|
Frameserver
A frameserver is any program that acts as a media source in the process called ''frameserving'', which transfers digital video data from one computer program to another without intermediate files. The program that receives the data – the ''frameclient'' – could be any type of video application. The process is controlled by the frameclient: the frameclient ''requests'' audio/video frames and the frameserver ''serves'' them. The client can request frames in any order, allowing it to pause or jump to an arbitrary frame, just as a media player does with a file on disk. The client is most commonly a media encoder, a non-linear editing system, or a media player. Some popular frameservers are: * AviSynth * VirtualDub * Blender * VapourSynth * Debugmode FrameServer See also * Client–server model The client–server model is a distributed application structure that partitions tasks or workloads between the providers of a resource or service, called servers, and service requeste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AviSynth
AviSynth is a frameserver program for Microsoft Windows, Linux and macOS initially developed by Ben Rudiak-Gould, Edwin van Eggelen, Klaus Post, Richard Berg and Ian Brabham in May 2000 and later picked up and maintained by the open source community which is still active nowadays. It is free software licensed under the GNU General Public License. Scripting video editor AviSynth acts as a non-linear video editor controlled entirely by scripting (without a GUI). It emulates an AVI video file (or WAV audio file) as seen by the VFW downstream application, which is typically a media player, video editing software, or an encoder. AviSynth is built upon ''filters'', which are much like DirectShow filters, but with a different binary interface. Filter capabilities include cropping, deinterlacing, inverse telecine, working with still images, doing basic color grading, reducing video noise, and many other things. AviSynth also performs traditional video editing tasks like cut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digital Video
Digital video is an electronic representation of moving visual images (video) in the form of encoded digital data. This is in contrast to analog video, which represents moving visual images in the form of analog signals. Digital video comprises a series of digital images displayed in rapid succession, usually at 24, 30, or 60 frames per second. Digital video has many advantages such as easy copying, multicasting, sharing and storage. Digital video was first introduced commercially in 1986 with the D1 (Sony), Sony D1 format, which recorded an uncompressed standard-definition component video signal in digital form. In addition to uncompressed formats, popular Data compression, compressed digital video formats today include H.264 and MPEG-4. Modern interconnect standards used for playback of digital video include HDMI, DisplayPort, Digital Visual Interface (DVI) and serial digital interface (SDI). Digital video can be copied and reproduced with no degradation in quality. In contra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Program
A computer program is a sequence or set of instructions in a programming language for a computer to Execution (computing), execute. It is one component of software, which also includes software documentation, documentation and other intangible components. A ''computer program'' in its human-readable form is called source code. Source code needs another computer program to Execution (computing), execute because computers can only execute their native machine instructions. Therefore, source code may be Translator (computing), translated to machine instructions using a compiler written for the language. (Assembly language programs are translated using an Assembler (computing), assembler.) The resulting file is called an executable. Alternatively, source code may execute within an interpreter (computing), interpreter written for the language. If the executable is requested for execution, then the operating system Loader (computing), loads it into Random-access memory, memory and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer File
A computer file is a System resource, resource for recording Data (computing), data on a Computer data storage, computer storage device, primarily identified by its filename. Just as words can be written on paper, so too can data be written to a computer file. Files can be shared with and transferred between computers and Mobile device, mobile devices via removable media, Computer networks, networks, or the Internet. Different File format, types of computer files are designed for different purposes. A file may be designed to store a written message, a document, a spreadsheet, an Digital image, image, a Digital video, video, a computer program, program, or any wide variety of other kinds of data. Certain files can store multiple data types at once. By using computer programs, a person can open, read, change, save, and close a computer file. Computer files may be reopened, modified, and file copying, copied an arbitrary number of times. Files are typically organized in a file syst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
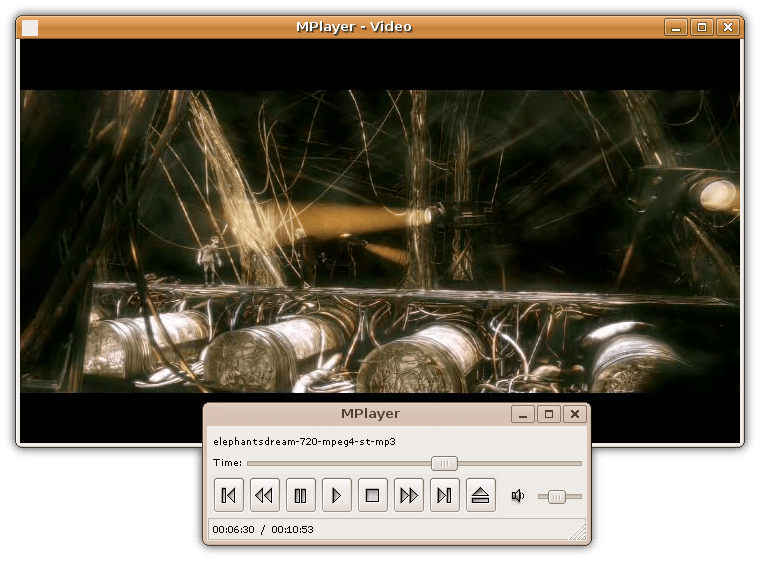
Media Player Software
Media player software is a type of application software for playing multimedia computer files like audio and video files. Media players commonly display standard media control icons known from physical devices such as tape recorders and CD players, such as play ( ), pause ( ), fastforward (⏩️), rewind (⏪), and stop ( ) buttons. In addition, they generally have progress bars (or "playback bars"), which are sliders to locate the current position in the duration of the media file. Mainstream operating systems have at least one default media player. For example, Windows comes with Windows Media Player, Microsoft Movies & TV and Groove Music, while macOS comes with QuickTime Player and Music. Linux distributions come with different media players, such as SMPlayer, Amarok, Audacious, Banshee, MPlayer, mpv, Rhythmbox, Totem, VLC media player, and xine. Android comes with YouTube Music for audio and Google Photos for video, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transcoding
Transcoding is the direct digital-to-digital conversion of one encoding to another, such as for video data files, audio files (e.g., MP3, WAV), or character encoding (e.g., UTF-8, ISO/IEC 8859). This is usually done in cases where a target device (or workflow) does not support the format or has limited storage capacity that mandates a reduced file size, "Advancements in Compression and Transcoding: 2008 and Beyond", Society of Motion Picture and Television Engineers (SMPTE), 2008, webpageSMPTE-spm or to convert incompatible or obsolete data to a better-supported or modern format. In the analog video world, transcoding can be performed just while files are being searched, as well as for presentation. For example, Cineon and DPX files have been widely used as a common format for digital cinema, but the data size of a two-hour movie is about 8 terabytes (TB). That large size can increase the cost and difficulty of handling movie files. However, transcoding into ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Non-linear Editing System
Non-linear editing (NLE) is a form of offline editing for audio, video, and image editing. In offline editing, the original content is not modified in the course of editing. In non-linear editing, edits are specified and modified by specialized software. A pointer-based playlist, effectively an edit decision list (EDL), for video and audio, or a directed acyclic graph for still images, is used to keep track of edits. Each time the edited audio, video, or image is rendered, played back, or accessed, it is reconstructed from the original source and the specified editing steps. Although this process is more computationally intensive than directly modifying the original content, changing the edits themselves can be almost instantaneous, and it prevents further generation loss as the audio, video, or image is edited. A non-linear editing system is a video editing (NLVE) program or application, or an audio editing (NLAE) digital audio workstation (DAW) system. These perform non ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
VirtualDub
VirtualDub is a free and open-source video capture and video processing utility for Microsoft Windows written by Avery Lee. It is designed to process linear video streams, including filtering and recompression. It uses AVI container format to store captured video. The first version of VirtualDub, written for Windows 95, to be released on SourceForge was uploaded on August 20, 2000. In 2009, the third-party software print guide ''Learning VirtualDub'' referred to VirtualDub as "the leading free Open Source video capture and processing tool". Due to its "powerful" versatility and usefulness especially in the field of video processing (see below), ''PC World'' has referred to VirtualDub as "something of a ' Photoshop' for video files", ''PC Perspective'' recommends it for its low overhead, and nextmedia's ''PC & Tech Authority'' particularly praises it for its ''Direct stream copy'' feature to avoid generational degradation of video quality when performing simple editing and trim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blender (software)
Blender is a Free and open-source software, free and open-source 3D computer graphics software tool set that runs on Microsoft Windows, Windows, macOS, BSD, Haiku (operating system), Haiku, IRIX and Linux. It is used for creating animated films, visual effects, art, 3D printing, 3D-printed models, motion graphics, interactive 3D applications, and virtual reality. It is also used in creating video games. Blender was used to produce the Academy Awards, Academy Award-winning film ''Flow (2024 film), Flow'' (2024). History Blender was initially developed as an in-house application by the Dutch animation studio NeoGeo (no relation to the Neo Geo, video game brand), and was officially launched on January 2, 1994. Version 1.00 was released in January 1995, with the primary author being the company co-owner and software developer Ton Roosendaal. The name ''Blender'' was inspired by a song by the Swiss electronic band Yello, from the album ''Baby (Yello album), Baby'', which NeoGeo used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Client–server Model
The client–server model is a distributed application structure that partitions tasks or workloads between the providers of a resource or service, called servers, and service requesters, called clients. Often clients and servers communicate over a computer network on separate hardware, but both client and server may be on the same device. A server host runs one or more server programs, which share their resources with clients. A client usually does not share its computing resources, but it requests content or service from a server and may share its own content as part of the request. Clients, therefore, initiate communication sessions with servers, which await incoming requests. Examples of computer applications that use the client–server model are email, network printing, and the World Wide Web. Client and server role The server component provides a function or service to one or many clients, which initiate requests for such services. Servers are classified by the servic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |