|
Frataraka
Frataraka (Aramaic: ''Prtkr’𐡐𐡓𐡕𐡊𐡓’'', "governor", or more specifically "sub-satrapal governor") is an ancient Persian title, interpreted variously as “leader, governor, forerunner”. It is an epithet or title of a series of rulers in Persis from 3rd to mid 2nd century BC, or alternatively between 295 and 220 BC, at the time of the Seleucid Empire, prior to the Parthian conquest of West Asia and Iran. Studies of ''frataraka coins'' are important to historians of this period. Rulers and period Several rulers have been identified as belonging to Fratarakā dynasty (from the title ''prtrk' zy alhaya'', or "governor of the gods" on their coins): ''bgdt'' ( Baydād), ''rtḥštry'' (Ardaxšīr I), ''whwbrz'' ( Vahbarz, who is called Oborzos in Polyenus 7.40), and ''wtprdt'' ( Vādfradād I). Traditionally, they used to be considered as independent, anti-Seleucid rulers of Persis in the 3rd century BC. It seems however that they were rather representatives of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oborzos Drachm
Wahbarz (also spelled Vahbarz), known in Greek sources as Oborzos, was a dynast ('' frataraka'') of Persis in the 1st half of the 2nd century BC, ruling from possibly to 164 BC. His reign was marked by his efforts to establish Persis as a kingdom independent from Seleucid authority. He was able to reign independently for three decades, and even expanded to the west, seizing the Seleucid province of Characene. In 164 BC, the Seleucids repelled Wahbarz's forces from Characene, forcing him to re-submit as a Seleucid vassal. He was succeeded by Baydad. Background Since the end of the 3rd or the beginning of the 2nd century BCE, Persis had been ruled by local dynasts subject to the Seleucid Empire. They held the ancient Persian title of '' frataraka'' ("leader, governor, forerunner"), which is also attested in the Achaemenid-era. The Achaemenid Empire, which had a century earlier ruled most of the Near East, originated from the region. The ''frataraka'' themselves emphasized their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
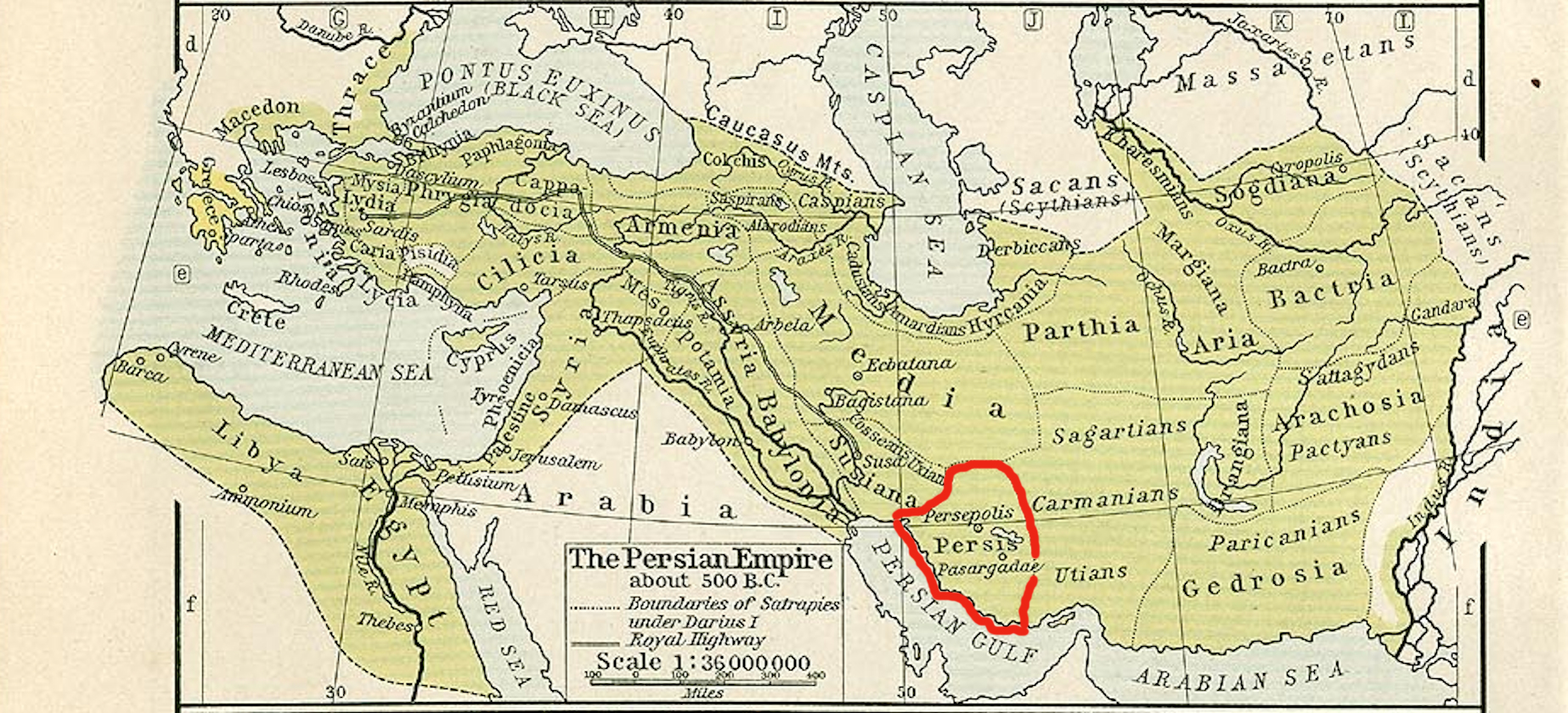
Persian Empire
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire, also known as the Persian Empire or First Persian Empire (; , , ), was an Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great of the Achaemenid dynasty in 550 BC. Based in modern-day Iran, it was the largest empire by that point in history, spanning a total of . The empire spanned from the Balkans and Egypt in the west, most of West Asia, the majority of Central Asia to the northeast, and the Indus Valley of South Asia to the southeast. Around the 7th century BC, the region of Persis in the southwestern portion of the Iranian plateau was settled by the Persians. From Persis, Cyrus rose and defeated the Median Empire as well as Lydia and the Neo-Babylonian Empire, marking the establishment of a new imperial polity under the Achaemenid dynasty. In the modern era, the Achaemenid Empire has been recognised for its imposition of a successful model of centralised bureaucratic administration, its multicultural policy, building complex inf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vahbarz
Wahbarz (also spelled Vahbarz), known in Greek sources as Oborzos, was a dynast ('' frataraka'') of Persis in the 1st half of the 2nd century BC, ruling from possibly to 164 BC. His reign was marked by his efforts to establish Persis as a kingdom independent from Seleucid authority. He was able to reign independently for three decades, and even expanded to the west, seizing the Seleucid province of Characene. In 164 BC, the Seleucids repelled Wahbarz's forces from Characene, forcing him to re-submit as a Seleucid vassal. He was succeeded by Baydad. Background Since the end of the 3rd or the beginning of the 2nd century BCE, Persis had been ruled by local dynasts subject to the Seleucid Empire. They held the ancient Persian title of '' frataraka'' ("leader, governor, forerunner"), which is also attested in the Achaemenid-era. The Achaemenid Empire, which had a century earlier ruled most of the Near East, originated from the region. The ''frataraka'' themselves emphasized their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bagadates
Baydad (also spelled Bagdates), was a dynast (''frataraka'') of Persis from 164 to 146 BC. Background Since the end of the 3rd or the beginning of the 2nd century BCE, Persis had been ruled by local dynasts subject to the Seleucid Empire. They held the ancient Persian title of ''frataraka'' ("leader, governor, forerunner"), which is also attested in the Achaemenid-era. The Achaemenid Empire, which had a century earlier ruled most of the Near East, originated from the region. The ''frataraka'' themselves emphasized their close affiliation with the prominent Achaemenid King of Kings, and their court was probably at the former Achaemenid capital of Persepolis, where they financed construction projects on and near the Achaemenid plateau. The ''frataraka'' had traditionally been regarded as priestly dynasts or advocates of religious (and political) opposition to Hellenism, however, this is no longer considered the case. Chronology of the ''frataraka'' The traditional view of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vādfradād II
Wadfradad II, Hellenized as Autophradates II, was a dynast (''frataraka'') of Persis in the late 2nd-century BC, ruling sometime after 138 BC. He was appointed as ''frataraka'' by the Parthian king Mithridates I (), who granted him more autonomy, most likely in an effort to maintain healthy relations with Persis as the Parthian Empire was under constant conflict with the Saka, Seleucids, and Characene. The coinage of Wadfradad II shows influence from the coins minted under Mithridates I. Wadfradad II was succeeded by Darayan I, the first of the Kings of Persis The Kings of Persis, also known as the Darayanids, were a series of Iranian kings, who ruled the region of Persis in southwestern Iran, from the 2nd century BCE to 224 CE. They ruled as vassal kings of the Parthian Empire, until they toppled them .... References Sources * . * * * * * {{Fratarakas of Persis 2nd-century BC Iranian people History of Fars province 2nd-century BC monarchs in Asia Vassa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vādfradād I
Wadfradad I, Hellenized as Autophradates I was a dynast ('' frataraka'') of Persis Persis (, ''Persís;'' Old Persian: 𐎱𐎠𐎼𐎿, ''Parsa''), also called Persia proper, is a historic region in southwestern Iran, roughly corresponding with Fars province. The Persian ethnic group are thought to have initially migrated ... in the late 2nd-century BC, ruling from 146 to 138 BC. He was succeeded by Wadfradad II. References Sources * . * * * * * {{Fratarakas of Persis 2nd-century BC Iranian people History of Fars province 2nd-century BC monarchs in Asia Zoroastrian monarchs Frataraka rulers of Persis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Persis
Persis (, ''Persís;'' Old Persian: 𐎱𐎠𐎼𐎿, ''Parsa''), also called Persia proper, is a historic region in southwestern Iran, roughly corresponding with Fars province. The Persian ethnic group are thought to have initially migrated either from Central Asia or, more probably, from the north through the Caucasus. They would then have migrated to the current region of Persis in the early 1st millennium BC. Achaemenid Empire The ancient Persians were present in the region of Persis from about the 10th century BC. They became the rulers of the largest empire the world had yet seen under the Achaemenid dynasty which was established in the late 6th century BC, at its peak stretching from Thrace- Macedonia, Bulgaria- Paeonia and Eastern Europe proper in the west, to the Indus Valley in its far east. The ruins of Persepolis and Pasargadae, two of the four capitals of the Achaemenid Empire, are located in Fars. Macedonian Empire The Achaemenid Empire was defeated by Al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Noumenios
Noumenios () was a Seleucid general and satrap of the Province of Mesene (Characene, capital Antiochia in Susiana), who is said to have defeated the Persians sometime in the 3rd or 2nd century BCE. Pliny describes his ruler as being "Antiochos", but it is unknown if this is referring to Antiochos I, Antiochos II or Antiochos III, although the battle necessarily took place before 190-189 BCE, date of the Battle of Magnesia where Antiochos III was vanquished by the Romans. Alternatively, these events may have taken place during the reign of Antiochos IV. Pliny writes: This event is often used to describe some kind of adversary relationship between the Frataraka rulers of Persis and the Seleucid Empire during the 3rd or 2nd centuries BCE. The rulers of Persis may have gained independence between 205 BCE, when Antiochos III visited Antiochia in Persis in peace, and 190-189 BCE, the latest possible date for the battle led by Noumenios if the Battle of Magnesia is consider ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seleucid Empire
The Seleucid Empire ( ) was a Greek state in West Asia during the Hellenistic period. It was founded in 312 BC by the Macedonian general Seleucus I Nicator, following the division of the Macedonian Empire founded by Alexander the Great, and ruled by the Seleucid dynasty until its annexation by the Roman Republic under Pompey in 63 BC. After receiving the Mesopotamian regions of Babylonia and Assyria in 321 BC, Seleucus I began expanding his dominions to include the Near Eastern territories that encompass modern-day Iraq, Iran, Afghanistan, Syria, and Lebanon, all of which had been under Macedonian control after the fall of the former Achaemenid Empire. At the Seleucid Empire's height, it had consisted of territory that covered Anatolia, Persia, the Levant, Mesopotamia, and what are now modern Kuwait, Afghanistan, and parts of Turkmenistan. The Seleucid Empire was a major center of Hellenistic culture. Greek customs and language were privileged; the wide vari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
KINGS Of PERSIS
The Kings of Persis, also known as the Darayanids, were a series of Iranian kings, who ruled the region of Persis in southwestern Iran, from the 2nd century BCE to 224 CE. They ruled as vassal kings of the Parthian Empire, until they toppled them and established the Sasanian Empire. They effectively formed some Persian dynastic continuity between the Achaemenid Empire (6th century BCE – 4th century BCE) and the Sasanian Empire (3rd century CE – 7th century CE). History Persis (also known as Pars), a region in the southwestern Iranian plateau, was the homeland of a southwestern branch of the Iranian peoples, the Persians. It was also the birthplace of the first Iranian Empire, the Achaemenids. The region served as the center of the empire until its conquest by the Macedonian king Alexander the Great (). Since the end of the 3rd or the beginning of the 2nd century BCE, Persis was ruled by local dynasts subject to the Hellenistic Seleucid Empire. These dynasts held the ancien ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |