|
Fradiomycin
Neomycin, also known as framycetin, is an aminoglycoside antibiotic that displays bactericidal activity against Gram-negative aerobic bacilli and some anaerobic bacilli where resistance has not yet arisen. It is generally not effective against Gram-positive bacilli and anaerobic Gram-negative bacilli. Neomycin comes in oral and topical formulations, including creams, ointments, and eyedrops. Neomycin belongs to the aminoglycoside class of antibiotics that contain two or more amino sugars connected by glycosidic bonds. Neomycin was discovered in 1949 by microbiologist Selman Waksman and his student Hubert Lechevalier at Rutgers University. Neomycin received approval for medical use in 1952. Rutgers University was granted the patent for neomycin in 1957. Discovery Neomycin was discovered in 1949 by the microbiologist Selman Waksman and his student Hubert Lechevalier at Rutgers University. It is produced naturally by the bacterium ''Streptomyces fradiae''. Synthesis requires spec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gastrointestinal Tract
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the Digestion, digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The tract is the largest of the body's systems, after the cardiovascular system. The GI tract contains all the major organ (biology), organs of the digestive system, in humans and other animals, including the esophagus, stomach, and intestines. Food taken in through the mouth is digestion, digested to extract nutrients and absorb energy, and the waste expelled at the anus as feces. ''Gastrointestinal'' is an adjective meaning of or pertaining to the stomach and intestines. Nephrozoa, Most animals have a "through-gut" or complete digestive tract. Exceptions are more primitive ones: sponges have small pores (ostium (sponges), ostia) throughout their body for digestion and a larger dorsal pore (osculum) for excretion, comb jellies have both a ventral mouth and dorsal anal pores, while cnidarians and acoels have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patch Test
A patch test is a diagnostic method used to determine which specific substances cause allergic inflammation of a patient's skin. Patch testing helps identify which substances may be causing a delayed-type allergic reaction in a patient and may identify allergens not identified by blood testing or skin prick testing. It is intended to produce a local allergic reaction on a small area of the patient's back, where the diluted chemicals were planted. The chemicals included in the patch test kit are the offenders in approximately 85–90 percent of contact allergic eczema and include chemicals present in metals (''e.g.'', nickel), rubber, leather, formaldehyde, lanolin, fragrance, toiletries, hair dyes, medicine, pharmaceutical items, food, drink, preservative, and other additives. Mechanism A patch test relies on the principle of a type IV hypersensitivity reaction. The first step in becoming allergic is sensitization. When skin is exposed to an allergen, the antigen-pre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
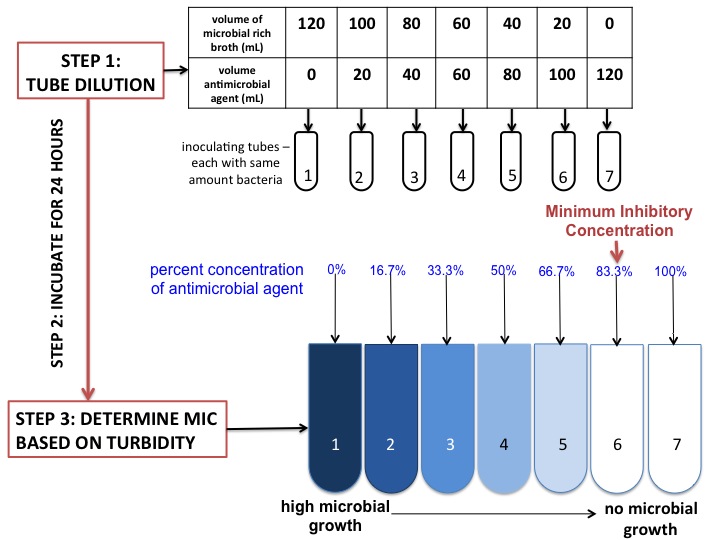
Minimum Inhibitory Concentration
In microbiology, the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) is the lowest concentration of a chemical, usually a drug, which prevents visible ''in vitro'' cell growth, growth of bacteria or Fungus, fungi. MIC testing is performed in both diagnostic and drug discovery laboratories. The MIC is determined by preparing a Serial dilution, dilution series of the chemical, adding agar dilution, agar or broth microdilution, broth, then inoculating with bacteria or fungi, and incubating at a suitable temperature. The value obtained is largely dependent on the susceptibility of the microorganism and the antimicrobial potency of the chemical, but other variables can affect results too. The MIC is often expressed in micrograms per milliliter (μg/mL) or milligrams per liter (mg/L). In diagnostic labs, MIC test results are used to grade the susceptibility of microbes. These grades are assigned based on agreed upon values called breakpoints. Breakpoints are published by standards organizati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polysporin
Bacitracin/polymyxin B, sold under the brand name Polysporin, among others, is a topical antibiotic cream or ointment. The active ingredients are polymyxin B, bacitracin and occasionally garamycin or gramicidin. Though Polysporin is marketed in the US, it holds a much smaller market share than in Canada and acts as a substitute to Johnson & Johnson's Neosporin for those allergic to the antibiotic neomycin Neomycin, also known as framycetin, is an aminoglycoside antibiotic that displays bactericidal activity against Gram-negative aerobic bacilli and some anaerobic bacilli where resistance has not yet arisen. It is generally not effective against .... However, allergy to bacitracin/polymyxin B has also been reported. There is also an ophthalmological ointment, eye and ear drops. References {{reflist External links Official Canadian SiteOfficial U.S. Site Combination antibiotics ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypersensitivity
Hypersensitivity (also called hypersensitivity reaction or intolerance) is an abnormal physiological condition in which there is an undesirable and adverse immune response to an antigen. It is an abnormality in the immune system that causes Immune disorder, immune diseases including allergies and autoimmunity. It is caused by many types of particles and substances from the external environment or from within the body that are recognized by the immune cells as antigens. The immune reactions are usually referred to as an over-reaction of the immune system and they are often damaging and uncomfortable. In 1963, Philip George Houthem Gell and Robin Coombs introduced a systematic classification of the different types of hypersensitivity based on the types of antigens and immune responses involved. According to this system, known as the #Gell and Coombs classification, Gell and Coombs classification or Gell-Coombs's classification, there are four types of hypersensitivity, namely: Typ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gram-positive Bacteria
In bacteriology, gram-positive bacteria are bacteria that give a positive result in the Gram stain test, which is traditionally used to quickly classify bacteria into two broad categories according to their type of cell wall. The Gram stain is used by microbiologists to place bacteria into two main categories, gram-positive (+) and gram-negative (−). Gram-positive bacteria have a thick layer of peptidoglycan within the cell wall, and gram-negative bacteria have a thin layer of peptidoglycan. Gram-positive bacteria retain the crystal violet stain used in the test, resulting in a purple color when observed through an optical microscope. The thick layer of peptidoglycan in the bacterial cell wall retains the stain after it has been fixed in place by iodine. During the decolorization step, the decolorizer removes crystal violet from all other cells. Conversely, gram-negative bacteria cannot retain the violet stain after the decolorization step; alcohol used in this stage ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gram-negative Bacteria
Gram-negative bacteria are bacteria that, unlike gram-positive bacteria, do not retain the Crystal violet, crystal violet stain used in the Gram staining method of bacterial differentiation. Their defining characteristic is that their cell envelope consists of a thin peptidoglycan gram-negative cell wall, cell wall sandwiched between an inner (Cytoplasm, cytoplasmic) Cell membrane, membrane and an Bacterial outer membrane, outer membrane. These bacteria are found in all environments that support life on Earth. Within this category, notable species include the model organism ''Escherichia coli'', along with various pathogenic bacteria, such as ''Pseudomonas aeruginosa'', ''Chlamydia trachomatis'', and ''Yersinia pestis''. They pose significant challenges in the medical field due to their outer membrane, which acts as a protective barrier against numerous Antibiotic, antibiotics (including penicillin), Detergent, detergents that would normally damage the inner cell membrane, and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polymyxin B
Polymyxin B, sold under the brand name Poly-Rx among others, is an antibiotic used to treat meningitis, pneumonia, sepsis, and urinary tract infections. While it is useful for many Gram negative infections, it is not useful for Gram positive infections. It can be given by injection into a vein, muscle, or cerebrospinal fluid or inhaled. The injectable form is generally only used if other options are not available. It is also available as the combinations bacitracin/polymyxin B and neomycin/polymyxin B/bacitracin for use on the skin. Common side effects when given by injection include kidney problems, neurological problems, fever, itchiness, and rash. Injections into muscle may result in significant pain. Other serious side effects may include fungal infections, anaphylaxis, and muscle weakness. It is unclear if use during pregnancy is safe for the baby. Polymyxin B works by breaking down the cytoplasmic membrane which generally results in bacterial cell death. Polymyxin B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dexamethasone
Dexamethasone is a fluorinated glucocorticoid medication used to treat rheumatic problems, a number of skin diseases, severe allergies, asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), croup, brain swelling, eye pain following eye surgery, superior vena cava syndrome (a complication of some forms of cancer), and along with antibiotics in tuberculosis. In adrenocortical insufficiency, it may be used in combination with a mineralocorticoid medication such as fludrocortisone. In preterm labor, it may be used to improve outcomes in the baby. It may be given by mouth, as an injection into a muscle, as an injection into a vein, as a topical cream or ointment for the skin or as a topical ophthalmic solution to the eye. The effects of dexamethasone are frequently seen within a day and last for about three days. The long-term use of dexamethasone may result in thrush, bone loss, cataracts, easy bruising, or muscle weakness. It is in pregnancy category C in the United S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nephrotoxic
Nephrotoxicity is toxicity in the kidneys. It is a poisonous effect of some substances, both toxic chemicals and medications, on kidney function. There are various forms, and some drugs may affect kidney function in more than one way. Nephrotoxins are substances displaying nephrotoxicity. Nephrotoxicity should not be confused with some medications predominantly excreted by the kidneys needing their dose adjusted for the decreased kidney function (e.g., heparin, lithium). Types of toxicity Cardiovascular * General: diuretics, β-blockers, vasodilator agents * Local: ACE inhibitors, ciclosporin, tacrolimus. Direct tubular effect * Proximal convoluted tubule: Aminoglycoside antibiotics (e.g., gentamicin), amphotericin B, cisplatin, radiocontrast media, immunoglobulins, mannitol * Distal tubule: NSAIDs (e.g. aspirin, ibuprofen, diclofenac), ACE inhibitors, ciclosporin, lithium salts, cyclophosphamide, amphotericin B * Tubular obstruction: sulphonamides, metho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth
Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO), also termed bacterial overgrowth, or small bowel bacterial overgrowth syndrome (SBBOS), is a disorder of excessive bacterial growth in the small intestine. Unlike the colon (or large bowel), which is rich with bacteria, the small bowel usually has fewer than 100,000 organisms per millilitre. Patients with SIBO typically develop symptoms which may include nausea, bloating, vomiting, diarrhea, malnutrition, weight loss, and malabsorption by various mechanisms. The diagnosis of SIBO is made by several techniques, with the gold standard being an aspirate from the jejunum that grows more than 105 bacteria per millilitre. Risk factors for the development of SIBO include dysmotility; anatomical disturbances in the bowel, including fistulae, diverticula and blind loops created after surgery, and resection of the ileo-cecal valve; gastroenteritis-induced alterations to the small intestine; and the use of certain medications, including proton ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |