|
Flexion Point
In obstetrics, the term flexion point refers to a spot on the fetal head on which the cup of a ventouse should to be placed for extraction of the child to be most effective. When the cup of the ventouse is applied on the flexion point, the fetal head will remain flexed under traction, hence the name ''flexion point''. Location The flexion point is located on the sagittal suture, 3 cm (about 1 inch) forward of the posterior fontanelle. Finding the flexion point * Use the middle finger to identify the posterior fontanelle, then move the finger forward along the sagittal suture approximately 3 cm / 1 inch. * With the finger on the flexion point and palmar surface in a superior direction, note where the back of the finger makes contact with the fourchette (this is used to determine how far the ventouse Vacuum extraction (VE), also known as ventouse, is a method to assist delivery of a baby using a vacuum device. It is used in the second stage of labor if it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Obstetrics
Obstetrics is the field of study concentrated on pregnancy, childbirth and the postpartum period. As a medical specialty, obstetrics is combined with gynecology under the discipline known as obstetrics and gynecology (OB/GYN), which is a surgical field. Main areas Prenatal care Prenatal care is important in screening for various complications of pregnancy. This includes routine office visits with physical exams and routine lab tests along with telehealth care for women with low-risk pregnancies: Image:Ultrasound_image_of_a_fetus.jpg, 3D ultrasound of fetus (about 14 weeks gestational age) Image:Sucking his thumb and waving.jpg, Fetus at 17 weeks Image:3dultrasound 20 weeks.jpg, Fetus at 20 weeks First trimester Routine tests in the first trimester of pregnancy generally include: * Complete blood count * Blood type ** Rh-negative antenatal patients should receive RhoGAM at 28 weeks to prevent Rh disease. * Indirect Coombs test (AGT) to assess risk of hemolyti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
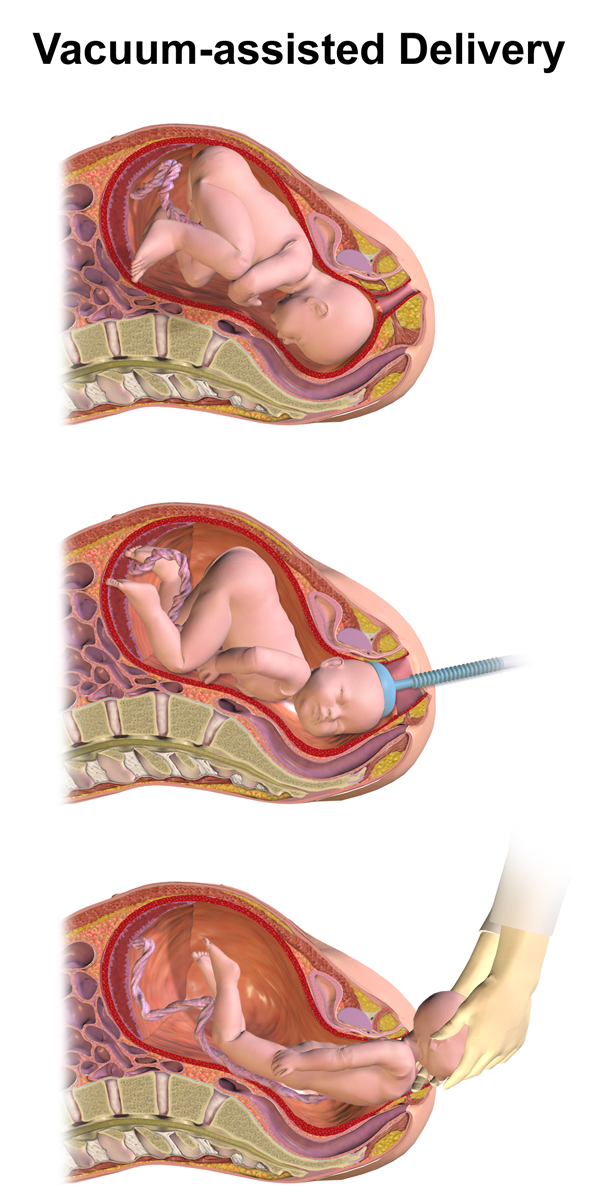
Ventouse
Vacuum extraction (VE), also known as ventouse, is a method to assist delivery of a baby using a vacuum device. It is used in the second stage of labor if it has not progressed adequately. It may be an alternative to a forceps delivery and caesarean section. It cannot be used when the baby is in the breech position or for premature births. The use of VE is generally safe, but it can occasionally have negative effects on either the mother or the child. The term comes from the French word for "suction cup". Medical uses There are several indications to use a vacuum extraction to aid delivery: * Maternal exhaustion * Prolonged second stage of labor * Foetal distress in the second stage of labor, generally indicated by changes in the foetal heart-rate (usually measured on a CTG) * Maternal illness where prolonged "bearing down" or pushing efforts would be risky (e.g. cardiac conditions, blood pressure, aneurysm, glaucoma). If these conditions are known about before the birth, or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sagittal Suture
The sagittal suture, also known as the interparietal suture and the ''sutura interparietalis'', is a dense, fibrous connective tissue joint between the two parietal bones of the skull. The term is derived from the Latin word ''sagitta'', meaning arrow. Structure The sagittal suture is formed from the fibrous connective tissue joint between the two parietal bones of the skull. It has a varied and irregular shape which arises during development. The pattern is different between the inside and the outside. Two anatomical landmarks are found on the sagittal suture: the bregma, and the vertex of the skull. The bregma is formed by the intersection of the sagittal and coronal sutures. The vertex is the highest point on the skull and is often near the midpoint of the sagittal suture. Development At birth, the bones of the skull do not meet. The gap that remains, which is approximately 5 mm wide, allows for the brain to continue to grow normally after birth. The inner pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Posterior Fontanelle
The posterior fontanelle (lambdoid fontanelle, occipital fontanelle) is a gap between bones in the human skull (known as fontanelle), triangular in form and situated at the junction of the sagittal suture and lambdoidal suture. It generally closes in 6–8 weeks from birth. The cranial point in adults corresponding the fontanelle is called 'lambda' A delay in closure is associated with congenital hypothyroidism Hypothyroidism (also called ''underactive thyroid'', ''low thyroid'' or ''hypothyreosis'') is a disorder of the endocrine system in which the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormone. It can cause a number of symptoms, such as .... See also * Lambda (anatomy) References Skull {{musculoskeletal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |