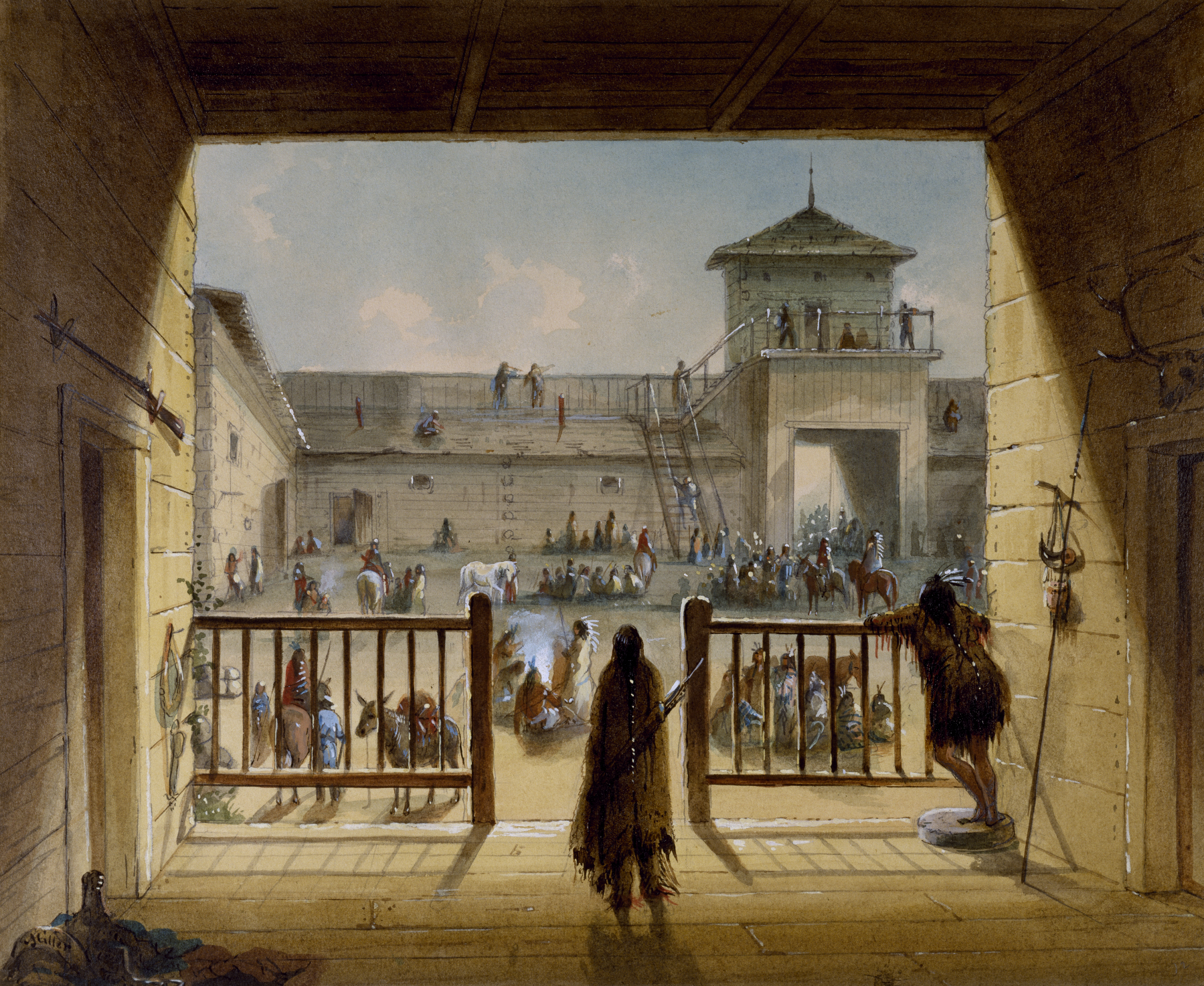
Fort Laramie National Historic Site
Fort Laramie (; founded as Fort William and known for a while as Fort John) was a significant 19th-century trading post, diplomatic site, and military installation located at the confluence of the Laramie River, Laramie and the North Platte Rivers. They joined in the upper Platte River Drainage basin, Valley in the eastern part of the present-day US state of Wyoming. The fort was founded as a private trading post in the 1830s to service the overland North American fur trade, fur trade; in 1849, it was purchased by the United States Army. The site was located east of the long climb leading to the best and lowest crossing over the Rocky Mountains at South Pass (Wyoming), South Pass and became a popular stop for migrants on the Oregon Trail. Along with Bent's Fort on the Arkansas River, the trading post and its supporting industries and businesses were the most significant Economic system, economic hub of commerce in the region. Fort William was founded by William Sublette and his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Conquest Of Central Asia
In the 16th century, the Tsardom of Russia embarked on a campaign to Territorial evolution of Russia, expand the Russian frontier to the east. This effort continued until the 19th century under the Russian Empire, when the Imperial Russian Army succeeded in conquering all of Central Asia. The majority of this land became known as Russian Turkestan—the name "Turkestan" was used to refer to the area due to the fact that it was and is inhabited by Turkic peoples, excluding the Tajiks, who are an Iranian peoples, Iranian ethnicity. Upon witnessing Russia's absorption of the various Central Asian realms, the British Empire sought to reinforce Presidencies and provinces of British India, India, triggering the Great Game, which ended when both sides eventually designated Emirate of Afghanistan, Afghanistan as a neutral buffer zone. Although the Russian Empire collapsed during World War I, the Russian sphere of influence remained in what was Soviet Central Asia until 1991. This regio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philippine–American War
The Philippine–American War, known alternatively as the Philippine Insurrection, Filipino–American War, or Tagalog Insurgency, emerged following the conclusion of the Spanish–American War in December 1898 when the United States annexed the Philippine Islands under the Treaty of Paris (1898), Treaty of Paris. Philippine nationalists constituted the First Philippine Republic in January 1899, seven months after signing the Philippine Declaration of Independence. The United States did not recognize either event as legitimate, and tensions escalated until fighting commenced on February 4, 1899, in the Battle of Manila (1899), Battle of Manila. Shortly after being denied a request for an armistice, the Philippine Council of Government issued a proclamation on June 2, 1899, urging the people to continue the war. Philippine forces initially attempted to engage U.S. forces conventionally but transitioned to guerrilla tactics by November 1899. Philippine President Emilio Aguinaldo w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spanish–American War
The Spanish–American War (April 21 – August 13, 1898) was fought between Restoration (Spain), Spain and the United States in 1898. It began with the sinking of the USS Maine (1889), USS ''Maine'' in Havana Harbor in Cuba, and resulted in the U.S. acquiring sovereignty over Puerto Rico, Guam, and the Philippines, and establishing a protectorate over Cuba. It represented U.S. intervention in the Cuban War of Independence and Philippine Revolution, with the latter later leading to the Philippine–American War. The Spanish–American War brought an end to almost four centuries of Spanish presence in the Americas, Asia, and the Pacific; the United States meanwhile not only became a major world power, but also gained several island possessions spanning the globe, which provoked rancorous debate over the wisdom of expansionism. The 19th century represented a clear decline for the Spanish Empire, while the United States went from a newly founded country to a rising power. In 1895, C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Matabele War
The Second Matabele War, also known as the First Chimurenga, was fought between 1896 and 1897 in the region that later became Southern Rhodesia (now Zimbabwe). The conflict was initially between the British South Africa Company and the Matabele people, later expanding to include the Shona people in the rest of Southern Rhodesia. In March 1896, the Matabele revolted against the authority of the British South Africa Company. The ''Mlimo'' (or ''M'limo'', or ''Umlimo'') the Matabele spiritual leader, was credited with fomenting much of the anger that led to this confrontation. He convinced the Matabele and the Shona that the settlers (almost 4,000-strong by then) were responsible for the drought, locust plagues and the cattle disease rinderpest ravaging the country at the time. The Mlimo's call to battle was well-timed. Only a few months earlier, the British South Africa Company's Administrator General for Matabeleland, Leander Starr Jameson, had sent most of his troops and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Sino-Japanese War
The First Sino-Japanese War (25 July 189417 April 1895), or the First China–Japan War, was a conflict between the Qing dynasty of China and the Empire of Japan primarily over influence in Joseon, Korea. In Chinese it is commonly known as the Jiawu War. After more than six months of unbroken successes by Japanese land and naval forces and the loss of the ports of Lüshunkou (Port Arthur) and Weihaiwei, the Qing government sued for peace in February 1895 and signed the Unequal treaties, unequal Treaty of Shimonoseki two months later, ending the war. In the late 19th century, Korea remained one of China's tributary states, while Japan viewed it as a target of imperial expansion. In June 1894, the Qing government, at the request of the Korean emperor Gojong of Korea, Gojong, sent 2,800 troops to aid in suppressing the Donghak Peasant Revolution. The Japanese considered this a violation of the 1885 Convention of Tientsin, and sent an expeditionary force of 8,000 troops, which la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Revolta Da Armada
The Brazilian Naval Revolts, or the Revoltas da Armada (in Portuguese), were armed mutiny, mutinies promoted mainly by admirals Custódio José de Melo and Saldanha da Gama and their fleet of rebel Brazilian navy ships against the claimed unconstitutional staying in power of president Floriano Peixoto. The United States supported the incumbent government against the insurgents. First revolt In November 1891, President Marshal Deodoro da Fonseca, amid a political crisis compounded by the effects of Encilhamento, an economic crisis, in flagrant violation of the new 1891 Brazilian Constitution, constitution, decided to "solve" the political crisis by ordering the closure of Congress, supported mainly by the São Paulo (State), Paulista oligarchy. The Navy, still resentful of the circumstances and outcomes of the Proclamation of the Republic (Brazil), coup that had put an end to the monarchy in Brazil, under the leadership of admiral Custódio José de Melo, rose up and threatene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Argentine Revolution Of 1893
The Argentine Revolution of 1893, or the Radical Revolution of 1893, was a failed insurrection by members of the Radical Civic Union (UCR) against the government of Argentina, then controlled by the National Autonomist Party (PAN). It continued the goals of the Revolution of the Park of 1890, whose themes were further echoed in the Revolution of 1905. In 1890, Bartolomé Mitre and Leandro N. Alem formed the Civic Union, which orchestrated the Revolution of the Park and forced the resignation of president Miguel Ángel Juárez Celman of the PAN in favor of his vice president, Carlos Pellegrini. Mitre himself stood for president for the 1892 elections, but sought accommodation with the PAN, leading Alem to break off and found the UCR in 1891. On April 2, 1892, barely a week before the election, Pellegrini declared a state of siege and arrested Alem and other opposition leaders, resulting in the overwhelming election of PAN candidate Luis Sáenz Peña. In the aftermath, the UCR ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Revolution Of The Park
The Revolution of the Park (''Revolución del Parque''), also known as the Revolution of '90, was an uprising against the national government of Argentina that took place on July 26, 1890, and started with the takeover of the Buenos Aires Artillery Park. It was led by members of the Civic Union (Argentina), Civic Union (which would later give rise to the modern Radical Civic Union) against the presidency of Miguel Juárez Celman (of the National Autonomist Party). Though it failed in its main goals, the revolution forced Celman's resignation (who would be replaced by his vice president Carlos Pellegrini) and marked the decline of the elite of the Generation of '80.Clarín''Yrigoyen, de la Ley Sáenz Peña al Golpe de Estado'' Buildup Near the end of 1889, general discontent (mainly due to high inflation) encouraged the Civic Union (led by Aristóbulo del Valle and Leandro Alem) to attempt to oust President Miguel Juárez Celman, whose conservative rule, like those of previous p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northwest Rebellion
The North-West Rebellion (), was an armed rebellion of Métis under Louis Riel and an associated uprising of Cree and Assiniboine mostly in the District of Saskatchewan, against the Canadian government. Important events included the Frog Lake incident, and the capture of Batoche. The North-West Rebellion began in March 1885 after Louis Riel returned from political exile in the U.S. With the assistance of Métis leader Gabriel Dumont, Riel declared a provisional government on March 18, and rebel territory was carved out. As government forces responded, fighting broke out, with the last shooting over by the end of June. Rebel forces included roughly 250 Métis and 250 First Nations men, largely Cree and Assiniboine, who were led by Big Bear and Poundmaker and other First Nations chiefs. A non-Indigenous man, Honoré Jackson, served as Riel's secretary. Defence of the government of Canada depended on a force of 5,500 men, including North-West Mounted Police, armed loyal r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colombian Civil War (1884–1885)
The Colombian Civil War of 1884–1885 was a conflict that took place in the United States of Colombia (present-day Colombia and Panama). It was the result of the reaction of the Radical faction of the Colombian Liberal Party, which did not agree with the Centralist Regeneration policy of President Rafael Núñez, a moderate Liberal who was supported by the Colombian Conservative Party. Background The Radical liberals, who were in power in the Sovereign State of Santander, accused Rafael Núñez, President of the United States of Colombia of interfering in the internal affairs of the States with his Centralist policies and Regeneration project. Course of events In August 1884, armed uprisings began in the state of Santander, directed against the state president, Solon Wilches. On 11 January 1885, the Tuluá Uprising took place in Cauca, which was suppressed by General Juan Evangelista Ulloa. However, General Francisco Escobar and Colonel Guillermo Marquez went over to the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |