|
Free Surface Effect
The free surface effect is a mechanism which can cause a watercraft to become unstable and capsize. It refers to the tendency of liquids — and of unbound aggregates of small solid objects, like seeds, gravel, or crushed ore, whose behavior approximates that of liquids — to move in response to changes in the attitude of a craft's cargo holds, decks, or liquid tanks in reaction to operator-induced motions (or sea states caused by waves and wind acting upon the craft). When referring to the free surface effect, the condition of a tank that is not full is described as a "slack tank", while a full tank is "pressed up". Stability and equilibrium In a normally loaded vessel any rolling from perpendicular is countered by a righting moment generated from the increased volume of water displaced by the hull on the lowered side. This assumes the center of gravity of the vessel is relatively constant. If a moving mass inside the vessel moves in the direction of the roll, this counters t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liquid In Container
Liquid is a state of matter with a definite volume but no fixed shape. Liquids adapt to the shape of their container and are nearly compressibility, incompressible, maintaining their volume even under pressure. The density of a liquid is usually close to that of a solid, and much higher than that of a gas. Therefore, liquid and solid are classified as Condensed matter physics, condensed matter. Meanwhile, since both liquids and gases can flow, they are categorized as fluids. A liquid is composed of atoms or molecules held together by intermolecular bonds of intermediate strength. These forces allow the particles to move around one another while remaining closely packed. In contrast, solids have particles that are tightly bound by strong intermolecular forces, limiting their movement to small vibrations in fixed positions. Gases, on the other hand, consist of widely spaced, freely moving particles with only weak intermolecular forces. As temperature increases, the molecules in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydraulic Tanker
Hydraulics () is a technology and applied science using engineering, chemistry, and other sciences involving the mechanical properties and use of liquids. At a very basic level, hydraulics is the liquid counterpart of pneumatics, which concerns gases. Fluid mechanics provides the theoretical foundation for hydraulics, which focuses on applied engineering using the properties of fluids. In its fluid power applications, hydraulics is used for the generation, control, and transmission of power by the use of pressurized liquids. Hydraulic topics range through some parts of science and most of engineering modules, and they cover concepts such as pipe flow, dam design, fluidics, and fluid control circuitry. The principles of hydraulics are in use naturally in the human body within the vascular system and erectile tissue. ''Free surface hydraulics'' is the branch of hydraulics dealing with free surface flow, such as occurring in rivers, canals, lakes, estuaries, and seas. Its sub-f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metacentric Height
The metacentric height (GM) is a measurement of the initial static stability of a floating body. It is calculated as the distance between the centre of gravity of a ship and its '' metacentre''. A larger metacentric height implies greater initial stability against overturning. The metacentric height also influences the natural period of rolling of a hull, with very large metacentric heights being associated with shorter periods of roll which are uncomfortable for passengers. Hence, a sufficiently, but not excessively, high metacentric height is considered ideal for passenger ships. Different centres The ''centre of buoyancy'' is at the centre of mass of the volume of water that the hull displaces. This point is referred to as B in naval architecture. The '' centre of gravity'' of the ship is commonly denoted as point G or CG. When a ship is at equilibrium, the centre of buoyancy is vertically in line with the centre of gravity of the ship. The metacentre is the point where th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Code On Intact Stability
The International Code on Intact Stability (IS Code) is the International Maritime Organization (IMO) standard for ship stability Ship stability is an area of naval architecture and ship design that deals with how a ship behaves at sea, both in still water and in waves, whether intact or damaged. Stability calculations focus on center of mass#center of gravity, centers of .... History The Code for Intact Stability was first issued in 1993 under IMO resolution A.749(18)). In 2008, the Code was updated by the IMO. In December 2019, amendments to the Code were adopted that entered into force on 1 January 2020. These amendments related to ships engaged in anchor handling operations and to ships carrying out lifting and towing operations. Content The Code contains both mandatory regulations and recommended provisions, setting out the minimum stability standards for ships. This includes information on precautions against capsizing, metacentric heights (GM), righting levers (GZ) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SOLAS Convention
The International Convention for the Safety of Life at Sea (SOLAS) is an international maritime treaty which sets out minimum safety standards in the construction, equipment and operation of merchant ships. The International Maritime Organization convention requires signatory flag states to ensure that ships flagged by them comply with at least these standards. Initially prompted by the sinking of the Titanic, the current version of SOLAS is the 1974 version, known as SOLAS 1974, which came into force on 25 May 1980, and has been amended several times. , SOLAS 1974 has 167 contracting states, which flag about 99% of merchant ships around the world in terms of gross tonnage. SOLAS in its successive forms is generally regarded as the most important of all international treaties concerning the safety of merchant ships. Signatories The non-parties to SOLAS 1974 include numerous landlocked countries, as well as El Salvador, Micronesia and East Timor. Some others including Bolivi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slosh Dynamics
In fluid dynamics, slosh refers to the movement of liquid inside another object (which is, typically, also undergoing motion). Strictly speaking, the liquid must have a free surface to constitute a slosh dynamics problem, where the dynamics of the liquid can interact with the container to alter the system dynamics significantly. Important examples include propellant slosh in spacecraft tanks and rockets (especially upper stages), and the free surface effect (cargo slosh) in ships and trucks transporting liquids (for example oil and gasoline). However, it has become common to refer to liquid motion in a completely filled tank, i.e. without a free surface, as "fuel slosh". Such motion is characterized by " inertial waves" and can be an important effect in spinning spacecraft dynamics. Extensive mathematical and empirical relationships have been derived to describe liquid slosh. These types of analyses are typically undertaken using computational fluid dynamics and finite element m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fire-fighting
Firefighting is a profession aimed at controlling and extinguishing fire. A person who engages in firefighting is known as a firefighter or fireman. Firefighters typically undergo a high degree of technical training. This involves structural firefighting and wildland firefighting. Specialized training includes aircraft firefighting, shipboard firefighting, aerial firefighting, maritime firefighting, and proximity firefighting. Firefighting is a dangerous profession due to the toxic environment created by combustible materials, with major risks being smoke, oxygen deficiency, elevated temperatures, poisonous atmospheres, and violent air flows. To combat some of these risks, firefighters carry self-contained breathing apparatus. Additional hazards include falls – a constant peril while navigating unfamiliar layouts or confined spaces amid shifting debris under limited visibility – and structural collapse that can exacerbate the problems encountered in a toxic environment. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aircraft
An aircraft ( aircraft) is a vehicle that is able to flight, fly by gaining support from the Atmosphere of Earth, air. It counters the force of gravity by using either Buoyancy, static lift or the Lift (force), dynamic lift of an airfoil, or, in a few cases, direct Powered lift, downward thrust from its engines. Common examples of aircraft include airplanes, rotorcraft (including helicopters), airships (including blimps), Glider (aircraft), gliders, Powered paragliding, paramotors, and hot air balloons. Part 1 (Definitions and Abbreviations) of Subchapter A of Chapter I of Title 14 of the U. S. Code of Federal Regulations states that aircraft "means a device that is used or intended to be used for flight in the air." The human activity that surrounds aircraft is called ''aviation''. The science of aviation, including designing and building aircraft, is called ''aeronautics.'' Aircrew, Crewed aircraft are flown by an onboard Aircraft pilot, pilot, whereas unmanned aerial vehicles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
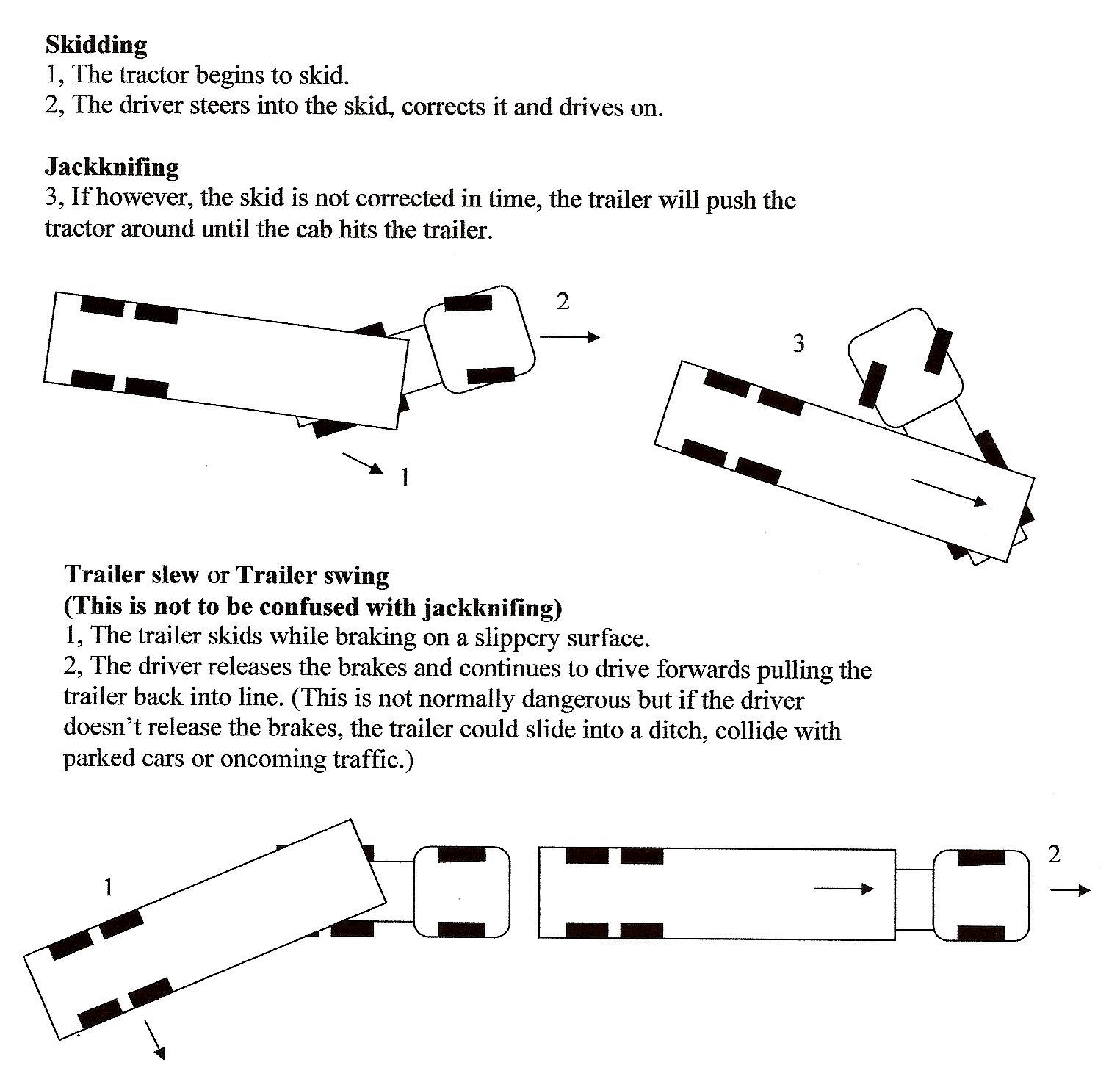
Jackknifing
Jackknifing is the folding of an articulated vehicle so that it resembles the acute angle of a folding pocket knife. If a vehicle towing a trailer skids, the trailer can push the towing vehicle from behind until it spins the vehicle around and faces backwards. This may be caused by equipment failure, improper braking, or adverse road conditions such as an icy road surface. In extreme circumstances, a driver may attempt to jackknife the vehicle deliberately to halt it following brake failure. Trailer swing When a trailer skids to one side, this is known as a trailer swing or trailer slew. This can occur on a slippery road surface, often where there is a cant. This is not the same as jackknifing and is not as serious, as the trailer will move back into line as the vehicle continues forwards. The driver must be aware, however, that the trailer could slide up against parked cars or a guard rail, or that the wheels could slide into a ditch. This situation can occur especially wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Truck
A truck or lorry is a motor vehicle designed to transport freight, carry specialized payloads, or perform other utilitarian work. Trucks vary greatly in size, power, and configuration, but the vast majority feature body-on-frame construction, with a cabin that is independent of the payload portion of the vehicle. Smaller varieties may be mechanically similar to some automobiles. Commercial trucks can be very large and powerful and may be configured to be mounted with specialized equipment, such as in the case of refuse trucks, fire trucks, concrete mixers, and suction excavators. In American English, a commercial vehicle without a trailer or other articulation is formally a "straight truck" while one designed specifically to pull a trailer is not a truck but a " tractor". The majority of trucks currently in use are powered by diesel engines, although small- to medium-size trucks with gasoline engines exist in North America. Electrically powered trucks are more popu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semi-trailer
A semi-trailer is a trailer (vehicle), trailer without a front axle. The combination of a semi-trailer and a tractor truck is called a ''semi-trailer truck'' (also known simply as a "semi-trailer", "tractor trailer", or "semi" in the United States). A large proportion of a semi-trailer's weight is supported by a tractor unit, or a detachable front-axle assembly known as a dolly (trailer), dolly, or the B-Train, tail of another trailer. The semi-trailer's weight is semi-supported (half-supported) by its own wheels, at the rear of the semi-trailer. A semi-trailer is normally equipped with landing gear (legs which can be lowered) to support it when it is uncoupled. Many semi-trailers have wheels that are capable of being totally dismounted and are also relocatable (repositionable) to better distribute load to bearing wheel weight factors. Semi-trailers are more popular for transport than Trailer (vehicle)#Full, full trailers, which have both front and rear axles. Ease of backing i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tanker (ship)
A tanker (or tank ship or tankship) is a ship designed to transport or store liquids or gases in Bulk liquids, bulk. Major types of tanker ship include the oil tanker (or petroleum tanker), the chemical tanker, Cargo ship, cargo ships, and a gas carrier. Tankers also carry commodities such as vegetable oils, molasses and wine. In the United States Navy and Military Sealift Command, a tanker used to refuel other ships is called an oiler (ship), oiler (or replenishment oiler if it can also supply dry stores) but many other navies use the terms tanker and replenishment tanker. Tankers were first developed in the late 19th century as iron and steel hulls and pumping systems were developed. As of 2005, there were just over 4,000 tankers and supertankers or greater operating worldwide. Description Tankers can range in size of capacity from several hundred tonnage, tons, which includes vessels for servicing small harbours and coastal settlements, to several hundred thousand tons, f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |