|
Fluorescence Anisotropy
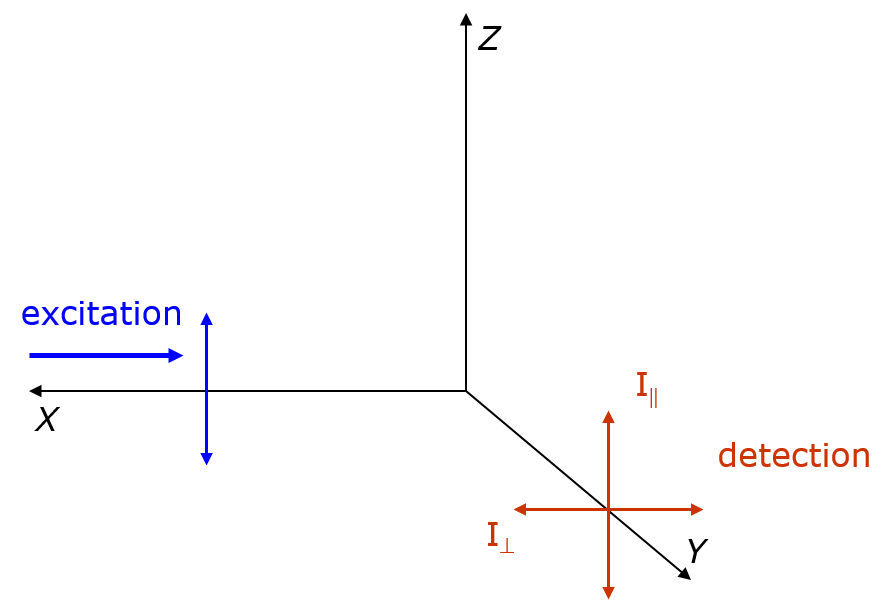
Fluorescence anisotropy or fluorescence polarization is the phenomenon where the light emitted by a fluorophore has unequal intensities along different axes of polarization. Early pioneers in the field include Aleksander Jablonski, Gregorio Weber, and Andreas Albrecht. The principles of fluorescence polarization and some applications of the method are presented in Lakowicz's book.Lakowicz, J.R., 2006. ''Principles of Fluorescence Spectroscopy'' (3rd ed., Springer. Chapter 10-12 deal with fluorescence polarization spectroscopy.) Definition of fluorescence anisotropy The anisotropy (r) of a light source is defined as the ratio of the polarized component to the total intensity (I_T): :r=\frac When the excitation is polarized along the z-axis, emission from the fluorophore is symmetric around the z-axis(Figure). Hence statistically we have I_x=I_y. As I_y=I_, and I_z=I_, we have :r=\frac=\frac. Principle – Brownian motion and photoselection In fluorescence, a molecule absorbs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluorophore
A fluorophore (or fluorochrome, similarly to a chromophore) is a fluorescent chemical compound that can re-emit light upon light excitation. Fluorophores typically contain several combined aromatic groups, or planar or cyclic molecules with several π bonds. Fluorophores are sometimes used alone, as a tracer in fluids, as a dye for staining of certain structures, as a substrate of enzymes, or as a probe or indicator (when its fluorescence is affected by environmental aspects such as polarity or ions). More generally they are covalently bonded to macromolecules, serving as a markers (or dyes, or tags, or reporters) for affine or bioactive reagents (antibodies, peptides, nucleic acids). Fluorophores are notably used to stain tissues, cells, or materials in a variety of analytical methods, such as fluorescent imaging and spectroscopy. Fluorescein, via its amine-reactive isothiocyanate derivative fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC), has been one of the most popular fluorophores ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Random Walk
In mathematics, a random walk, sometimes known as a drunkard's walk, is a stochastic process that describes a path that consists of a succession of random steps on some Space (mathematics), mathematical space. An elementary example of a random walk is the random walk on the integer number line \mathbb Z which starts at 0, and at each step moves +1 or −1 with equal probability. Other examples include the path traced by a molecule as it travels in a liquid or a gas (see Brownian motion), the search path of a foraging animal, or the price of a fluctuating random walk hypothesis, stock and the financial status of a gambler. Random walks have applications to engineering and many scientific fields including ecology, psychology, computer science, physics, chemistry, biology, economics, and sociology. The term ''random walk'' was first introduced by Karl Pearson in 1905. Realizations of random walks can be obtained by Monte Carlo Simulation, Monte Carlo simulation. Lattice random ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perrin Friction Factors
In hydrodynamics, the Perrin friction factors are multiplicative adjustments to the translational and rotational friction of a rigid spheroid, relative to the corresponding frictions in spheres of the same volume. These friction factors were first calculated by Jean-Baptiste Perrin. These factors pertain to spheroids (i.e., to ellipsoids of revolution), which are characterized by the axial ratio ''p = (a/b)'', defined here as the axial semiaxis ''a'' (i.e., the semiaxis along the axis of revolution) divided by the equatorial semiaxis ''b''. In prolate spheroids, the axial ratio ''p > 1'' since the axial semiaxis is longer than the equatorial semiaxes. Conversely, in oblate spheroids, the axial ratio ''p < 1'' since the axial semiaxis is shorter than the equatorial semiaxes. Finally, in s, the axial ratio ''p = 1'', since all three semiaxes are equal in length. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic Anisotropy
In condensed matter physics, magnetic anisotropy describes how an object's magnetic properties can be anisotropy, different depending on direction. In the simplest case, there is no preferential direction for an object's magnetic moment. It will respond to an applied magnetic field in the same way, regardless of which direction the field is applied. This is known as magnetic isotropy. In contrast, magnetically anisotropic materials will be easier or harder to magnetize depending on which way the object is rotated. For most magnetically anisotropic materials, there are two easiest directions to magnetize the material, which are a 180° rotation apart. The line parallel to these directions is called the easy axis. In other words, the easy axis is an energetically favorable direction of spontaneous magnetization. Because the two opposite directions along an easy axis are usually equivalently easy to magnetize along, the actual direction of magnetization can just as easily settle int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bioluminescence Resonance Energy Transfer
Bioluminescence is the emission of light during a chemiluminescence reaction by living organisms. Bioluminescence occurs in multifarious organisms ranging from marine vertebrates and invertebrates, as well as in some fungi, microorganisms including some bioluminescent bacteria, dinoflagellates and terrestrial arthropods such as fireflies. In some animals, the light is bacteriogenic, produced by symbiotic bacteria such as those from the genus ''Vibrio''; in others, it is autogenic, produced by the animals themselves. In most cases, the principal chemical reaction in bioluminescence involves the reaction of a substrate called luciferin and an enzyme, called luciferase. Because these are generic names, luciferins and luciferases are often distinguished by the species or group, e.g. firefly luciferin or cypridina luciferin. In all characterized cases, the enzyme catalyzes the oxidation of the luciferin resulting in excited state oxyluciferin, which is the light emitter of the reac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Springer US
Springer Science+Business Media, commonly known as Springer, is a German multinational publishing company of books, e-books and peer-reviewed journals in science, humanities, technical and medical (STM) publishing. Originally founded in 1842 in Berlin, it expanded internationally in the 1960s, and through mergers in the 1990s and a sale to venture capitalists it fused with Wolters Kluwer and eventually became part of Springer Nature in 2015. Springer has major offices in Berlin, Heidelberg, Dordrecht, and New York City. History Julius Springer founded Springer-Verlag in Berlin in 1842 and his son Ferdinand Springer grew it from a small firm of 4 employees into Germany's then second-largest academic publisher with 65 staff in 1872.Chronology ". Springer Science+Business Media. In 1964, Springer expanded its business internationally, op ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Förster Resonance Energy Transfer
Förster resonance energy transfer (FRET), fluorescence resonance energy transfer, resonance energy transfer (RET) or electronic energy transfer (EET) is a mechanism describing energy transfer between two light-sensitive molecules (chromophores). A donor chromophore, initially in its electronic excited state, may transfer energy to an acceptor chromophore through nonradiative dipole–dipole coupling. The efficiency of this energy transfer is inversely proportional to the sixth power of the distance between donor and acceptor, making FRET extremely sensitive to small changes in distance. Measurements of FRET efficiency can be used to determine if two fluorophores are within a certain distance of each other. Such measurements are used as a research tool in fields including biology and chemistry. FRET is analogous to Near and far field, near-field communication, in that the radius of interaction is much smaller than the Light, wavelength of light emitted. In the near-field region, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magic Angle
The magic angle is a precisely defined angle, the value of which is approximately 54.7356°. The magic angle is a root of a second-order Legendre polynomial, , and so any interaction which depends on this second-order Legendre polynomial vanishes at the magic angle. This property makes the magic angle of particular importance in magic angle spinning solid-state NMR spectroscopy. In magnetic resonance imaging, structures with ordered collagen, such as tendons and ligaments, oriented at the magic angle may appear hyperintense in some sequences; this is called the magic angle artifact or effect. Mathematical definition The magic angle ''θ''m is \theta_\mathrm = \arccos \frac = \arctan \sqrt \approx 0.955\,32\ \text \approx 54.7^\circ \! , where arccos and arctan are the inverse cosine and tangent functions respectively. is the angle between the space diagonal of a cube and any of its three connecting edges, see image. Another representation of the magic angle is half of the o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyol
In organic chemistry, a polyol is an organic compound containing multiple hydroxyl groups (). The term "polyol" can have slightly different meanings depending on whether it is used in food science or polymer chemistry. Polyols containing two, three and four hydroxyl groups are diols, triols, and tetrols, respectively. Classification Polyols may be classified according to their chemistry. Some of these chemistries are polyether, polyester, polycarbonate and also acrylic polyols. Polyether polyols may be further subdivided and classified as polyethylene oxide or polyethylene glycol (PEG), polypropylene glycol (PPG) and Polytetrahydrofuran or PTMEG. These have 2, 3 and 4 carbons respectively per oxygen atom in the repeat unit. Polycaprolactone polyols are also commercially available. There is also an increasing trend to use biobased (and hence renewable) polyols. Uses Polyether polyols have numerous uses. As an example, polyurethane foam is a big user of polyether polyols. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Humana Press
Humana Press was an American academic publisher of science, technology, and medical books and journals founded in 1976. It was bought by Springer Science+Business Media in 2006. History Humana published more than 100 new books and 25 journals per year with a backlist of approximately 1,500 titles in areas such as molecular biology, neuroscience, and medicine. The company was founded in 1976 in Clifton, New Jersey, by Thomas L. Lanigan and his wife, Julia Lanigan, both chemists, and published its first book in 1977. The company was acquired by Springer Science+Business Media in the fall of 2006 and continues to publish titles of book series under the Humana Press imprint. "Springer Buys Humana; Blackwell Adds Brandywine." September 5, 2006. Selected publications Book ser ...
|
Nanoparticle
A nanoparticle or ultrafine particle is a particle of matter 1 to 100 nanometres (nm) in diameter. The term is sometimes used for larger particles, up to 500 nm, or fibers and tubes that are less than 100 nm in only two directions. At the lowest range, metal particles smaller than 1 nm are usually called atom clusters instead. Nanoparticles are distinguished from microparticles (1-1000 μm), "fine particles" (sized between 100 and 2500 nm), and "coarse particles" (ranging from 2500 to 10,000 nm), because their smaller size drives very different physical or chemical properties, like colloidal properties and ultrafast optical effects or electric properties. Being more subject to the Brownian motion, they usually do not sediment, like colloid, colloidal particles that conversely are usually understood to range from 1 to 1000 nm. Being much smaller than the wavelengths of visible light (400-700 nm), nanoparticles cannot be seen with ordinary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |