|
Galactorrhea
Galactorrhea ( also spelled galactorrhoea) ( galacto- + -rrhea) or lactorrhea ( lacto- + -rrhea) is the spontaneous flow of milk from the breast, unassociated with childbirth or nursing. Galactorrhea is reported to occur in 5–32% of females. Much of the difference in reported incidence can be attributed to different definitions of galactorrhea. Although frequently benign, it may be caused by serious underlying conditions and should be properly investigated. Galactorrhea also occurs in males, newborn infants and adolescents of both sexes. Causes Galactorrhea can take place as a result of dysregulation of certain hormones. Hormonal causes most frequently associated with galactorrhea are hyperprolactinemia and thyroid conditions with elevated levels of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) or thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH). No obvious cause is found in about 50% of cases. Lactation requires the presence of prolactin, and the evaluation of galactorrhea includes eliciting a h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperprolactinemia
Hyperprolactinaemia (also spelled hyperprolactinemia) is a condition characterized by abnormally high levels of prolactin in the blood. In women, normal prolactin levels average to about 13 ng/mL, while in men, they average 5 ng/mL. The upper normal limit of serum prolactin is typically between 15 and 25 ng/mL for both genders. Levels exceeding this range indicate hyperprolactinemia. Prolactin (PRL) is a peptide hormone produced by lactotroph cells in the anterior pituitary gland. It plays a vital role in lactation and breast development. Hyperprolactinemia, characterized by abnormally high levels of prolactin, may cause galactorrhea (production and spontaneous flow of breast milk), infertility, and menstrual disruptions in women. In men, it can lead to hypogonadism, infertility and erectile dysfunction. Prolactin is crucial for milk production during pregnancy and lactation. Together with estrogen, progesterone, insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1), and horm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prolactin
Prolactin (PRL), also known as lactotropin and mammotropin, is a protein best known for its role in enabling mammals to produce milk. It is influential in over 300 separate processes in various vertebrates, including humans. Prolactin is secreted from the pituitary gland in response to eating, mating, estrogen treatment, ovulation and nursing. It is secreted heavily in pulses in between these events. Prolactin plays an essential role in metabolism, regulation of the immune system and pancreatic development. Discovered in non-human animals around 1930 by Oscar Riddle and confirmed in humans in 1970 by Henry Friesen, prolactin is a peptide hormone, encoded by the ''PRL'' gene. In mammals, prolactin is associated with milk production; in fish it is thought to be related to the control of water and salt balance. Prolactin also acts in a cytokine-like manner and as an important regulator of the immune system. It has important cell cycle-related functions as a growth-, diffe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lactation
Lactation describes the secretion of milk from the mammary glands and the period of time that a mother lactates to feed her young. The process naturally occurs with all sexually mature female mammals, although it may predate mammals. The process of feeding milk in all female creatures is called ''nursing'', and in humans it is also called ''breastfeeding''. Newborn infants often produce some milk from their own breast tissue, known colloquially as witch's milk. In most species, lactation is a sign that the female has been pregnant at some point in her life, although in humans and goats, it can happen without pregnancy. Nearly every species of mammal has teats; except for monotremes, egg-laying mammals, which instead release milk through ducts in the abdomen. In only a handful of species of mammals, certain bat species, is milk production a normal Male lactation, male function. ''Galactopoiesis'' is the maintenance of milk production. This stage requires prolactin. Oxytocin is cr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breast
The breasts are two prominences located on the upper ventral region of the torso among humans and other primates. Both sexes develop breasts from the same embryology, embryological tissues. The relative size and development of the breasts is a major secondary sex distinction between females and males. There is also considerable Bra size, variation in size between individuals. Permanent Breast development, breast growth during puberty is caused by estrogens in conjunction with the growth hormone. Female humans are the only mammals that permanently develop breasts at puberty; all other mammals develop their mammary tissue during the latter period of pregnancy. In females, the breast serves as the mammary gland, which produces and secretes milk to feed infants. Subcutaneous fat covers and envelops a network of lactiferous duct, ducts that converge on the nipple, and these tissue (biology), tissues give the breast its distinct size and globular shape. At the ends of the ducts are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pituitary Adenoma
Pituitary adenomas are tumors that occur in the pituitary gland. Most pituitary tumors are benign, approximately 35% are invasive and just 0.1% to 0.2% are carcinomas.Pituitary Tumors Treatment (PDQ®)–Health Professional Version NIH National Cancer Institute Pituitary adenomas represent from 10% to 25% of all intracranial neoplasia, neoplasms, with an estimated prevalence, prevalence rate in the general population of approximately 17%. Non-invasive and non-secreting pituitary adenomas are considered to be Benign tumors, benign in the literal as well as the clinical sense, though a 2011 meta-analysis of available research showed that research to either support or refute this assumption was scant and of questionable qua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cimetidine
Cimetidine, sold under the brand name Tagamet among others, is a histamine H2 receptor antagonist that inhibits stomach acid production. It is mainly used in the treatment of heartburn and peptic ulcers. With the development of proton pump inhibitors, such as omeprazole, approved for the same indications, cimetidine is available as an over-the-counter formulation to prevent heartburn or acid indigestion, along with the other H2-receptor antagonists. Cimetidine was developed in 1971 and came into commercial use in 1977. Cimetidine was approved in the United Kingdom in 1976, and was approved in the United States by the Food and Drug Administration in 1979. Medical uses Cimetidine is indicated for the treatment of duodenal ulcers, gastric ulcers, gastroesophageal reflux disease, and pathological hypersecretory conditions. Cimetidine is also used to relieve or prevent heartburn. Side effects Reported side effects of cimetidine include diarrhea, rashes, dizziness, fatig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
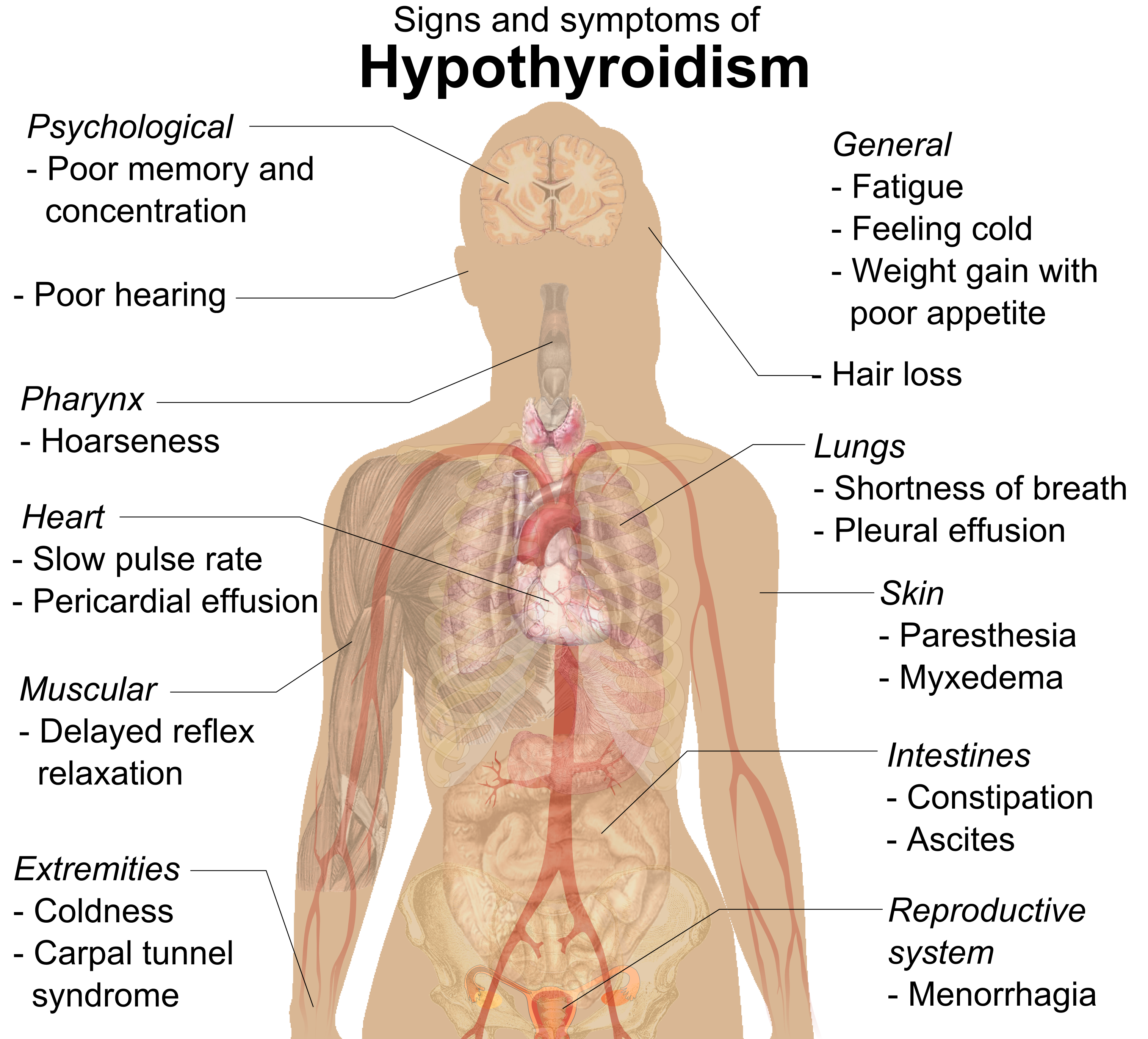
Hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism is an endocrine disease in which the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormones. It can cause a number of symptoms, such as cold intolerance, poor ability to tolerate cold, fatigue, extreme fatigue, muscle aches, constipation, slow heart rate, Depression (mood), depression, and weight gain. Occasionally there may be swelling of the front part of the neck due to goiter. Untreated cases of hypothyroidism during pregnancy can lead to delays in child development, growth and intellectual development in the baby or congenital iodine deficiency syndrome. Worldwide, iodine deficiency, too little iodine in the diet is the most common cause of hypothyroidism. Hashimoto's thyroiditis, an autoimmune disease where the body's immune system reacts to the thyroid gland, is the most common cause of hypothyroidism in countries with sufficient dietary iodine. Less common causes include previous treatment with iodine-131, radioactive iodine, injury to the hypothalamus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infertility
In biology, infertility is the inability of a male and female organism to Sexual reproduction, reproduce. It is usually not the natural state of a healthy organism that has reached sexual maturity, so children who have not undergone puberty, which is the body's start of fertility, reproductive capacity, are excluded. It is also a normal state in women after menopause. In humans, ''infertility'' is defined as the inability to become pregnant after at least one year of unprotected and regular sexual intercourse involving a male and female partner. There are many causes of infertility, including some that Assisted reproductive technology, medical intervention can treat. Estimates from 1997 suggest that worldwide about five percent of all heterosexual couples have an unresolved problem with infertility. Many more couples, however, experience involuntary childlessness for at least one year, with estimates ranging from 12% to 28%. Male infertility is responsible for 20–30% of infert ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
H2 Receptor Antagonist
H2 antagonists, sometimes referred to as H2RAs and also called H2 blockers, are a class of medications that block the action of histamine at the histamine H2 receptors of the parietal cells in the stomach. This decreases the production of stomach acid. H2 antagonists can be used in the treatment of dyspepsia, peptic ulcers and gastroesophageal reflux disease. They have been surpassed by proton pump inhibitors (PPIs). The PPI omeprazole was found to be more effective at both healing and alleviating symptoms of ulcers and reflux oesophagitis than the H2 blockers ranitidine and cimetidine. H2 antagonists, which all end in "-tidine", are a type of antihistamine. In general usage, however, the term "antihistamine" typically refers to H1 antagonists, which relieve allergic reactions. Like the H1 antagonists, some H2 antagonists function as inverse agonists rather than receptor antagonists, due to the constitutive activity of these receptors. The prototypical H2 antagoni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American And British English Spelling Differences
Despite the various list of dialects of English, English dialects spoken from country to country and within different regions of the same country, there are only slight regional variations in English orthography, the two most notable variations being British and American spelling. Many of Comparison of American and British English, the differences between American English, American and British English, British or English in the Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth English date back to a time before spelling standards were developed. For instance, some spellings seen as "American" today were once commonly used in Britain, and some spellings seen as "British" were once commonly used in the United States. A "British standard" began to emerge following the 1755 publication of Samuel Johnson's ''A Dictionary of the English Language'', and an "American standard" started following the work of Noah Webster and, in particular, his ''Webster's Dictionary, An American Dictionary of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Risperidone
Risperidone, sold under the brand name Risperdal among others, is an atypical antipsychotic used to treat schizophrenia and bipolar disorder, as well as aggressive and self-injurious behaviors associated with autism spectrum disorder. It is taken either by mouth or by injection (i.e., subcutaneous or intramuscular). The injectable versions are long-acting and last for 2–4 weeks. Common side effects include weight gain, drowsiness, fatigue, insomnia, dry mouth, constipation, elevated prolactin levels, and restlessness. Serious side effects may include the potentially permanent movement disorder tardive dyskinesia, as well as neuroleptic malignant syndrome, an increased risk of suicide, and high blood sugar levels. In older people with psychosis as a result of dementia, it may increase the risk of death. It is unknown if it is safe for use in pregnancy. Its mechanism of action is not entirely clear, but is believed to be related to its action as a dopamine and ser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proton-pump Inhibitor
Proton-pump inhibitors (PPIs) are a class of medications that cause a profound and prolonged reduction of gastric acid, stomach acid production. They do so by irreversibly inhibiting the stomach's H+/K+ ATPase, H+/K+ ATPase proton pump. The body eventually synthesizes new proton pumps to replace the irreversibly inhibited ones, a process driven by normal cellular turnover, which gradually restores acid production. Proton-pump inhibitors have largely superseded the H2-receptor antagonist, H2-receptor antagonists, a group of medications with similar effects but a different mode of action, and heavy use of antacids. A potassium-competitive acid blocker (PCAB) revaprazan was marketed in Korea as an alternative to a PPI. A newer PCAB vonoprazan with a faster and longer lasting action than revaprazan, and PPIs has been marketed in Japan (2013), Russia (2021), and the US (2023). PPIs are among the most widely sold medications in the world. The class of proton-pump inhibitor medication ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |