|
Formamide
Formamide is an amide derived from formic acid. It is a colorless liquid which is miscible with water and has an ammonia-like odor. It is chemical feedstock for the manufacture of sulfa drugs and other pharmaceuticals, herbicides and pesticides, and in the manufacture of hydrocyanic acid. It has been used as a softener for paper and fiber. It is a solvent for many ionic compounds. It has also been used as a solvent for resins and plasticizers. Some astrobiologists suggest that it may be an alternative to water as the main solvent in other forms of life. Formamides are compounds of the type RR′NCHO. One important formamide is dimethylformamide, (CH3)2NCHO. Production Historical production In the past, formamide was produced by treating formic acid with ammonia, which produces ammonium formate, which in turn yields formamide upon heating: : HCOOH + NH3 → : → HCONH2 + H2O Formamide is also generated by aminolysis of ethyl formate: :HCOOCH2CH3 + NH3 → HCONH2 + CH3 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dimethylformamide
Dimethylformamide, DMF is an organic compound with the chemical formula . Its structure is . Commonly abbreviated as DMF (although this initialism is sometimes used for 2,5-dimethylfuran, dimethylfuran, or dimethyl fumarate), this colourless liquid is Miscibility, miscible with Water (molecule), water and the majority of organic liquids. DMF is a common solvent for chemical reactions. Dimethylformamide is odorless, but chemical purity, technical-grade or degraded samples often have a fishy smell due to impurity of dimethylamine. Dimethylamine degradation impurities can be removed by Sparging (chemistry), sparging samples with an inert gas such as argon or by sonication, sonicating the samples under reduced pressure. As its name indicates, it is structurally related to formamide, having two methyl groups in the place of the two hydrogens. DMF is a polar molecule, polar (hydrophilic) aprotic solvent with a high boiling point. It facilitates reactions that follow polar mechanisms, such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amide
In organic chemistry, an amide, also known as an organic amide or a carboxamide, is a chemical compound, compound with the general formula , where R, R', and R″ represent any group, typically organyl functional group, groups or hydrogen atoms. The amide group is called a peptide bond when it is part of the Polymer backbone, main chain of a protein, and an isopeptide bond when it occurs in a side chain, as in asparagine and glutamine. It can be viewed as a Derivative (chemistry), derivative of a carboxylic acid () with the hydroxyl group () replaced by an amino group (); or, equivalently, an acyl group, acyl (alkanoyl) group () joined to an amino group. Common amides are formamide (), acetamide (), benzamide (), and dimethylformamide (). Some uncommon examples of amides are ''N''-chloroacetamide () and chloroformamide (). Amides are qualified as primary (chemistry), primary, secondary (chemistry), secondary, and tertiary (chemistry), tertiary according to the number of acyl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solvent
A solvent (from the Latin language, Latin ''wikt:solvo#Latin, solvō'', "loosen, untie, solve") is a substance that dissolves a solute, resulting in a Solution (chemistry), solution. A solvent is usually a liquid but can also be a solid, a gas, or a supercritical fluid. Water is a solvent for Chemical polarity#Polarity of molecules, polar molecules, and the most common solvent used by living things; all the ions and proteins in a Cell (biology), cell are dissolved in water within the cell. Major uses of solvents are in paints, paint removers, inks, and dry cleaning. Specific uses for Organic compound, organic solvents are in dry cleaning (e.g. tetrachloroethylene); as paint thinners (toluene, turpentine); as nail polish removers and solvents of glue (acetone, methyl acetate, ethyl acetate); in spot removers (hexane, petrol ether); in detergents (D-limonene, citrus terpenes); and in perfumes (ethanol). Solvents find various applications in chemical, pharmaceutical, oil, and gas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ammonium Formate
Ammonium formate, NH4HCO2, is the ammonium salt of formic acid. It is a colorless, hygroscopic, crystalline solid. Reductive amination Acetone can be transformed into isopropylamine as follows: :CH3C(O)CH3 + 2 HCO2− +NH4 → (CH3)2CHNHCHO + 2 H2O + NH3 + CO2 :(CH3)2CHNHCHO + H2O → (CH3)2CHNH2 + HCO2H Uses Pure ammonium formate decomposes into formamide and water when heated, and this is its primary use in industry. Formic acid can also be obtained by reacting ammonium formate with a dilute acid, and since ammonium formate is also produced from formic acid, it can serve as a way of storing formic acid. Ammonium formate can also be used in palladium on carbon (Pd/C) reduction of functional groups. In the presence of Pd/C, ammonium formate decomposes to hydrogen, carbon dioxide, and ammonia. This hydrogen gas is adsorbed onto the surface of the palladium metal, where it can react with various functional groups. For example, alkenes can be reduced to alkanes, formaldehyde to me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methyl Formate
Methyl formate, also called methyl methanoate, is the methyl ester of formic acid. The simplest example of a carboxylate ester, it is a colourless liquid with an ethereal odour, high vapor pressure, and low surface tension. The gas form is odourless and toxic, and used to be used in fridges. It is a precursor to many other compounds of commercial interest.Werner Reutemann and Heinz Kieczka "Formic Acid" in ''Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry'' 2002, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. Production In the laboratory, methyl formate can be produced by the condensation reaction of methanol and formic acid, as follows: :HCOOH + CH3OH → HCOOCH3 + H2O Industrial methyl formate, however, is usually produced by the combination of methanol and carbon monoxide ( carbonylation) in the presence of a strong base, such as sodium methoxide: This process, practiced commercially by BASF among other companies gives 96% selectivity toward methyl formate. The catalyst for this process is s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyacrylonitrile
Polyacrylonitrile (PAN) is a synthetic, semicrystalline organic polymer resin, with the linear formula (CH2CHCN)n. Almost all PAN resins are copolymers with acrylonitrile as the main monomer. PAN is used to produce large variety of products including ultra filtration membranes, hollow fibers for reverse osmosis, fibers for textiles, and oxidized PAN fibers. PAN fibers are the chemical precursor of very high-quality carbon fiber. PAN is first thermally oxidized in air at 230 °C to form an oxidized PAN fiber and then carbonized above 1000 °C in inert atmosphere to make carbon fibers found in a variety of both high-tech and common daily applications such as civil and military aircraft primary and secondary structures, missiles, solid propellant rocket motors, pressure vessels, fishing rods, tennis rackets and bicycle frames. It is a component repeat unit in several important copolymers, such as styrene-acrylonitrile (SAN) and acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Formic Acid
Formic acid (), systematically named methanoic acid, is the simplest carboxylic acid. It has the chemical formula HCOOH and structure . This acid is an important intermediate in chemical synthesis and occurs naturally, most notably in some ants. Esters, salts, and the anion derived from formic acid are called formates. Industrially, formic acid is produced from methanol. Natural occurrence Formic acid, which has a pungent, penetrating odor, is found naturally in insects, weeds, fruits and vegetables, and forest emissions. It appears in most ants and in stingless bees of the genus '' Oxytrigona''. Wood ants from the genus ''Formica'' can spray formic acid on their prey or to defend the nest. The puss moth caterpillar (''Cerura vinula'') will spray it as well when threatened by predators. It is also found in the trichomes of stinging nettle (''Urtica dioica''). Apart from that, this acid is incorporated in many fruits such as pineapple (0.21 mg per 100 g), apple (2 mg per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ammonia
Ammonia is an inorganic chemical compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the chemical formula, formula . A Binary compounds of hydrogen, stable binary hydride and the simplest pnictogen hydride, ammonia is a colourless gas with a distinctive pungent smell. It is widely used in fertilizers, refrigerants, explosives, cleaning agents, and is a precursor for numeous chemicals. Biologically, it is a common nitrogenous waste, and it contributes significantly to the nutritional needs of terrestrial organisms by serving as a precursor to fertilisers. Around 70% of ammonia produced industrially is used to make fertilisers in various forms and composition, such as urea and diammonium phosphate. Ammonia in pure form is also applied directly into the soil. Ammonia, either directly or indirectly, is also a building block for the synthesis of many chemicals. In many countries, it is classified as an List of extremely hazardous substances, extremely hazardous substance. Ammonia is toxic, cau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon Monoxide
Carbon monoxide (chemical formula CO) is a poisonous, flammable gas that is colorless, odorless, tasteless, and slightly less dense than air. Carbon monoxide consists of one carbon atom and one oxygen atom connected by a triple bond. It is the simplest oxocarbon, carbon oxide. In coordination complexes, the carbon monoxide ligand is called ''metal carbonyl, carbonyl''. It is a key ingredient in many processes in industrial chemistry. The most common source of carbon monoxide is the partial combustion of carbon-containing compounds. Numerous environmental and biological sources generate carbon monoxide. In industry, carbon monoxide is important in the production of many compounds, including drugs, fragrances, and fuels. Indoors CO is one of the most acutely toxic contaminants affecting indoor air quality. CO may be emitted from tobacco smoke and generated from malfunctioning fuel-burning stoves (wood, kerosene, natural gas, propane) and fuel-burning heating systems (wood, oil, n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dimethyl Sulfoxide
Dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) is an organosulfur compound with the formula . This colorless liquid is the sulfoxide most widely used commercially. It is an important polar aprotic solvent that dissolves both polar and nonpolar compounds and is miscible in a wide range of organic solvents as well as water. It has a relatively high boiling point. DMSO is metabolised to compounds that leave a garlic-like taste in the mouth after DMSO is absorbed by skin. In terms of chemical structure, the molecule has idealized Cs symmetry. It has a trigonal pyramidal molecular geometry consistent with other three-coordinate S(IV) compounds, with a nonbonded electron pair on the approximately tetrahedral sulfur atom. Synthesis and production Dimethyl sulfoxide was first synthesized in 1866 by the Russian scientist Alexander Zaytsev, who reported his findings in 1867. Its modern use as an industrial solvent began through popularization by Thor Smedslund at the Stepan Chemical Company. Dimeth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
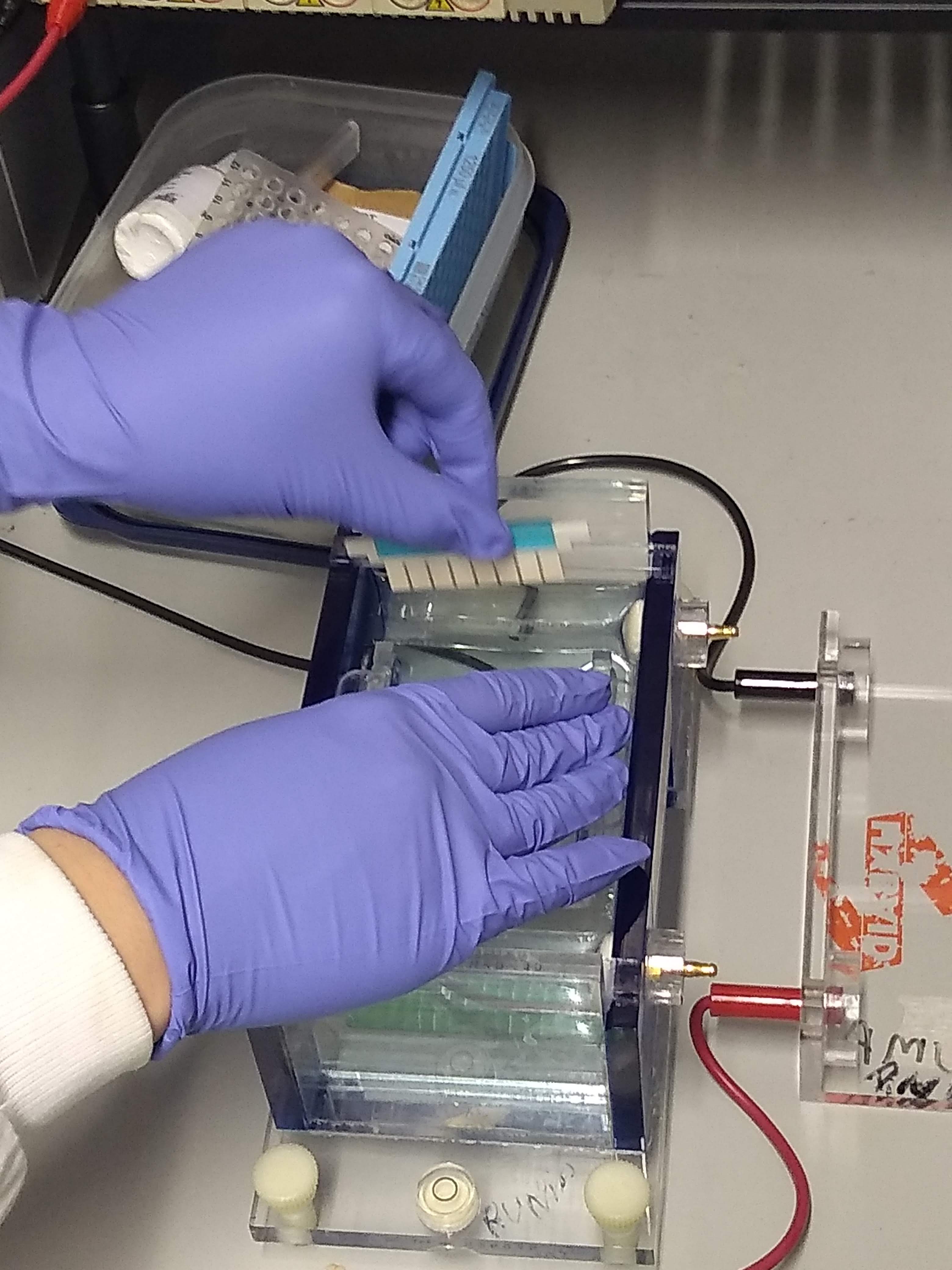
Gel Electrophoresis
Gel electrophoresis is an electrophoresis method for separation and analysis of biomacromolecules (DNA, RNA, proteins, etc.) and their fragments, based on their size and charge through a gel. It is used in clinical chemistry to separate proteins by charge or size (IEF agarose, essentially size independent) and in biochemistry and molecular biology to separate a mixed population of DNA and RNA fragments by length, to estimate the size of DNA and RNA fragments, or to separate proteins by charge. Nucleic acid molecules are separated by applying an electric field to move the negatively charged molecules through a gel matrix of agarose, polyacrylamide, or other substances. Shorter molecules move faster and migrate farther than longer ones because shorter molecules migrate more easily through the pores of the gel. This phenomenon is called sieving. Proteins are separated by the charge in agarose because the pores of the gel are too large to sieve proteins. Gel electrophoresi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |