|
Flag Of The Sovereign Military Order Of Malta
The flag and coat of arms of the Sovereign Military Order of Malta, or the Jerusalem flag, display a white cross on a red field (blazon ''gules a cross argent''), ultimately derived from the design worn by the Knights Hospitaller during the Crusades. The flag represents the Sovereign Military Order of Malta as a sovereign institution. The state flag bears a Latin cross that extends to the edges of the flag. The flag of the Order's works represents its humanitarian and medical activities, and bears a white Maltese cross on a red field. Both flags together represent the Sovereign Military Order of Malta. Its constitution states: "The flag of the Order bears either the white Latin cross on a red field or the white eight-pointed cross (cross of Malta) on a red field." History The arms of the Knights Hospitaller were granted in 1130 by Pope Innocent II, for differentiation from the Templars who displayed the reversed colours. The "eight-pointed cross" is also said to originate in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pope Alexander IV
Pope Alexander IV (1199 or 1185 – 25 May 1261) was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 12 December 1254 to his death. Early career He was born as Rinaldo di Jenne in Jenne, Italy, Jenne (now in the Province of Rome), he was, on his mother's side, a member of the house Counts of Segni, Conti di Segni, the counts of Segni, like Pope Innocent III and Pope Gregory IX. His uncle Gregory IX made him cardinal deacon and Protector of the Franciscans, Order of Franciscans in 1227, Camerlengo of the Holy Roman Church from 1227 until 1231 and Bishop of Ostia in 1231 (or 1232). On the death of Pope Innocent IV in 1254 he was Papal election, 1254, elected pope at Naples on 12 December 1254. Pontificate Alexander's pontificate was signalled by efforts to reunite the Eastern Orthodox churches with the Catholic Church, by the establishment of the Inquisition in France, by favours shown to the mendicant orders, and by an attempt to organize a crusade against the Mon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
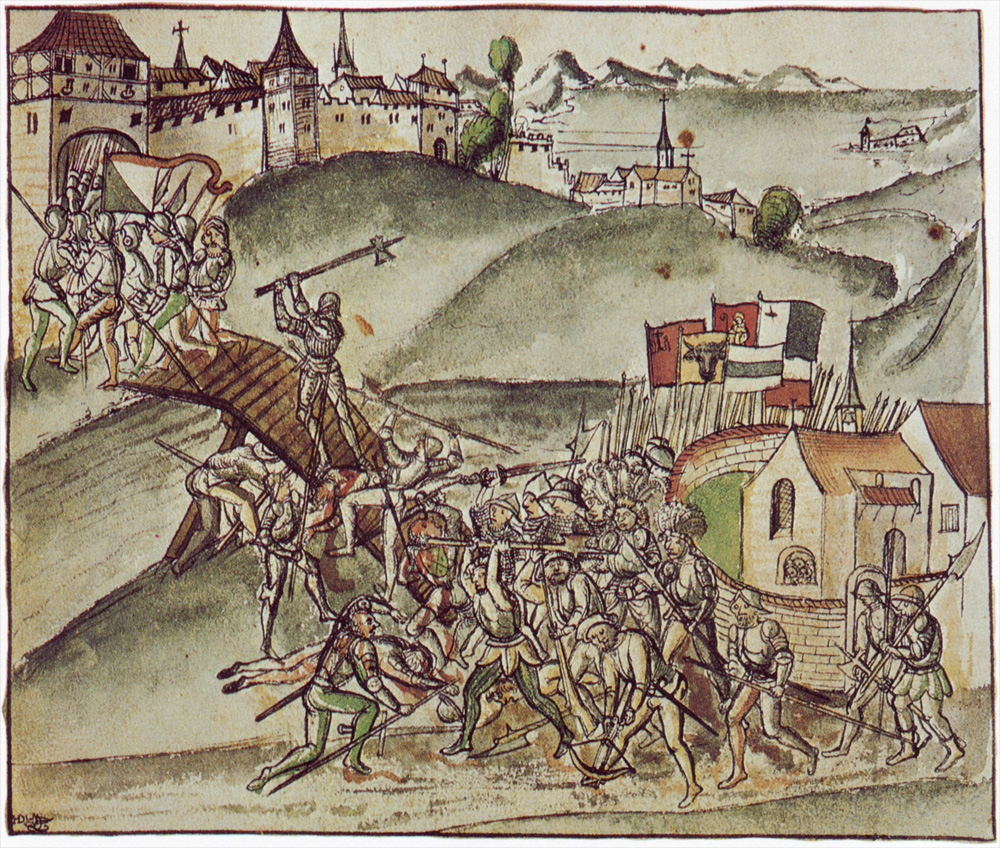
Old Zürich War
The Old Zurich War (; 1440–1446) was a conflict between the canton of Zurich and the other seven cantons of the Old Swiss Confederacy over the succession to the Count of Toggenburg. In 1436, Count Friedrich VII of Toggenburg died, leaving neither heir nor will. The canton of Zurich, led by burgomaster Rudolf Stüssi, claimed the Toggenburg lands; the cantons of Schwyz and Glarus made counter-claims, backed by the other cantons. In 1438, Zurich occupied the disputed area and cut off grain supplies to Schwyz and Glarus. In 1440, the other cantons expelled Zurich from the confederation and declared war. Zurich retaliated by making an alliance with Frederick III, Holy Roman Emperor of the house of Habsburg. The forces of Zurich were defeated in the Battle of St. Jakob an der Sihl on 22 July 1443 and Zurich was besieged. Frederick appealed to Charles VII of France to attack the confederates and the latter sent a force of about 30,000 Armagnac mercenaries under the command of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Langue (Knights Hospitaller)
A langue or tongue () was an administrative division of the Knights Hospitaller (also known as the Order of St. John of Jerusalem) between 1319 and 1798. The term referred to a rough ethno-linguistic division of the geographical distribution of the Order's members and possessions. Each langue was subdivided into Priories or Grand Priories, Bailiwicks and Commanderies. Each langue had an ''auberge'' as its headquarters, some of which still survive in Rhodes, Birgu and Valletta. History The Knights Hospitaller began to take the features of a state following its acquisition of Rhodes and nearby islands in the early 14th century. The subdivision of the Order into ''langues'' began in 1319 during a meeting of the Chapter General in Montpellier. For the purposes of administration of the Order's possessions in Europe, the langues were divided into ''grand priories'', some of which were further divided into ''priories'' or ''bailiwicks'', and at the lowest level into '' commandrie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johann Loesel
Johann Loesel (c. 1390–1460) was a knight of the Order of Saint John, during 1440–1444 grand bailiff from and 1445–1460 grand prior of the grand priory of Alemannia (Upper Germany), a division of the order within the langue of Germany. A native of Strasbourg, Loesel joined the order at Eichen (Eichhof) near Weißenburg. In 1426, he was given the commandery of Mainz. He acted as commander at Mainz during 1429–1439. In 1434, he also received command of Rheinfelden. In 1440, he was given the rank of great bailiff at Rhodes, an office created for the German tongue of the order in 1428. The grand bailiff of the German tongue was responsible for the fortifications of Rhodes. In 1444, Loesel was made grand prior of Germany, resigning from the office of grand bailiff and returning to Europe. He was responsible for the commanderies of Basel, Bubikon, Leuggern and Wädenswil, mostly residing in Wädenswil. In February 1446 he acted as mediator between Züric ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philibert De Naillac
Philibert de Naillac ( – 1421) was grand master of the Knights Hospitaller from 1396 until his death in Rhodes in 1421. Prior to his election he was grand-prior of Aquitaine. Life Philibert de Naillac was born about 1340 of a noble family.Wokjian 1876, p. 833. But little is known of his personal history. He became master of the Order of the Knights of St. John of Jerusalem in 1376, and engaged in the Crusades, and was greatly distinguished by his valour and skill in warfare. He was prominently engaged in the battle of Nicopolis, and served the Christian interests by his treaties with the Saracen upright 1.5, Late 15th-century German woodcut depicting Saracens ''Saracen'' ( ) was a term used both in Greek and Latin writings between the 5th and 15th centuries to refer to the people who lived in and near what was designated by the Rom ...s. Thus he concluded a treaty with the sultan of Egypt, which gave the Christians permission to enclose the Holy Sepulchre at Jerusalem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edward III Of England
Edward III (13 November 1312 – 21 June 1377), also known as Edward of Windsor before his accession, was King of England from January 1327 until his death in 1377. He is noted for his military success and for restoring royal authority after the disastrous and unorthodox reign of his father, Edward II. Edward III transformed the Kingdom of England into one of the most formidable military powers in Europe. His fifty-year reign is List of monarchs in Britain by length of reign#Ten longest-reigning British monarchs, one of the longest in English history, and saw vital developments in legislation and government, in particular the evolution of the English Parliament, as well as the ravages of the Black Death. He outlived his eldest son, Edward the Black Prince, and was succeeded by his grandson, Richard II. Edward was crowned at age fourteen after his father was deposed by his mother, Isabella of France, and her lover, Roger Mortimer, 1st Earl of March, Roger Mortimer. At the age of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Arms Of England
The coat of arms of England is the coat of arms historically used as arms of dominion by the monarchs of the Kingdom of England, and now used to symbolise England generally.: "The three golden lions upon a ground of red have certainly continued to be the royal and national arms of England." The arms were adopted 1200 by the House of Plantagenet, Plantagenet kings and continued to be used by successive English and British monarchs; they are currently Quartering (heraldry), quartered with the arms of Scotland and Ireland in the Royal coat of arms of the United Kingdom, coat of arms of the United Kingdom. Historically they were also quartered with the arms of English claims to the French throne, France, representing the English claim to the French throne, and Electorate of Hanover, Hanover. The arms continue to be used in heraldry to represent England, for example in the arms of Canada, although they rarely appear in isolation in royal or government contexts. They have also been ad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dieudonné De Gozon
Dieudonné de Gozon was the Grand Master of the Knights of Rhodes from 1346 to 1353. He was born to a noble family in Languedoc, France. He carried the nickname ''Extinctor Draconis'', which means "The Dragon Slayer" in Latin. In 1347 and 1348, Gozon led his order in a march to aid King Constantine V of Armenia, who was threatened by the army of the Sultan of Egypt. The Dragon of Rhodes A story tells of a dragon in the island of Rhodes, Greece, hiding in the local swamp and killing the cattle of the local farmers. Despite the orders of the previous Grand Master not to disturb the beast, Gozon slew the dragon and hung the head on one of the seven gates of the medieval town of Rhodes Rhodes (; ) is the largest of the Dodecanese islands of Greece and is their historical capital; it is the List of islands in the Mediterranean#By area, ninth largest island in the Mediterranean Sea. Administratively, the island forms a separ .... The head was on display until around 1837, whe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hélion De Villeneuve
image:Elie de Ville Neuve.jpg, Hélion de Villeneuve Hélion de Villeneuve (27May 1346) was a France, French-born Grand Master (order), Grand Master of the Knights of St. John. He was the brother of Roseline of Villeneuve, OCart. Hélion died on the island of Rhodes. The blazon of Hélion's coat-of-arms was ''Gules six tilting spears in fretty, in-between the spears semy of escutcheons, all or''. There is a legend told of Hélion involving a dragon and a young knight. References {{DEFAULTSORT:Helion de Villeneuve Grand masters of the Knights Hospitaller, Villeneuve, Helion de 1270s births 1346 deaths 14th-century French people ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Street Of The Knights Of Rhodes
The history of Rhodes under the Order of Saint John lasted from 1310 until 1522. The island of Rhodes was a sovereign territorial entity of the Knights Hospitaller who settled on the island from Kingdom of Jerusalem and from Cyprus, where they did not exercise temporal power. The first Grand Master was the Frenchman Foulques de Villaret (1305–1319). History After the extinction of the Kingdom of Jerusalem with the fall of Acre in 1291, the order sought refuge in the Kingdom of Cyprus. Finding themselves becoming enmeshed in Cypriot politics, their Master, Guillaume de Villaret, created a plan of acquiring their own temporal domain, selecting Rhodes to be their new home, part of the Byzantine Empire. Due to repeated disagreements with the king of Cyprus Henry II, which left the privileges of the Knights Hospitaller unaltered, Foulques de Villaret made the decision to transfer the Order to the nearby island of Rhodes which was under the formal authority of the Byzantine empero ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matthew Paris
Matthew Paris, also known as Matthew of Paris (; 1200 – 1259), was an English people, English Benedictine monk, English historians in the Middle Ages, chronicler, artist in illuminated manuscripts, and cartographer who was based at St Albans Cathedral, St Albans Abbey in Hertfordshire. He authored a number of historical works, many of which he scribed and illuminated himself, typically in drawings partly coloured with watercolour washes, sometimes called "tinted drawings". Some were written in Latin, others in Anglo-Norman language, Anglo-Norman or Old French, French verse. He is sometimes confused with the nonexistent Matthew of Westminster. His is a renowned Medieval work, in many cases being a key source for mid-13th century Europe, partially due to his verbose insertion of personal opinions into his narrative and his use of sources such as records, letters, and conversations with witnesses to events including the English king Henry III of England, Henry III, earl Ri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |