|
Floppase
Flippases are transmembrane lipid transporter proteins located in the cell membrane. They are responsible for aiding the movement of phospholipid molecules between the two layers, or leaflets, that comprise the membrane. This is called transverse diffusion, also known as "flip-flop" transition. Flippases move lipids to the cytosolic layer, usually from the extracellular layer. Floppases do the opposite, moving lipids to the extracellular layer. Both flippases and floppases are powered by ATP hydrolysis and are either P4-ATPases or ATP-Binding Cassette transporters. Scramblases are energy-independent and transport lipids in both directions. Lateral and transverse movements In organisms, the cell membrane consists of a phospholipid bilayer. Phospholipid molecules are movable in the bilayer. These movements are categorized into two types: lateral movements and transverse movements (also called flip-flop). The first is the lateral movement, where the phospholipid moves horizontall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scramblase
Scramblase is a protein responsible for the translocation of phospholipids between the two monolayers of a lipid bilayer of a cell membrane. In humans, phospholipid scramblases (PLSCRs) constitute a family of five homologous proteins that are named as hPLSCR1–hPLSCR5. Scramblases are members of the general family of transmembrane lipid transporters known as flippases. Scramblases are distinct from flippases and floppases. Scramblases, flippases, and floppases are three different types of enzymatic groups of phospholipid transportation enzymes. The inner-leaflet, facing the inside of the cell, contains negatively charged amino-phospholipids and phosphatidylethanolamine. The outer-leaflet, facing the outside environment, contains phosphatidylcholine and sphingomyelin. Scramblase is an enzyme, present in the cell membrane, that can transport (''scramble'') the negatively charged phospholipids from the inner-leaflet to the outer-leaflet, and vice versa. Expression Whereas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flippase Mechanism
Flippases are transmembrane lipid transporter proteins located in the cell membrane. They are responsible for aiding the movement of phospholipid molecules between the two layers, or leaflets, that comprise the membrane. This is called transverse diffusion, also known as "flip-flop" transition. Flippases move lipids to the cytosolic layer, usually from the extracellular layer. Floppases do the opposite, moving lipids to the extracellular layer. Both flippases and floppases are powered by ATP hydrolysis and are either P4-ATPases or ATP-Binding Cassette transporters. Scramblases are energy-independent and transport lipids in both directions. Lateral and transverse movements In organisms, the cell membrane consists of a phospholipid bilayer. Phospholipid molecules are movable in the bilayer. These movements are categorized into two types: lateral movements and transverse movements (also called flip-flop). The first is the lateral movement, where the phospholipid moves horizontally ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
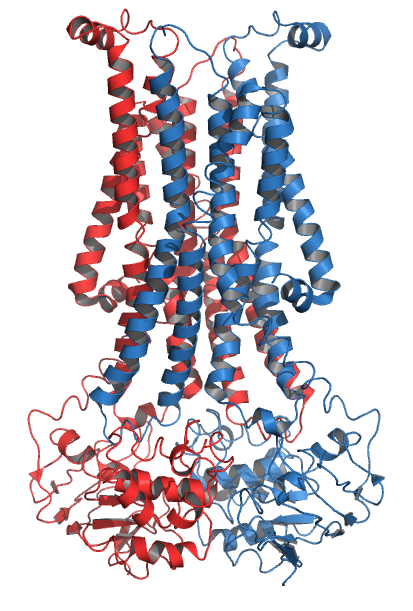
Flippase PglK Pdb 5c73
Flippases are transmembrane lipid transporter Protein, proteins located in the cell membrane. They are responsible for aiding the movement of phospholipid molecules between the two layers, or leaflets, that comprise the membrane. This is called transverse diffusion, also known as "flip-flop" transition. Flippases move lipids to the cytosolic layer, usually from the extracellular layer. Floppases do the opposite, moving lipids to the extracellular layer. Both flippases and floppases are powered by ATP hydrolysis and are either P-type ATPase, P4-ATPases or ABC transporter, ATP-Binding Cassette transporters. Scramblases are energy-independent and transport lipids in both directions. Lateral and transverse movements In organisms, the cell membrane consists of a phospholipid bilayer. Phospholipid molecules are movable in the bilayer. These movements are categorized into two types: lateral movements and transverse movements (also called flip-flop). The first is the lateral movement, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phospholipid
Phospholipids are a class of lipids whose molecule has a hydrophilic "head" containing a phosphate group and two hydrophobic "tails" derived from fatty acids, joined by an alcohol residue (usually a glycerol molecule). Marine phospholipids typically have omega-3 fatty acids EPA and DHA integrated as part of the phospholipid molecule. The phosphate group can be modified with simple organic molecules such as choline, ethanolamine or serine. Phospholipids are a key component of all cell membranes. They can form lipid bilayers because of their amphiphilic characteristic. In eukaryotes, cell membranes also contain another class of lipid, sterol, interspersed among the phospholipids. The combination provides fluidity in two dimensions combined with mechanical strength against rupture. Purified phospholipids are produced commercially and have found applications in nanotechnology and materials science. The first phospholipid identified in 1847 as such in biological tissues w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phospholipid Bilayer
The lipid bilayer (or phospholipid bilayer) is a thin polar membrane made of two layers of lipid molecules. These membranes form a continuous barrier around all cells. The cell membranes of almost all organisms and many viruses are made of a lipid bilayer, as are the nuclear membrane surrounding the cell nucleus, and membranes of the membrane-bound organelles in the cell. The lipid bilayer is the barrier that keeps ions, proteins and other molecules where they are needed and prevents them from diffusing into areas where they should not be. Lipid bilayers are ideally suited to this role, even though they are only a few nanometers in width, because they are impermeable to most water-soluble ( hydrophilic) molecules. Bilayers are particularly impermeable to ions, which allows cells to regulate salt concentrations and pH by transporting ions across their membranes using proteins called ion pumps. Biological bilayers are usually composed of amphiphilic phospholipids that hav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
P-type ATPase
The P-type ATPases, also known as E1-E2 ATPases, are a large group of evolutionarily related ion and lipid pumps that are found in bacteria, archaea, and eukaryotes. P-type ATPases are α-helical bundle primary transporters named based upon their ability to catalyze auto- (or self-) phosphorylation (hence P) of a key conserved aspartate residue within the pump and their energy source, adenosine triphosphate (ATP). In addition, they all appear to interconvert between at least two different conformations, denoted by E1 and E2. P-type ATPases fall under the P-type ATPase (P-ATPase) SuperfamilyTC# 3.A.3 which, as of early 2016, includes 20 different protein families. Most members of this transporter superfamily catalyze cation uptake and/or efflux, however one subfamily, the flippases,TC# 3.A.3.8 is involved in flipping phospholipids to maintain the asymmetric nature of the biomembrane. In humans, P-type ATPases serve as a basis for nerve impulses, relaxation of muscles, secre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ABC Transporter
The ABC transporters, ATP synthase (ATP)-binding cassette transporters are a transport system superfamily that is one of the largest and possibly one of the oldest gene families. It is represented in all extant phyla, from prokaryotes to humans. ABC transporters belong to translocases. ABC transporters often consist of multiple subunits, one or two of which are transmembrane proteins and one or two of which are membrane-associated AAA ATPases. The ATPase subunits utilize the energy of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) binding and hydrolysis to provide the energy needed for the translocation of substrates across membranes, either for uptake or for export of the substrate. Most of the uptake systems also have an extracytoplasmic receptor, a solute binding protein. Some homologous ATPases function in non-transport-related processes such as translation of RNA and DNA repair. ABC transporters are considered to be an ABC superfamily based on the similarities of the sequence and organiz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Polarity
In chemistry, polarity is a separation of electric charge leading to a molecule or its chemical groups having an electric dipole moment, with a negatively charged end and a positively charged end. Polar molecules must contain one or more polar bonds due to a difference in electronegativity between the bonded atoms. Molecules containing polar bonds have no molecular polarity if the bond dipoles cancel each other out by symmetry. Polar molecules interact through dipole-dipole intermolecular forces and hydrogen bonds. Polarity underlies a number of physical properties including surface tension, solubility, and melting and boiling points. Polarity of bonds Not all atoms attract electrons with the same force. The amount of "pull" an atom exerts on its electrons is called its electronegativity. Atoms with high electronegativitiessuch as fluorine, oxygen, and nitrogenexert a greater pull on electrons than atoms with lower electronegativities such as alkali metals and alkaline ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrophobic
In chemistry, hydrophobicity is the chemical property of a molecule (called a hydrophobe) that is seemingly repelled from a mass of water. In contrast, hydrophiles are attracted to water. Hydrophobic molecules tend to be nonpolar and, thus, prefer other neutral molecules and nonpolar solvents. Because water molecules are polar, hydrophobes do not dissolve well among them. Hydrophobic molecules in water often cluster together, forming micelles. Water on hydrophobic surfaces will exhibit a high contact angle. Examples of hydrophobic molecules include the alkanes, oils, fats, and greasy substances in general. Hydrophobic materials are used for oil removal from water, the management of oil spills, and chemical separation processes to remove non-polar substances from polar compounds. The term ''hydrophobic''—which comes from the Ancient Greek (), "having a fear of water", constructed Liddell, H.G. & Scott, R. (1940). ''A Greek-English Lexicon. revised and augmented ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lateral And Transverse Movements Of Lipid
Lateral is a geometric term of location which may also refer to: Biology and healthcare * Lateral (anatomy), a term of location meaning "towards the side" * Lateral cricoarytenoid muscle, an intrinsic muscle of the larynx * Lateral release (surgery), a surgical procedure to release tight capsular structures Other uses * ''Lateral'', a digital journal and production of the Cultural Studies Association * ''Lateral'', a podcast by English YouTuber and web developer Tom Scott * Lateral canal, a canal built along the same right-of-way as an existing stream * Lateral consonant, a consonant in which the airstream proceeds along one or both of the sides of the tongue * Lateral mark, a sea mark used in maritime pilotage to indicate the edge of a channel * Lateral modes, an aspect of dynamic stability and control in the field of aircraft flight dynamics * Lateral pass, a non-advancing move in gridiron football * Lateral release (phonetics), the release of a plosive consonant into a lat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, Cell signaling, responding to stimuli, providing Cytoskeleton, structure to cells and Fibrous protein, organisms, and Intracellular transport, transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the Nucleic acid sequence, nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific Protein structure, 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called pep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ATP Hydrolysis
ATP hydrolysis is the catabolic reaction process by which chemical energy that has been stored in the high-energy phosphoanhydride bonds in adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is released after splitting these bonds, for example in muscles, by producing work in the form of mechanical energy. The product is adenosine diphosphate (ADP) and an inorganic phosphate (Pi). ADP can be further hydrolyzed to give energy, adenosine monophosphate (AMP), and another inorganic phosphate (Pi). ATP hydrolysis is the final link between the energy derived from food or sunlight and useful work such as muscle contraction, the establishment of electrochemical gradients across membranes, and biosynthetic processes necessary to maintain life. Anhydridic bonds are often labelled as "''high-energy bonds"''. P-O bonds are in fact fairly strong (~30 kJ/mol stronger than C-N bonds) Darwent, B. deB. (1970). "Bond Dissociation Energies in Simple Molecules", Nat. Stand. Ref. Data Ser., Nat. Bur. Stand. (U.S.) 31, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |