|
Fertility (soil)
Soil fertility refers to the ability of soil to sustain agricultural plant growth, i.e. to provide plant habitat and result in sustained and consistent Crop yield, yields of high quality.Bodenfruchtbarkeit Retrieved on 2015-11-09. It also refers to the soil's ability to supply plant/crop nutrients in the right quantities and qualities over a sustained period of time. A fertile soil has the following properties: * The ability to supply Plant nutrition, essential plant nutrients and water in adequate amounts and proportions for plant growth and reproduction; and * The absence of Phytotoxicity, toxic substances which may inhibit plant growth e.g. Fe2+ which leads to nutrient toxicity. The following properties contribute to soil fertility in most situations: * Sufficient soil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soil Horizons
A soil horizon is a layer parallel to the soil surface whose physical, chemical and biological characteristics differ from the layers above and beneath. Horizons are defined in many cases by obvious physical features, mainly colour and texture. These may be described both in absolute terms (particle size distribution for texture, for instance) and in terms relative to the surrounding material, i.e. 'coarser' or 'sandier' than the horizons above and below. The identified horizons are indicated with symbols, which are mostly used in a hierarchical way. Master horizons (main horizons) are indicated by capital letters. Suffixes, in form of lowercase letters and figures, further differentiate the master horizons. There are many different systems of horizon symbols in the world. No one system is more correct—as artificial constructs, their utility lies in their ability to accurately describe local conditions in a consistent manner. Due to the different definitions of the horizon sym ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
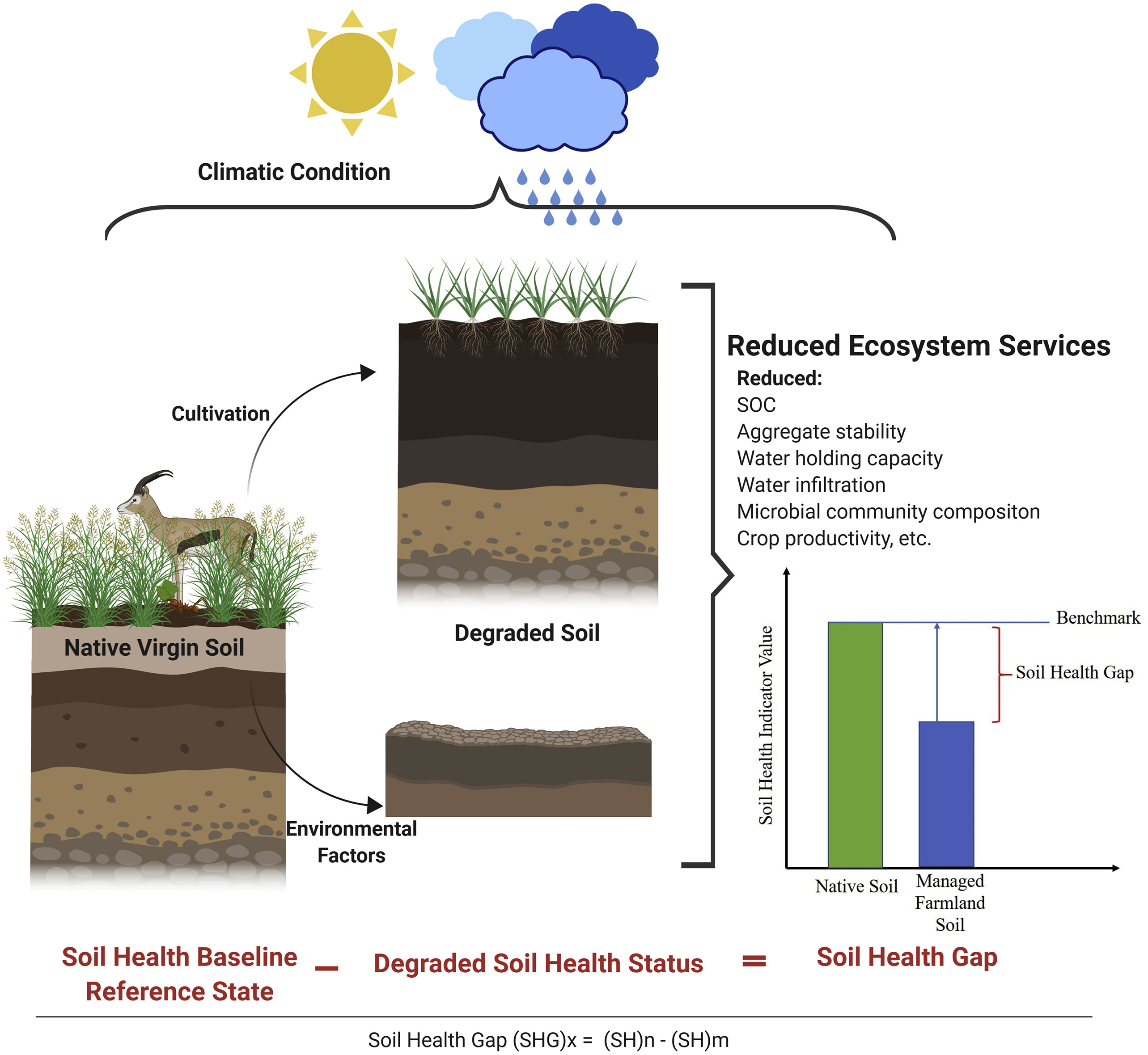
Soil Degradation
Soil retrogression and degradation are two regressive evolution processes associated with the loss of equilibrium of a soil health, stable soil. Retrogression is primarily due to soil erosion and corresponds to a phenomenon where succession reverts the land to its natural physical state. Degradation or ''pedolysis'' is an evolution, different from natural evolution, related to the local climate and vegetation. It is due to the replacement of primary Plant community, plant communities (known as climax vegetation) by the secondary communities. This replacement modifies the humus composition and amount, and affects the soil formation, formation of the soil. It is directly related to human activity. Soil degradation may also be viewed as any change or ecological disturbance to the soil perceived to be deleterious or undesirable.Johnson, D.L., S.H. Ambrose, T.J. Bassett, M.L. Bowen, D.E. Crummey, J.S. Isaacson, D.N. Johnson, P. Lamb, M. Saul, and A.E. Winter-Nelson. 1997. Meanings of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compost
Compost is a mixture of ingredients used as plant fertilizer and to improve soil's physical, chemical, and biological properties. It is commonly prepared by Decomposition, decomposing plant and food waste, recycling organic materials, and manure. The resulting mixture is rich in plant nutrients and beneficial organisms, such as bacteria, protozoa, nematodes, and fungi. Compost improves soil fertility in gardens, landscaping, horticulture, urban agriculture, and organic farming, reducing dependency on commercial chemical fertilizers. The benefits of compost include providing nutrients to crops as fertilizer, acting as a soil conditioner, increasing the humus or Humic acids, humic acid contents of the soil, and introducing beneficial microbes that help to suppress pathogens in the soil and reduce soil-borne diseases. At the simplest level, composting requires gathering a mix of green waste (nitrogen-rich materials such as leaves, grass, and food scraps) and brown waste (woody ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Food Loss And Waste
The causes of food going uneaten are numerous and occur throughout the food system, during production, processing, distribution, retail and food service sales, and consumption. Overall, about one-third of the world's food is thrown away. A similar amount is lost on top of that by feeding human-edible food to farm animals (the net effect wastes an estimated 1144 kcal/person/day). A 2021 meta-analysis, that did not include food lost during production, by the United Nations Environment Programme found that food waste was a challenge in all countries at all levels of economic development. The analysis estimated that global food waste was 931 million tonnes of food waste (about 121 kg per capita) across three sectors: 61 percent from households, 26 percent from food service and 13 percent from retail. Food loss and waste is a major part of the impact of agriculture on climate change (it amounts to 3.3 billion tons of CO2e emissions annually) and other environmental issues, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soil Health
Soil health is a state of a soil meeting its range of ecosystem functions as appropriate to its environment. In more colloquial terms, the health of soil arises from favorable interactions of all soil components (living and non-living) that belong together, as in microbiota, plants and animals. It is possible that a soil can be healthy in terms of ecosystem functioning but not necessarily serve crop production or human nutrition directly, hence the scientific debate on terms and measurements. Soil health testing is pursued as an assessment of this status but tends to be confined largely to agronomic objectives. Soil health depends on soil biodiversity (with a robust soil biology, soil biota), and it can be improved via soil management, especially by care to keep protective living covers on the soil and by natural (carbon-containing) soil amendments. Inorganic fertilizers do not necessarily damage soil health if they are not used in excess, and if they bring about a general improveme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biochar
Biochar is a form of charcoal, sometimes modified, that is intended for organic use, as in soil. It is the lightweight black remnants remaining after the pyrolysis of biomass, consisting of carbon and ashes. Despite its name, biochar is sterile immediately after production and only gains biological life following assisted or incidental exposure to biota. Biochar is defined by the International Biochar Initiative as the "solid material obtained from the thermochemical conversion of biomass in an oxygen-limited environment". Biochar is mainly used in soils to increase soil aeration, reduce soil emissions of greenhouse gases, reduce nutrient leaching, reduce soil acidity, and potentially increase the water content of coarse soils. Biochar application may increase soil fertility and agricultural productivity. However, when applied excessively or made from feedstock unsuitable for the soil type, biochar soil amendments also have the potential for negative effects, including harm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soil Quality
Soil quality refers to the condition of soil based on its capacity to perform ecosystem services that meet the needs of human and non-human life.Tóth, G., Stolbovoy, V. and Montanarella, 2007. Soil Quality and Sustainability Evaluation - An integrated approach to support soil-related policies of the European Union", EUR 22721 EN. 40 pp. Office for Official Publications of the European Communities, Luxembourg. . Soil quality reflects how well a soil performs the functions of maintaining biodiversity and productivity, partitioning water and solute flow, filtering and buffering, nutrient cycling, and providing support for plants and other structures. Soil management has a major impact on soil quality. Soil quality relates to soil functions. Unlike water or air, for which established standards have been set, soil quality is difficult to define or quantify. Indicators of soil quality Soil quality can be evaluated using the Soil Management Assessment Framework. Soil quality in agric ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soil Conditioner
A soil conditioner is a product which is added to soil to improve the soil’s physical qualities, usually its fertility (ability to provide nutrition for plants) and sometimes its mechanics. In general usage, the term "soil conditioner" is often thought of as a subset of the category soil amendments (or soil improvement, soil condition), which more often is understood to include a wide range of fertilizers and non-organic materials. In the context of construction soil conditioning is also called soil stabilization. Soil conditioners can be used to improve poor soils, or to rebuild soils which have been damaged by improper soil management. They can make poor soils more usable, and can be used to maintain soils in peak condition. Composition A wide variety of materials have been described as soil conditioners due to their ability to improve soil quality. Some examples include biochar, bone meal, blood meal, coffee grounds, compost, compost tea, coir, manure, straw, peat, spha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peak Phosphorus
Phosphorus is a chemical element; it has symbol P and atomic number 15. All elemental forms of phosphorus are highly reactive and are therefore never found in nature. They can nevertheless be prepared artificially, the two most common allotropes being white phosphorus and red phosphorus. With as its only stable isotope, phosphorus has an occurrence in Earth's crust of about 0.1%, generally as phosphate rock. A member of the pnictogen family, phosphorus readily forms a wide variety of organic and inorganic compounds, with as its main oxidation states +5, +3 and −3. The isolation of white phosphorus in 1669 by Hennig Brand marked the scientific community's first discovery since Antiquity of an element. The name phosphorus is a reference to the god of the Morning star in Greek mythology, inspired by the faint glow of white phosphorus when exposed to oxygen. This property is also at the origin of the term ''phosphorescence'', meaning glow after illumination, although white pho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eutrophication
Eutrophication is a general term describing a process in which nutrients accumulate in a body of water, resulting in an increased growth of organisms that may deplete the oxygen in the water; ie. the process of too many plants growing on the surface of a river, lake, etc., often because chemicals that are used to help crops grow have been carried there by rain. Eutrophication may occur naturally or as a result of human actions. Manmade, or cultural, eutrophication occurs when sewage, Industrial wastewater treatment, industrial wastewater, fertilizer runoff, and other nutrient sources are released into the environment. Such nutrient pollution usually causes algal blooms and bacterial growth, resulting in the depletion of dissolved oxygen in water and causing substantial environmental degradation. Many policies have been introduced to combat eutrophication, including the United Nations Development Program (UNDP)'s sustainability development goals. Approaches for prevention and re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cation-exchange Capacity
Cation-exchange capacity (CEC) is a measure of how many cations can be retained on soil particle surfaces. Negative charges on the surfaces of soil particles bind positively-charged atoms or molecules (cations), but allow these to exchange with other positively charged particles in the surrounding soil water. This is one of the ways that solid materials in soil alter the chemistry of the soil. CEC affects many aspects of soil chemistry, and is used as a measure of soil fertility, as it indicates the capacity of the soil to retain several nutrients (e.g. K+, NH4+, Ca2+) in plant-available form. It also indicates the capacity to retain pollutant cations (e.g. Pb2+). Definition and principles Cation-exchange capacity is defined as the amount of positive charge that can be exchanged per mass of soil, usually measured in cmolc/kg. Some texts use the older, equivalent units me/100g or meq/100g. CEC is measured in moles of electric charge, so a cation-exchange capacity of 10 cmolc/kg co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immobilization (soil Science)
Immobilization in soil science is the conversion of inorganic compounds to organic compounds by microorganisms or plants by which the compounds become inaccessible to plants. Immobilization is the opposite of mineralization. In immobilization, inorganic nutrients are taken up by soil microbes and become unavailable for plant uptake. Immobilization is therefore a biological process controlled by bacteria that consume inorganic nitrogen and form amino acids and biological macromolecules (organic forms). Immobilization and mineralization are continuous processes that occur concurrently whereby nitrogen of the decomposing system is steadily transformed from an inorganic to an organic state by immobilization and from an organic to an inorganic state by decay and mineralization. C:N Ratio Whether nitrogen is mineralized or immobilized depends on the C/N ratio of the plant residues. For example, incorporating materials high in carbon to nitrogen ratio such as saw dust and straw will sti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |