|
Frameshifting
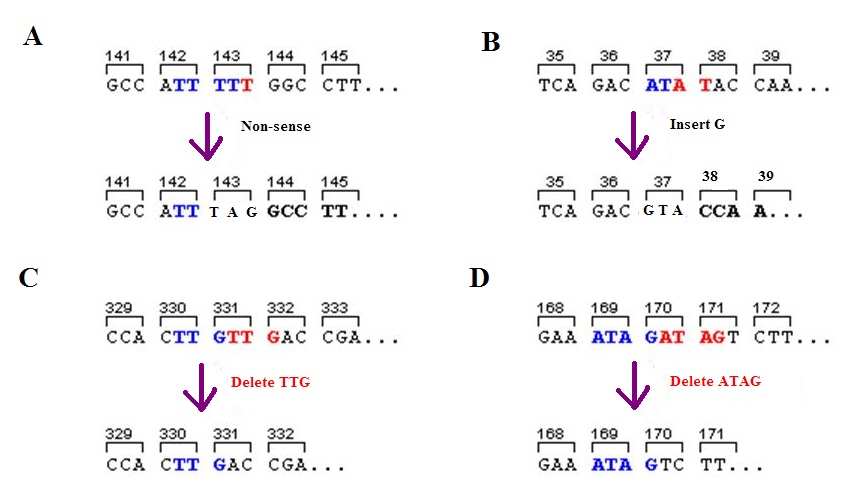
A frameshift mutation (also called a framing error or a reading frame shift) is a genetic mutation caused by indels ( insertions or deletions) of a number of nucleotides in a DNA sequence that is not divisible by three. Due to the triplet nature of gene expression by codons, the insertion or deletion can change the reading frame (the grouping of the codons), resulting in a completely different translation from the original. The earlier in the sequence the deletion or insertion occurs, the more altered the protein. A frameshift mutation is not the same as a single-nucleotide polymorphism in which a nucleotide is replaced, rather than inserted or deleted. A frameshift mutation will in general cause the reading of the codons after the mutation to code for different amino acids. The frameshift mutation will also alter the first stop codon ("UAA", "UGA" or "UAG") encountered in the sequence. The polypeptide being created could be abnormally short or abnormally long, and will most like ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frameshift
Ribosomal frameshifting, also known as translational frameshifting or translational recoding, is a biological phenomenon that occurs during translation that results in the production of multiple, unique proteins from a single mRNA. The process can be programmed by the nucleotide sequence of the mRNA and is sometimes affected by the secondary, 3-dimensional mRNA structure. It has been described mainly in viruses (especially retroviruses), retrotransposons and bacterial insertion elements, and also in some cellular genes. Small molecules, proteins, and nucleic acids have also been found to stimulate levels of frameshifting. In December 2023, it was reported that ''in vitro''-transcribed (IVT) mRNAs in response to BNT162b2 (Pfizer–BioNTech) anti-COVID-19 vaccine caused ribosomal frameshifting. Process overview Proteins are translated by reading tri-nucleotides on the mRNA strand, also known as codons, from one end of the mRNA to the other (from the 5' to the 3' end) starting wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frameshift Mutation
A frameshift mutation (also called a framing error or a reading frame shift) is a genetic mutation caused by indels ( insertions or deletions) of a number of nucleotides in a DNA sequence that is not divisible by three. Due to the triplet nature of gene expression by codons, the insertion or deletion can change the reading frame (the grouping of the codons), resulting in a completely different translation from the original. The earlier in the sequence the deletion or insertion occurs, the more altered the protein. A frameshift mutation is not the same as a single-nucleotide polymorphism in which a nucleotide is replaced, rather than inserted or deleted. A frameshift mutation will in general cause the reading of the codons after the mutation to code for different amino acids. The frameshift mutation will also alter the first stop codon ("UAA", "UGA" or "UAG") encountered in the sequence. The polypeptide being created could be abnormally short or abnormally long, and will most li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indel
Indel (insertion-deletion) is a molecular biology term for an insertion or deletion of bases in the genome of an organism. Indels ≥ 50 bases in length are classified as structural variants. In coding regions of the genome, unless the length of an indel is a multiple of 3, it will produce a frameshift mutation. For example, a common microindel which results in a frameshift causes Bloom syndrome in the Jewish or Japanese population. Indels can be contrasted with a point mutation. An indel inserts or deletes nucleotides from a sequence, while a point mutation is a form of substitution that ''replaces'' one of the nucleotides without changing the overall number in the DNA. Indels can also be contrasted with Tandem Base Mutations (TBM), which may result from fundamentally different mechanisms. A TBM is defined as a substitution at adjacent nucleotides (primarily substitutions at two adjacent nucleotides, but substitutions at three adjacent nucleotides have been observed). In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Codon
Genetic code is a set of rules used by living cells to translate information encoded within genetic material (DNA or RNA sequences of nucleotide triplets or codons) into proteins. Translation is accomplished by the ribosome, which links proteinogenic amino acids in an order specified by messenger RNA (mRNA), using transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to carry amino acids and to read the mRNA three nucleotides at a time. The genetic code is highly similar among all organisms and can be expressed in a simple table with 64 entries. The codons specify which amino acid will be added next during protein biosynthesis. With some exceptions, a three-nucleotide codon in a nucleic acid sequence specifies a single amino acid. The vast majority of genes are encoded with a single scheme (see the RNA codon table). That scheme is often called the canonical or standard genetic code, or simply ''the'' genetic code, though variant codes (such as in mitochondria) exist. History Efforts to understan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proofreading
Proofreading is a phase in the process of publishing where galley proofs are compared against the original manuscripts or graphic artworks, to identify transcription errors in the typesetting process. In the past, proofreaders would place corrections or proofreading marks along the margins. In modern publishing, material is generally provided in electronic form, traditional typesetting is no longer used and thus (in general) this kind of transcription no longer occurs. Professional Traditional method A "galley proof" (familiarly, "a proof") is a typeset version of copy or a manuscript document. It may contain typographical errors ("printer's errors"), as a result of human error during typesetting. Traditionally, a proofreader looks at a portion of text on the copy, compares it to the corresponding typeset portion, and then marks any errors (sometimes called "line edits") using standard proofreaders' marks. Unlike copy editing, the defining procedure of a proofreading serv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catalytic
Catalysis () is the increase in reaction rate, rate of a chemical reaction due to an added substance known as a catalyst (). Catalysts are not consumed by the reaction and remain unchanged after it. If the reaction is rapid and the catalyst recycles quickly, very small amounts of catalyst often suffice; mixing, surface area, and temperature are important factors in reaction rate. Catalysts generally react with one or more reactants to form reaction intermediate, intermediates that subsequently give the final reaction product, in the process of regenerating the catalyst. The rate increase occurs because the catalyst allows the reaction to occur by an alternative mechanism which may be much faster than the noncatalyzed mechanism. However the noncatalyzed mechanism does remain possible, so that the total rate (catalyzed plus noncatalyzed) can only increase in the presence of the catalyst and never decrease. Catalysis may be classified as either homogeneous catalysis, homogeneou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell (biology)
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all life, forms of life. Every cell consists of cytoplasm enclosed within a Cell membrane, membrane; many cells contain organelles, each with a specific function. The term comes from the Latin word meaning 'small room'. Most cells are only visible under a light microscope, microscope. Cells Abiogenesis, emerged on Earth about 4 billion years ago. All cells are capable of Self-replication, replication, protein synthesis, and cell motility, motility. Cells are broadly categorized into two types: eukaryotic cells, which possess a Cell nucleus, nucleus, and prokaryotic, prokaryotic cells, which lack a nucleus but have a nucleoid region. Prokaryotes are single-celled organisms such as bacteria, whereas eukaryotes can be either single-celled, such as amoebae, or multicellular organism, multicellular, such as some algae, plants, animals, and fungi. Eukaryotic cells contain organelles including Mitochondrion, mitochondria, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organism
An organism is any life, living thing that functions as an individual. Such a definition raises more problems than it solves, not least because the concept of an individual is also difficult. Many criteria, few of them widely accepted, have been proposed to define what an organism is. Among the most common is that an organism has autonomous reproduction, Cell growth, growth, and metabolism. This would exclude viruses, despite the fact that they evolution, evolve like organisms. Other problematic cases include colonial organisms; a colony of eusocial insects is organised adaptively, and has Germ-Soma Differentiation, germ-soma specialisation, with some insects reproducing, others not, like cells in an animal's body. The body of a siphonophore, a jelly-like marine animal, is composed of organism-like zooids, but the whole structure looks and functions much like an animal such as a jellyfish, the parts collaborating to provide the functions of the colonial organism. The evolutiona ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genome
A genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding genes, other functional regions of the genome such as regulatory sequences (see non-coding DNA), and often a substantial fraction of junk DNA with no evident function. Almost all eukaryotes have mitochondrial DNA, mitochondria and a small mitochondrial genome. Algae and plants also contain chloroplast DNA, chloroplasts with a chloroplast genome. The study of the genome is called genomics. The genomes of many organisms have been Whole-genome sequencing, sequenced and various regions have been annotated. The first genome to be sequenced was that of the virus φX174 in 1977; the first genome sequence of a prokaryote (''Haemophilus influenzae'') was published in 1995; the yeast (''Saccharomyces cerevisiae'') genome was the first eukaryotic genome to be sequenced in 1996. The Human Genome Project ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mismatch Repair
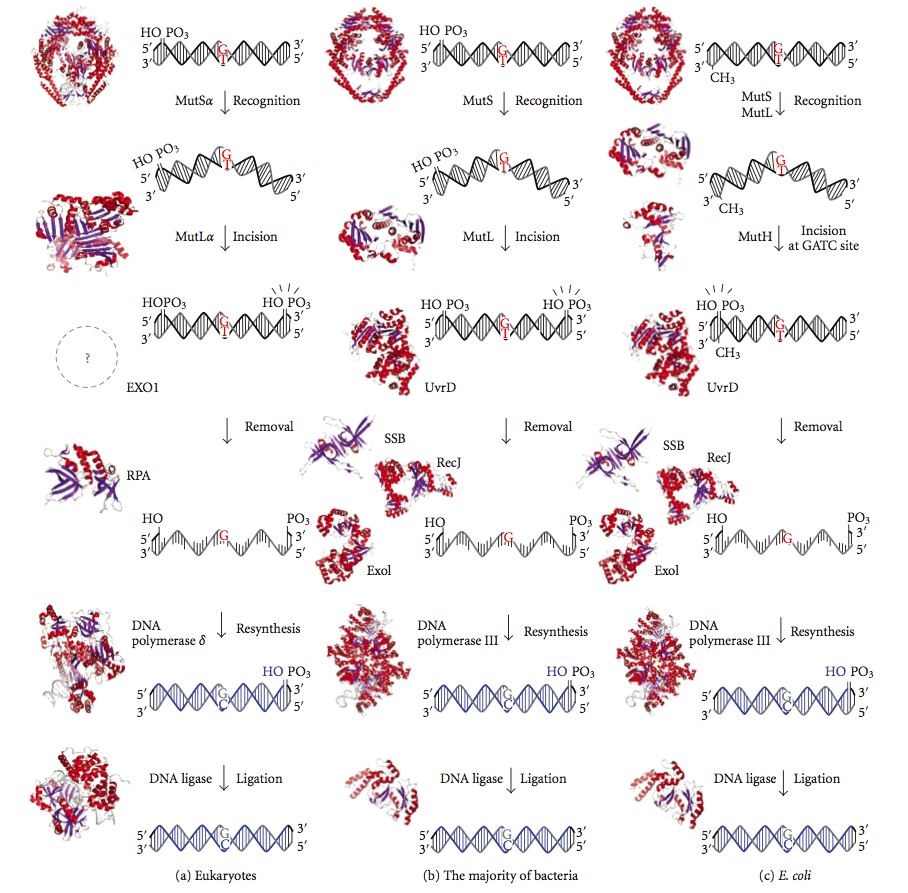
DNA mismatch repair (MMR) is a system for recognizing and repairing erroneous insertion, deletion, and mis-incorporation of nucleobase, bases that can arise during DNA replication and Genetic recombination, recombination, as well as DNA repair, repairing some forms of DNA damage. Mismatch repair is strand-specific. During DNA synthesis the newly synthesised (daughter) strand will commonly include errors. In order to begin repair, the mismatch repair machinery distinguishes the newly synthesised strand from the template (parental). In gram-negative bacteria, transient methylase, hemimethylation distinguishes the strands (the parental is methylated and daughter is not). However, in other prokaryotes and eukaryotes, the exact mechanism is not clear. It is suspected that, in eukaryotes, newly synthesized lagging-strand DNA transiently contains Nick (DNA), nicks (before being sealed by DNA ligase) and provides a signal that directs mismatch proofreading systems to the appropriate st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exonuclease
Exonucleases are enzymes that work by cleaving nucleotides one at a time from the end (exo) of a polynucleotide chain. A hydrolyzing reaction that breaks phosphodiester bonds at either the 3′ or the 5′ end occurs. Its close relative is the endonuclease, which cleaves phosphodiester bonds in the middle (endo) of a polynucleotide chain. Eukaryotes and prokaryotes have three types of exonucleases involved in the normal turnover of mRNA: 5′ to 3′ exonuclease (Xrn1), which is a dependent decapping protein; 3′ to 5′ exonuclease, an independent protein; and poly(A)-specific 3′ to 5′ exonuclease. In both archaea and eukaryotes, one of the main routes of RNA degradation is performed by the multi-protein exosome complex, which consists largely of 3′ to 5′ exoribonucleases. Significance to polymerase RNA polymerase II is known to be in effect during transcriptional termination; it works with a 5' exonuclease (human gene Xrn2) to degrade the newly formed transcr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Francis Crick
Francis Harry Compton Crick (8 June 1916 – 28 July 2004) was an English molecular biologist, biophysicist, and neuroscientist. He, James Watson, Rosalind Franklin, and Maurice Wilkins played crucial roles in deciphering the Nucleic acid double helix, helical structure of the DNA molecule. Crick and Watson's paper in ''Nature (journal), Nature'' in 1953 laid the groundwork for understanding DNA structure and functions. Together with Maurice Wilkins, they were jointly awarded the 1962 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine "for their discoveries concerning the molecular geometry, molecular structure of nucleic acids and its significance for information transfer in living material". Crick was an important theoretical molecular biologist and played a crucial role in research related to revealing the helical structure of DNA. He is widely known for the use of the term "central dogma" to summarise the idea that once information is transferred from nucleic acids (DNA or RNA) to prot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |