|
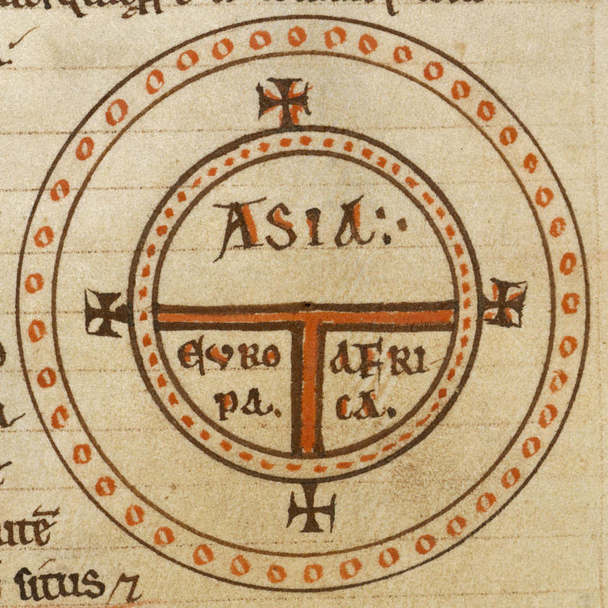
Four Corners Of The World
Several cosmological and mythological systems portray four corners of the world or four quarters of the world corresponding approximately to the four points of the compass (or the two solstices and two equinoxes). At the center may lie a sacred mountain, garden, world tree, or other beginning-point of creation. Often four rivers run to the four corners of the world, and water or irrigate the four quadrants of Earth. Ancient near eastern traditions In Mesopotamian cosmology, four rivers flowing out of the garden of creation, which is the center of the world, define the four corners of the world. From the point of view of the Akkadians, the northern geographical horizon was marked by Subartu, the west by , the east by Elam and the south by Sumer; later rulers of all of Mesopotamia, such as Cyrus, claimed among their titles ', "King of the Four Corners". Semitic traditions In Christianity and Judaism, the Old Testament (Book of Genesis, ) identifies the Garden of Eden, and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earth Symbol
A variety of symbols or iconographic conventions are used to represent :wikt:Earth, Earth, whether in the sense of Earth, planet Earth, or the world, inhabited world, or as a classical element. A circle representing the round world, with the rivers of Garden of Eden separating the four corners of the world, or rotated 45° to suggest the four continents, remains a common pictographic convention to express the notion of "worldwide". The current astronomical symbols for the planet are a circle with an intersecting cross, file:Earth symbol (fixed width).svg, 20px, 🜨, alt=An equilateral cross enclosed in a circle, and a ''globus cruciger'', file:Globus cruciger (fixed width).svg, 20px, ♁. Although the International Astronomical Union (IAU) now discourages the use of planetary symbols, this is an exception, being used in abbreviations such as ''M''🜨 or ''M''♁ for Earth mass. History The earliest type of symbols are allegory, allegories, personifications or deifications, most ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Testament
The Old Testament (OT) is the first division of the Christian biblical canon, which is based primarily upon the 24 books of the Hebrew Bible, or Tanakh, a collection of ancient religious Hebrew and occasionally Aramaic writings by the Israelites. The second division of Christian Bibles is the New Testament, written in Koine Greek. The Old Testament consists of many distinct books by various authors produced over a period of centuries. Christians traditionally divide the Old Testament into four sections: the first five books or Pentateuch (which corresponds to the Jewish Torah); the history books telling the history of the Israelites, from their conquest of Canaan to their defeat and exile in Babylon; the poetic and wisdom literature, which explore themes of human experience, morality, and divine justice; and the books of the biblical prophets, warning of the consequences of turning away from God. The Old Testament canon differs among Christian denominations. The Ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hinduism
Hinduism () is an Hypernymy and hyponymy, umbrella term for a range of Indian religions, Indian List of religions and spiritual traditions#Indian religions, religious and spiritual traditions (Sampradaya, ''sampradaya''s) that are unified by adherence to the concept of ''dharma'', a Ṛta, cosmic order maintained by its followers through rituals and righteous living, as expounded in the Vedas. The word ''Hindu'' is an exonym, and while Hinduism has been called the oldest religion in the world, it has also been described by the modern term ''Sanātana Dharma'' () emphasizing its eternal nature. ''Vaidika Dharma'' () and ''Arya dharma'' are historical endonyms for Hinduism. Hinduism entails diverse systems of thought, marked by a range of shared Glossary of Hinduism terms, concepts that discuss God in Hinduism, theology, Hindu mythology, mythology, among other topics in Hindu texts, textual sources. Hindu texts have been classified into Śruti () and Smṛti (). The major Hin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Book Of Revelation
The Book of Revelation, also known as the Book of the Apocalypse or the Apocalypse of John, is the final book of the New Testament, and therefore the final book of the Bible#Christian Bible, Christian Bible. Written in Greek language, Greek, its title is derived from the Incipit, first word of the text, ''apocalypse'' (), which means "revelation" or "unveiling". The Book of Revelation is the only Apocalyptic literature, apocalyptic book in the Development of the New Testament canon, New Testament canon, and occupies a central place in Christian eschatology. The book spans three literary genres: the Letter (message), epistolary, the Apocalyptic literature, apocalyptic, and the prophetic. It begins with John, on the island of Patmos in the Aegean Sea, addressing letters to the "Seven Churches of Asia" with exhortations from Christ. He then describes a series of prophetic and symbolic Vision (spirituality), visions, including figures such as a Woman clothed with the sun with the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aethiopia
Ancient Aethiopia, () first appears as a geographical term in classical documents in reference to the skin color of the inhabitants of the upper Nile in northern Sudan, of areas south of the Sahara, and of certain areas in Asia. Its earliest mention is in the works of Homer: twice in the ''Iliad'', and three times in the ''Odyssey''. The Greek historian Herodotus uses the appellation to refer to regions south of Egypt when describing "Aethiopians," indicating Nubia, not the modern nation of Ethiopia. Etymology The Greek name ''Aithiopia'' (, from ) is a compound derived of two Greek words: + . According to the Perseus Project, this designation properly translates in noun form as ''burnt-face'' and in adjectival form as ''red-brown''. As such, it was used as a vague term for darker skinned populations than the Greeks since the time of Homer.“” Homer, ''Iliad'', 1.423, whence nom. “” ''Call.Del.208'': (, ):—properly, ''Burnt-face'', i.e. ''Ethiopian, negro'', , etc.; ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Havilah
Havilah () refers to both a land and people in several books of the Bible; one is mentioned in Genesis 2:10–11, while the other is mentioned in the Generations of Noah (Genesis 10:7). In Genesis 2:10–11, Havilah is associated with the Garden of Eden. Two individuals named Havilah are listed in the Table of Nations as descendants of Noah. The name also appears in Toledot, Genesis 25:18, defining the territory of the Ishmaelites. Extrabiblical literature mentions Havilah as the source of precious jewels used by the Amorites. The exact location of Havilah is debated, with various scholars suggesting southwest of the Arabian Peninsula or Somalia. Biblical mentions In one case, Havilah is associated with the Garden of Eden, that mentioned in the Book of Genesis (2:10–11): In addition to the region described in chapter 2 of Genesis, two individuals named Havilah are listed in the Table of Nations. The Table lists the descendants of Noah, who are considered eponymous ancestors o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armenia
Armenia, officially the Republic of Armenia, is a landlocked country in the Armenian Highlands of West Asia. It is a part of the Caucasus region and is bordered by Turkey to the west, Georgia (country), Georgia to the north and Azerbaijan to the east, and Iran and the Azerbaijani exclave of Nakhchivan Autonomous Republic, Nakhchivan to the south. Yerevan is the Capital city, capital, largest city and Economy of Armenia, financial center. The Armenian Highlands has been home to the Hayasa-Azzi, Shupria and Nairi. By at least 600 BC, an archaic form of Proto-Armenian language, Proto-Armenian, an Indo-European languages, Indo-European language, had diffused into the Armenian Highlands.Robert Drews (2017). ''Militarism and the Indo-Europeanizing of Europe''. Routledge. . p. 228: "The vernacular of the Great Kingdom of Biainili was quite certainly Armenian. The Armenian language was obviously the region's vernacular in the fifth century BC, when Persian commanders and Greek writers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Assyria
Assyria (Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , ''māt Aššur'') was a major ancient Mesopotamian civilization that existed as a city-state from the 21st century BC to the 14th century BC and eventually expanded into an empire from the 14th century BC to the 7th century BC. Spanning from the early Bronze Age to the late Iron Age, modern historians typically divide ancient Assyrian history into the Early Assyrian period, Early Assyrian ( 2600–2025 BC), Old Assyrian period, Old Assyrian ( 2025–1364 BC), Middle Assyrian Empire, Middle Assyrian ( 1363–912 BC), Neo-Assyrian Empire, Neo-Assyrian (911–609 BC), and Post-imperial Assyria, post-imperial (609 BC– AD 240) periods, based on political events and gradual changes in language. Assur, the first Assyrian capital, was founded 2600 BC, but there is no evidence that the city was independent until the collapse of the Third Dynasty of Ur, in the 21st century BC, when a line of independent kings starting with Puzur-Ashur I began rulin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gihon
Gihon is the name of the second river mentioned in the second chapter of the biblical Book of Genesis. The Gihon is mentioned as one of four rivers (along with the Tigris, Euphrates, and Pishon) issuing out of Eden, branching from a single river that split after watering the Garden of Eden (Genesis 2:10–14). Overview The name (Hebrew ''Gīḥōn'' גיחון) may be interpreted as "bursting forth, gushing". The book of Genesis describes Gihon as "encircling the entire land of Cush", a name associated with Ethiopia elsewhere in the Bible. This is the reason that Ethiopians have long identified the Gihon (''Giyon'') with the Abay River (Blue Nile), which encircles the former kingdom of Gojjam. From a geographic standpoint this would seem impossible, since two of the other rivers said to issue out of Eden, the Tigris and the Euphrates, are in Mesopotamia. However, the scholar Edward Ullendorff has argued in support of this identification. In the Italian (Venetian) Fra Mauro map ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pishon
The Pishon ( ''Pīšōn''; Koine Greek: Φισών ''Phisṓn'') is one of four rivers (along with Hiddekel (Tigris), Perath (Euphrates) and Gihon) mentioned in the Biblical Book of Genesis. In that passage, a source river flows out of Eden to water the Garden of Eden and from there divides into the four named rivers. The Pishon is described as encircling "the entire land of Havilah where is gold; bdellium and onyx stone." Identification Unlike the Tigris and the Euphrates, the Pishon has never been clearly located. It is briefly mentioned together with the Tigris in the Wisdom of Sirach (24:25/35), but this reference throws no more light on the location of the river. The Jewish–Roman historian Flavius Josephus, in the beginning of his ''Antiquities of the Jews'' (1st century AD) identified the Pishon with the Ganges. The medieval French rabbi Rashi identified it with the Nile. Some early modern scholars such as Antoine Augustin Calmet (1672–1757) and later figures su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euphrates
The Euphrates ( ; see #Etymology, below) is the longest and one of the most historically important rivers of West Asia. Tigris–Euphrates river system, Together with the Tigris, it is one of the two defining rivers of Mesopotamia (). Originating in Turkey, the Euphrates flows through Syria and Iraq to join the Tigris in the Shatt al-Arab in Iraq, which empties into the Persian Gulf. The Euphrates is the List of longest rivers of Asia, fifteenth-longest river in Asia and the longest in West Asia, at about , with a drainage area of that covers six countries. Etymology The term ''Euphrates'' derives from the Koine Greek, Greek ''Euphrátēs'' (), adapted from , itself from . The Elamite name is ultimately derived from cuneiform 𒌓𒄒𒉣; read as ''Buranun'' in Sumerian language, Sumerian and ''Purattu'' in Akkadian language, Akkadian; many cuneiform signs have a Sumerian pronunciation and an Akkadian pronunciation, taken from a Sumerian word and an Akkadian word that mean ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tigris
The Tigris ( ; see #Etymology, below) is the eastern of the two great rivers that define Mesopotamia, the other being the Euphrates. The river flows south from the mountains of the Armenian Highlands through the Syrian Desert, Syrian and Arabian Deserts, before merging with the Euphrates and reaching to the Persian Gulf. The Tigris passes through historical cities like Mosul, Tikrit, Samarra, and Baghdad. It is also home to archaeological sites and ancient religious communities, including the Mandaeans, who use it for Masbuta, baptism. In ancient times, the Tigris nurtured the Assyria, Assyrian Empire, with remnants like the relief of Tiglath-Pileser I, King Tiglath-Pileser. Today, the Tigris faces modern threats from geopolitical instability, dam projects, poor water management, and climate change, leading to concerns about its sustainability. Efforts to protect and preserve the river's legacy are ongoing, with local archaeologists and activists working to safeguard its future ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |