|
Food Rent
Food render or food rent (Old English: ''foster'') was a form of tax in kind (Old English: ''feorm'') levied in Anglo-Saxon England, consisting of essential foodstuffs provided by territories such as ''regiones'', multiple estates or hundreds to kings and other members of royal households at a territory's royal vill. The early medieval British Isles lacked the sophisticated trade in essential foodstuffs that had supported the urban economies of Roman Britain, and which would be necessary to support large agriculturally unproductive households remaining static in a single location. Kings and their entourages therefore constantly toured the subdivisions of their kingdoms, staying at networks of royal properties where they could expect to be supported by the territory's inhabitants. In the words of historian Thomas Charles-Edwards: "it made much more sense to take a royal household to the food than the food to the royal household". Food renders were distinct from the tribute that Kin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old English
Old English ( or , or ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the Early Middle Ages. It developed from the languages brought to Great Britain by Anglo-Saxon settlers in the mid-5th century, and the first Old English literature dates from the mid-7th century. After the Norman Conquest of 1066, English was replaced for several centuries by Anglo-Norman language, Anglo-Norman (a langues d'oïl, type of French) as the language of the upper classes. This is regarded as marking the end of the Old English era, since during the subsequent period the English language was heavily influenced by Anglo-Norman, developing into what is now known as Middle English in England and Early Scots in Scotland. Old English developed from a set of Anglo-Frisian or Ingvaeonic dialects originally spoken by Germanic tribes traditionally known as the Angles (tribe), Angles, Saxons and Jutes. As the Germanic settlers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tax In Kind
Tax in kind or tax-in-kind refers to any taxation that is paid in kind, that is with goods or services rather than money. Some notable examples of tax in kind include: * ''corvée'', a tax paid in manual labour, such as on a public works project. * ''fisc'', in the Frankish kingdoms of the Medieval period * food render, a ''feorm'' or tax-in-kind provided through royal vills in Anglo-Saxon England * ''kharaj'', instituted during the period of the Islamic Empire * a tax on agricultural produce imposed by the Confederate States of America in 1863 * '' Prodnalog'', paid by private farms in Soviet Russia during the 1920s under the New Economic Policy. * An agricultural tax in North Korea imposed in 1947 and abolished in 1966 See also *Barter In trade, barter (derived from ''bareter'') is a system of exchange (economics), exchange in which participants in a financial transaction, transaction directly exchange good (economics), goods or service (economics), services for other g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anglo-Saxon England
Anglo-Saxon England or early medieval England covers the period from the end of Roman Empire, Roman imperial rule in Roman Britain, Britain in the 5th century until the Norman Conquest in 1066. Compared to modern England, the territory of the Anglo-Saxons stretched north to present day Lothian in southeastern Scotland, whereas it did not initially include western areas of England such as Cornwall, Herefordshire, Shropshire, Cheshire, Lancashire, and Cumbria. The 5th and 6th centuries involved the collapse of economic networks and political structures and also saw a radical change to a new Anglo-Saxon language and culture. This change was driven by movements of peoples as well as changes which were happening in both northern Gaul and the North Sea coast of what is now Germany and the Netherlands. The Anglo-Saxon language, also known as Old English, was a close relative of languages spoken in the latter regions, and genetic studies have confirmed that there was significant migrat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
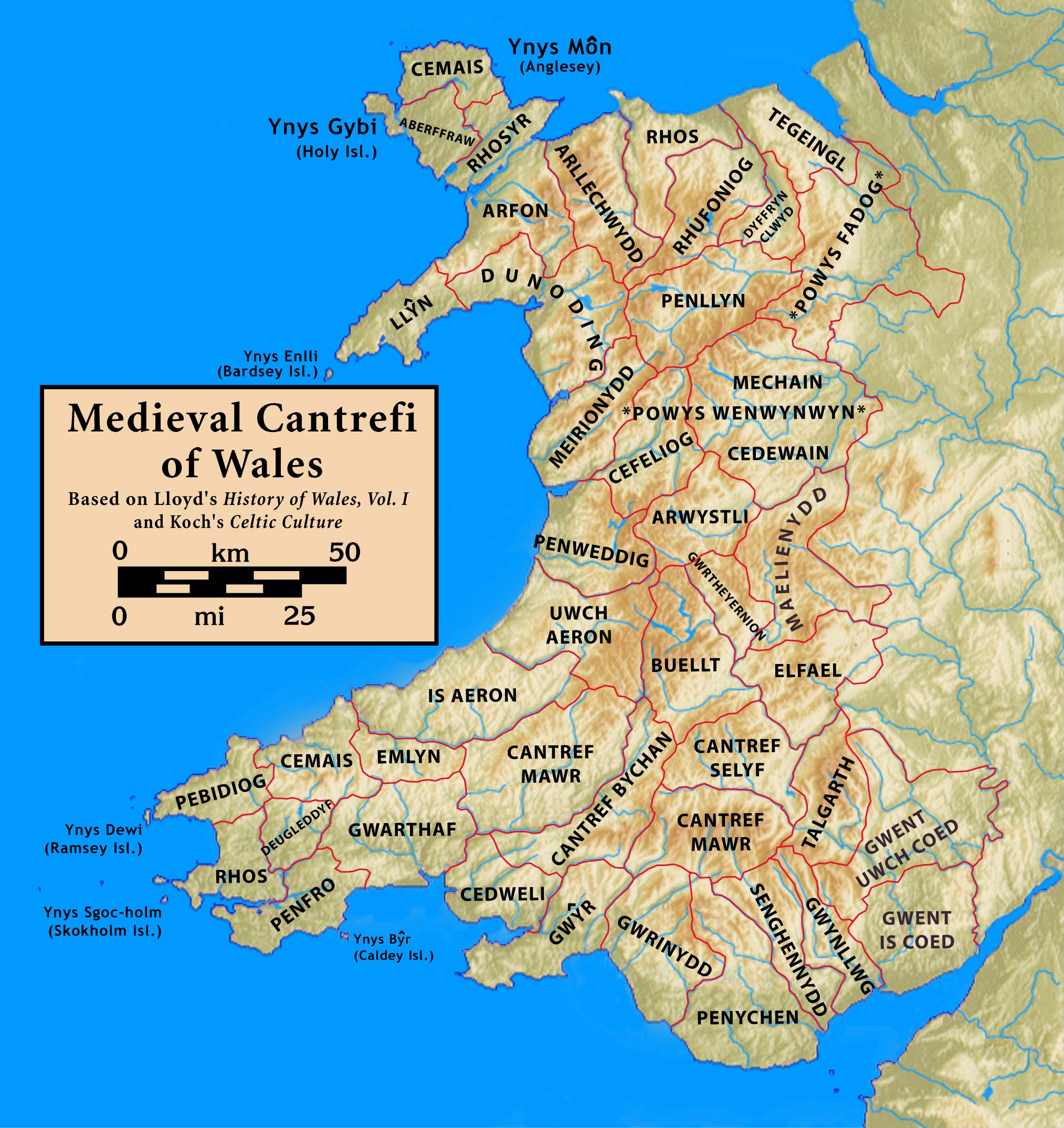
Regiones
''Regiones'' (singular: ''regio'') or ''provinciae'',(singular: ''provincia''), also referred to by historians as small shires or early folk territories, were early territorial divisions of Anglo-Saxon England, referred to in sources such as Anglo-Saxon charters and the writings of Bede. They are likely to have originated in the years before 600, and most evidence for them occurs in sources from or about the 7th century. ''Regiones'' were self-sufficient units of mixed subsistence agriculture consisting of scattered settlements producing the range of foodstuffs and other forms of produce necessary to support their population. They formed the defined territories of tribes or similar social groupings and were the building-blocks around which the larger Anglo-Saxon kingdoms were governed. ''Regiones'' gradually fragmented in the later Anglo-Saxon period as land was granted into private or ecclesiastical ownership by charter, and the smaller manors that emerged were gradually re-orga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anglo-Saxon Multiple Estate
An Anglo-Saxon multiple estate was a large landholding controlled from a central location with surrounding subsidiary settlements. These estates were present in the early Anglo-Saxon period, but fragmented into smaller units in the late Anglo-Saxon period. Despite some academic criticism, the concept has been widely used and a large number of possible examples have been proposed. Definition The concept of an Anglo-Saxon multiple estate was developed by Professor Glanville Jones of Leeds University. The idea originally appeared in a paper published in 1961 and was fleshed out in a 1976 book on medieval settlement. The term "great estate" is sometimes used as an alternative to multiple estate. These estates typically contained various features: * a central '' caput'' from which the estate was managed * a minster church providing parochial support to the whole estate * surrounding agricultural settlements specialising in particular crops. The specialised settlements, dependent on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hundred (county Subdivision)
A hundred is an administrative division that is geographically part of a larger region. It was formerly used in England, Wales, some parts of the United States, Denmark, Sweden, Finland, Norway, and in Cumberland County, New South Wales, Cumberland County in the British Colony of New South Wales. It is still used in other places, including in Australia (in South Australia and the Northern Territory). Other terms for the hundred in English and other languages include ''#wapentake, wapentake'', ''herred'' (Danish and Bokmål, Bokmål Norwegian), ''herad'' (Nynorsk, Nynorsk Norwegian), ''härad'' or ''hundare'' (Swedish), ''Harde'' (German), ''hiird'' (North Frisian language, North Frisian), ''kihlakunta'' (Finnish), and ''cantref'' (Welsh). In Ireland, a similar subdivision of counties is referred to as a Barony (Ireland), barony, and a hundred is a subdivision of a particularly large townland (most townlands are not divided into hundreds). Etymology The origin of the division of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Vill
A royal vill, royal ''tun'' or ''villa regalis'' () was the central settlement of a rural territory in Anglo-Saxon England, which would be visited by the King and members of the royal household on regular circuits of their kingdoms. The royal vill was the centre for the administration of a subdivision of a kingdom, and the location where the subdivision would support the royal household through the provision of food rent. Royal vills have been identified as the centres of the '' regiones'' of the early Anglo-Saxon period, and of the smaller multiple estates into which ''regiones'' were gradually divided by the 8th century. The British Isles during the early Middle Ages lacked the sophisticated long-distance trade in essential foodstuffs required to support agriculturally unproductive households in a single location. Kings and their entourages could therefore only support themselves by constantly moving between territories with an obligation to support them, and they maintained net ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Isles
The British Isles are an archipelago in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean off the north-western coast of continental Europe, consisting of the islands of Great Britain, Ireland, the Isle of Man, the Inner Hebrides, Inner and Outer Hebrides, Outer Hebrides, the Northern Isles (Orkney and Shetland), and over six thousand smaller islands. They have a total area of and a combined population of almost 72 million, and include two sovereign states, the Republic of Ireland (which covers roughly five-sixths of Ireland), and the United Kingdom, United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland. The Channel Islands, off the north coast of France, are normally taken to be part of the British Isles, even though geographically they do not form part of the archipelago. Under the UK Interpretation Act 1978, the Channel Islands are clarified as forming part of the British Islands, not to be confused with the British Isles. The oldest rocks are 2.7 billion years old and are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Britain
Roman Britain was the territory that became the Roman province of ''Britannia'' after the Roman conquest of Britain, consisting of a large part of the island of Great Britain. The occupation lasted from AD 43 to AD 410. Julius Caesar invaded Britain in 55 and 54 BC as part of his Gallic Wars. According to Caesar, the Britons had been overrun or culturally assimilated by the Belgae during the British Iron Age and had been aiding Caesar's enemies. The Belgae were the only Celtic tribe to cross the sea into Britain, for to all other Celtic tribes this land was unknown. He received tribute, installed the friendly king Mandubracius over the Trinovantes, and returned to Gaul. Planned invasions under Augustus were called off in 34, 27, and 25 BC. In 40 AD, Caligula assembled 200,000 men at the Channel on the continent, only to have them gather seashells () according to Suetonius, perhaps as a symbolic gesture to proclaim Caligula's victory over th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Charles-Edwards
Thomas Mowbray Owen Charles-Edwards (born 11 November 1943) is an emeritus academic at the University of Oxford. He formerly held the post of Jesus Professor of Celtic and is a Professorial Fellow at Jesus College. Biography He was educated at Ampleforth College before reading History at Corpus Christi College, Oxford, where he studied for a doctorate after taking the Diploma in Celtic Studies under Sir Idris Foster. He studied at the Dublin Institute for Advanced Studies from 1967 to 1969. He then was a junior research fellow and then a fellow in history at Corpus Christi College before being appointed to the chair of Celtic. His expertise is in the fields of the history and language of Wales and Ireland, during the so-called Irish Dark Age (during the Roman Empire) and the general " Dark Ages", which followed the collapse of the Roman Empire in the west. He is a Fellow of the Royal Historical Society, a Fellow of the British Academy and a Founding Fellow of the Learned ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tribute
A tribute (; from Latin ''tributum'', "contribution") is wealth, often in kind, that a party gives to another as a sign of submission, allegiance or respect. Various ancient states exacted tribute from the rulers of lands which the state conquered. In the case of alliances, lesser parties may pay tribute to more powerful parties as a sign of allegiance. Tributes are different from taxes, as they are not collected in the same regularly routine manner that taxes are. Further, with tributes, a recognition of political submission by the payer to the payee is uniquely required. Overview The Aztec Empire is another example, as it received tribute from the various city-states and provinces that it conquered. Ancient China received tribute from various states such as Japan, Korea, Vietnam, Cambodia, Borneo, Indonesia, Sri Lanka, Nepal, Myanmar and Central Asia. Aztec Empire Tributes as a form of government The Aztecs used tributes as a means for maintaining control over con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Balanced Diet
A healthy diet is a diet that maintains or improves overall health. A healthy diet provides the body with essential nutrition: fluid, macronutrients such as protein, micronutrients such as vitamins, and adequate fibre and food energy. A healthy diet may contain fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, and may include little to no ultra-processed foods or sweetened beverages. The requirements for a healthy diet can be met from a variety of plant-based and animal-based foods, although additional sources of vitamin B12 are needed for those following a vegan diet. Various nutrition guides are published by medical and governmental institutions to educate individuals on what they should be eating to be healthy. Advertising may drive preferences towards unhealthy foods. To reverse this trend, consumers should be informed, motivated and empowered to choose healthy diets. Nutrition facts labels are also mandatory in some countries to allow consumers to choose between foods based on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |