|
Feedback Carburetor
A feedback carburetor (also known as electronic or computer controlled carburetor) is a specific type of carburetor made mostly during the 1980s to improve emissions on certain vehicles in the US. History Before the 1970s, most vehicles didn't have many emissions systems on them, but as time went on, smog pumps, charcoal canisters, and thermal reactors were added to meet new regulations. As vehicle emissions standards became more stringent due to the Clean Air Act and CAFE standards, vehicle engineers had to come up with different ways to meet this problem. Initially decreasing the engine compression and installing EGR systems and two way catalytic converters were able to solve this problem but later this became more difficult. In the 1980s, many vehicle manufacturers were required to use three-way catalytic converters and oxygen sensors to determine the air fuel ratio (AFR) of the vehicle to determine if the car is running correctly. This was paired with either an earl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emission Standard
Emission standards are the legal requirements governing air pollutants released into the atmosphere. Emission standards set quantitative limits on the permissible amount of specific air pollutants that may be released from specific sources over specific timeframes. They are generally designed to achieve air quality standards and to protect human life. Different regions and countries have different standards for vehicle emissions. Regulated sources Many emissions standards focus on regulating pollutants released by automobiles (motor cars) and other powered vehicles. Others regulate emissions from industry, power plants, small equipment such as lawn mowers and diesel generators, and other sources of air pollution. The first automobile emissions standards were enacted in 1963 in the United States, mainly as a response to Los Angeles' smog problems. Three years later Japan enacted their first emissions rules, followed between 1970 and 1972 by Canada, Australia, and several ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jeep Wagoneer (SJ)
The Jeep Wagoneer is a luxury 4x4 produced and marketed under the Jeep brand from the 1963 to 1991 model years. Introduced as the replacement for the Jeep Station Wagon, the Wagoneer was the first Jeep model line completely distinct from the Jeep CJ. Designed as a truck-based station wagon, the model line became a progenitor of the modern sport-utility vehicle (SUV). Designed under contract by industrial designer Brooks Stevens, the exterior of the Wagoneer was styled by engineer Dave Nutting. Sharing the Jeep SJ chassis (full-size Jeep) with the Jeep Gladiator/J-Series, the Wagoneer also shared its underpinnings with the introductory Jeep Cherokee. In 1966, Jeep introduced the high-content Super Wagoneer, upgrading the model line with features from higher-priced sedans. Though the trim was short-lived, the Wagoneer became upgraded in content and features throughout the 1970s. For 1984, the Jeep Grand Wagoneer was introduced (to distinguish the SJ from the smal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CVCC
CVCC, or , is an internal combustion engine technology developed and trademarked by the Honda Motor Company. The technology's name refers to its primary features: Compound refers to the use of two combustion chambers; Vortex refers to the vortex generated in the main combustion chamber, increasing combustion speed, and Controlled Combustion refers to combustion occurring in a timely, controlled manner. The engine innovatively used a secondary, smaller auxiliary inlet valve to feed a richer air-fuel mixture to the combustion chamber around the spark plug, while the standard inlet valve fed a leaner air-fuel mixture to the remainder of the chamber, creating a more efficient and complete combustion. History Following the establishment of an "Air Pollution Research Group" by Honda in 1965, its collection of emissions data from American automakers, and subsequent research into emissions control and prechambers, the first mention of CVCC technology was by Soichiro Honda on F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ford EEC
The Ford EEC or Electronic Engine Control is a series of ECU (or Engine Control Unit) that was designed and built by Ford Motor Company. The first system, EEC I, used processors and components developed by Toshiba in 1973. It began production in 1974, and went into mass production in 1975. It subsequently went through several model iterations. EEC I and II The EEC I and EEC II modules used a common processor and memory so they can be described together. The microprocessor was a 12-bit central processing unit manufactured by Toshiba, the TLCS-12, which began development in 1971 and was completed in 1973. It was a 32mm² chip with about 2,800 silicon gates, manufactured on a 6 μm process. The system's semiconductor memory included 512-bit RAM, 2 kb ROM and 2kb EPROM. The system began production in 1974, and went into mass production in 1975. The EEC-II controlled air-fuel ratio via Ford's model 7200 Variable Venturi (VV) Carburetor, the last carburetor designed and b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Venturi Effect
The Venturi effect is the reduction in fluid pressure that results when a moving fluid speeds up as it flows from one section of a pipe to a smaller section. The Venturi effect is named after its discoverer, the Italian physicist Giovanni Battista Venturi, and was first published in 1797. The effect has various engineering applications, as the reduction in pressure inside the constriction can be used both for measuring the fluid flow and for moving other fluids (e.g. in a vacuum ejector). Background In inviscid fluid dynamics, an incompressible fluid's velocity must ''increase'' as it passes through a constriction in accord with the principle of mass continuity, while its static pressure must ''decrease'' in accord with the principle of conservation of mechanical energy (Bernoulli's principle) or according to the Euler equations. Thus, any gain in kinetic energy a fluid may attain by its increased velocity through a constriction is balanced by a drop in pressure because ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chevrolet Chevette
The Chevrolet Chevette is a front-engine, rear-drive subcompact manufactured and marketed by Chevrolet for model years 1976–1987 as a three-door or five-door hatchback. Introduced in North America in September 1975, the Chevette superseded the Vega as Chevrolet's entry-level subcompact. Production reached 2.8 million over 12 years, and the Chevette was the best-selling small car in the U.S. for model years 1979-1980. It was the first American car built to metric measurements, and also the first American car to feature a diagnostic plug for pinpointing service issues. Overview The Chevette used General Motors' global rear-drive T platform which was co-developed by Opel and Isuzu in 1973. The first to use the T plaform was the Brazilian Chevrolet Chevette released in 1973. Six months later the Opel Kadett C was released in Europe. Worldwide, GM manufactured and marketed more than 7 million T-cars – either as rebadged models or locally-built versions in different c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Checker Marathon
The Checker Marathon is an automobile produced by the Checker Motors Corporation of Kalamazoo, Michigan, between 1960 and 1982. It was marketed as a passenger car for consumers, as opposed to the similar Taxi, which was aimed at fleet buyers. History Marathons were produced in both four-door sedan and four-door station wagon forms, and the rarer six-door 9-seater and eight-door, 12-seater " Aerobus" sedans and wagons. The Marathon was introduced in September 1960 for the 1961 model year, alongside, and later superseding, the Checker Superba Custom and differing from the Superba with its better interior appointments. Originally, it retained the Superba's A10 body code, whereas A9 was the code used for taxis. The exterior of the Marathon had a full-width egg-crate grille, differing from the Superba's narrower grille and inboard parking lights. After a minor facelift for 1963, chassis codes changed to A11 for taxis and A12 for passenger versions. Also in 1963, the Marathon Town ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
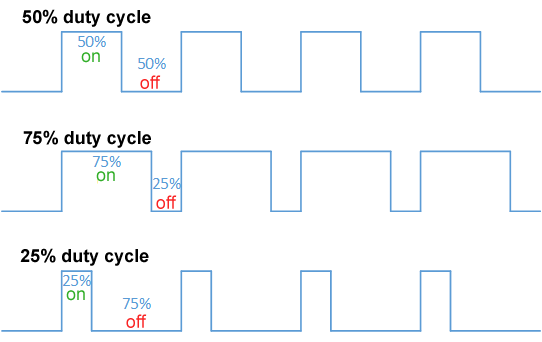
Pulse-width Modulation
Pulse-width modulation (PWM), also known as pulse-duration modulation (PDM) or pulse-length modulation (PLM), is any method of representing a signal as a rectangular wave with a varying duty cycle (and for some methods also a varying period). PWM is useful for controlling the average power or amplitude delivered by an electrical signal. The average value of voltage (and current) fed to the load is controlled by switching the supply between 0 and 100% at a rate faster than it takes the load to change significantly. The longer the switch is on, the higher the total power supplied to the load. Along with maximum power point tracking (MPPT), it is one of the primary methods of controlling the output of solar panels to that which can be utilized by a battery. PWM is particularly suited for running inertial loads such as motors, which are not as easily affected by this discrete switching. The goal of PWM is to control a load; however, the PWM switching frequency must be sele ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cadillac V8 Engine
The term Cadillac V8 may refer to any of a number of V8 engines produced by the Cadillac, Cadillac division of General Motors since it pioneered the first such mass-produced engine in 1914. Most commonly, such a reference is to one of the manufacturer's most successful, best known, or longest-lived 90° V8 engine series. These include the pioneering overhead valve #331 series, cu in introduced in 1949, made in three displacements up to ; a #390 series, introduced in 1963 that grew to #429 series, ; and a #472 series, introduced in 1968 and enlarged to . Also notable was the #Northstar, Northstar, which debuted in 1992 as a 4.6 litre, and was also produced in 4.4 L and 4.2 L versions. When the Northstar engine series ended production in 2010, it became the last General Motors Corporation, General Motors division to retain its own proprietary V8 design. This changed when Cadillac created the twin-turbo "Cadillac twin-turbo V8, Blackwing" engine in 2019. L-head The Type 51 was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rochester Ramjet
The Rochester Ramjet is an automotive fuel injection system developed by the Rochester Products Division of General Motors and first offered as a high-performance option on the Corvette and GM passenger cars in 1957. It was discontinued partway through 1965 in favor of the Chevrolet Big Block as a performance option. Unlike electronic fuel injection systems that would become common decades later, the Ramjet is purely mechanical and relies on vacuum and pressure signals to measure airflow and meter fuel. History In the early 1950s, fuel injection was the topic of a significant amount of research by the auto industry in the US and internationally. Ed Cole, who had become the chief engineer of Chevrolet in 1952, pushed for Chevrolet to be the first GM brand to offer a fuel injection option on a production car. Much of the development of the Ramjet was done by engineer John Dolza, with supporting effort from Zora Arkus-Duntov. Dynamometer-based tests of a 265 cid small block engine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chrysler K Platform
The K-car platform was a key automotive design platform introduced by Chrysler Corporation for the 1981 model year, featuring a transverse engine, front-wheel drive, independent front and semi-independent rear suspension configuration—a stark departure from the company's previous reliance on solid axle, rear-drive unibody configurations during the 1970s. Derived from Chrysler's L-cars, the Plymouth Horizon and Dodge Omni, the platform was developed just as the company faltered in the market, at first underpinning a modest range of compact/mid-size sedans and wagons—and eventually underpinning nearly fifty different models, including all-wheel drive variants—and playing a vital role in the company's subsequent resurgence. Common platforms The use of a common platform is a widely used practice for reducing the number of parts and engineering time. Before creating the K platform, Chrysler was building vehicles on a small number of common platforms (e.g. F/L/J/M and R), but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |