|
Fat Body
300px, Stained cells of an insect fat body Fat body is a highly dynamic insect tissue composed primarily of storage cells. It is distributed throughout the insect's internal body cavity (the haemocoel), in close proximity to the hemolymph as well as organs such as the epidermis, digestive organs and ovaries. Its main functions are nutrient storage and metabolism, for which it is commonly compared to a combination of adipose tissue and liver in mammals. However, it may also serve a variety of other roles, such as: endocrine regulation, systemic immunity, vitellogenesis, and the main site of production of antimicrobial molecules called antimicrobial peptides (or AMPs). Its presence, structure, cellular composition, location, and functions vary widely among insects, even between different species of the same genus or between developmental stages of the same individual, with other specialized organs taking over some or all of its functions. Functions The fat body serves diffe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fat Pad
A fat pad (aka haversian gland) is a mass of closely packed fat cells surrounded by fibrous tissue septa.TheFreeDictionary > Fat padCiting: Mosby's Medical Dictionary, 8th edition. 2009 They may be extensively supplied with capillaries and nerve endings. Examples are: * ''Intraarticular fat pads''. These are also covered by a layer of synovial cells. A fat pad sign is an elevation of the anterior and posterior fat pads of the elbow joint, and suggests the presence of an occult fracture. * Buccal fat pad can be seen in nursing babies. * The fat pad of the labia majora, which can be used as a graft Graft or grafting may refer to: *Graft (politics), a form of political corruption *Graft, Netherlands, a village in the municipality of Graft-De Rijp Science and technology *Graft (surgery), a surgical procedure *Grafting, the joining of plant ti ..., often as a so-called "Martius labial fat pad graft", which can be used, for example, in urethrolysis. *Fat pads within the heels which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Species
A species () is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. It is the basic unit of Taxonomy (biology), classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. Other ways of defining species include their karyotype, DNA sequence, morphology (biology), morphology, behaviour, or ecological niche. In addition, palaeontologists use the concept of the chronospecies since fossil reproduction cannot be examined. The most recent rigorous estimate for the total number of species of eukaryotes is between 8 and 8.7 million. About 14% of these had been described by 2011. All species (except viruses) are given a binomial nomenclature, two-part name, a "binomen". The first part of a binomen is the name of a genus to which the species belongs. The second part is called the specific name (zoology), specific name or the specific ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myriapoda
Myriapods () are the members of subphylum Myriapoda, containing arthropods such as millipedes and centipedes. The group contains about 13,000 species, all of them terrestrial. Although molecular evidence and similar fossils suggests a diversification in the Cambrian Period, the oldest known fossil record of myriapods dates between the Late Silurian and Early Devonian, with '' Pneumodesmus'' preserving the earliest known evidence of air-breathing on land. Other early myriapod fossil species around the similar time period include '' Kampecaris obanensis'' and '' Archidesmus'' sp. The phylogenetic classification of myriapods is still debated. The scientific study of myriapods is myriapodology, and those who study myriapods are myriapodologists. Anatomy Myriapods have a single pair of antennae and, in most cases, simple eyes. Exceptions are the two classes of symphylans and pauropods, the millipede order Polydesmida and the centipede order Geophilomorpha, which are all ey ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crustacea
Crustaceans (from Latin meaning: "those with shells" or "crusted ones") are invertebrate animals that constitute one group of arthropods that are traditionally a part of the subphylum Crustacea (), a large, diverse group of mainly aquatic arthropods including decapods (shrimps, prawns, crabs, lobsters and crayfish), seed shrimp, branchiopods, fish lice, krill, remipedes, isopods, barnacles, copepods, opossum shrimps, amphipods and mantis shrimp. The crustacean group can be treated as a subphylum under the clade Mandibulata. It is now well accepted that the hexapods (insects and entognathans) emerged deep in the Crustacean group, with the completed pan-group referred to as Pancrustacea. The three classes Cephalocarida, Branchiopoda and Remipedia are more closely related to the hexapods than they are to any of the other crustaceans ( oligostracans and multicrustaceans). The 67,000 described species range in size from '' Stygotantulus stocki'' at , to the Japanese spider ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chelicerata
The subphylum Chelicerata (from Neo-Latin, , ) constitutes one of the major subdivisions of the phylum Arthropoda. Chelicerates include the sea spiders, horseshoe crabs, and arachnids (including harvestmen, scorpions, spiders, solifuges, ticks, and mites, among many others), as well as a number of extinct lineages, such as the eurypterids (sea scorpions) and chasmataspidids. Chelicerata split from Mandibulata by the mid-Cambrian, as evidenced by stem-group chelicerates like Habeliida and '' Mollisonia'' present by this time. The surviving marine species include the four species of xiphosurans (horseshoe crabs), and possibly the 1,300 species of pycnogonids (sea spiders), if the latter are indeed chelicerates. On the other hand, there are over 77,000 well-identified species of air-breathing chelicerates, and there may be about 500,000 unidentified species. Like all arthropods, chelicerates have segmented bodies with jointed limbs, all covered in a cuti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subphyla
In zoological nomenclature, a subphylum is a taxonomic rank below the rank of phylum. The taxonomic rank of " subdivision" in fungi and plant taxonomy is equivalent to "subphylum" in zoological taxonomy. Some plant taxonomists have also used the rank of subphylum, for instance monocotyledons as a subphylum of phylum Angiospermae and vertebrates as a subphylum of phylum Chordata. Taxonomic rank Subphylum is: #subordinate to the phylum #superordinate to the infraphylum, which is in turn superordinate to parvphylum. Where convenient, subphyla in turn can be divided into infraphyla; in turn such an infraphylum also would be superordinate to any classes or superclasses in the hierarchy. Examples Not all fauna phyla are divided into subphyla. Those that are include: *Arthropoda: divided into subphyla Trilobitomorpha, Chelicerata, Myriapoda, and Pancrustacea *Brachiopoda: divided into subphyla Linguliformea, Craniformea and Rhynchonelliformea *Chordata: divided into Tuni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Insect
Insects (from Latin ') are Hexapoda, hexapod invertebrates of the class (biology), class Insecta. They are the largest group within the arthropod phylum. Insects have a chitinous exoskeleton, a three-part body (Insect morphology#Head, head, Thorax (insect anatomy), thorax and abdomen (insect anatomy), abdomen), three pairs of jointed Arthropod leg, legs, compound eyes, and a pair of antenna (biology), antennae. Insects are the most diverse group of animals, with more than a million described species; they represent more than half of all animal species. The insect nervous system consists of a insect brain, brain and a ventral nerve cord. Most insects reproduce Oviparous, by laying eggs. Insects Respiratory system of insects, breathe air through a system of Spiracle (arthropods), paired openings along their sides, connected to Trachea#Invertebrates, small tubes that take air directly to the tissues. The blood therefore does not carry oxygen; it is only partly contained in ves ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
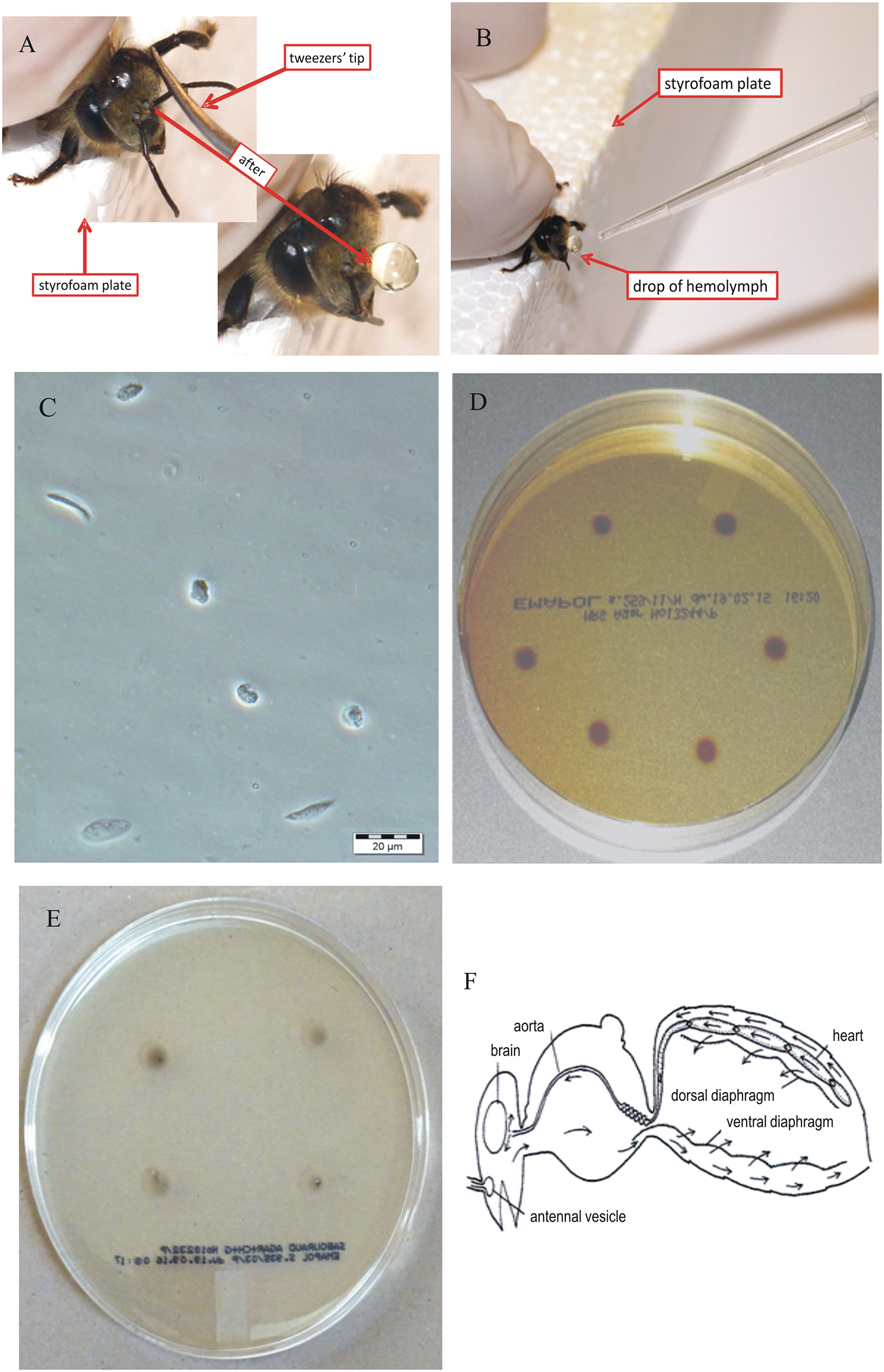
Hemolymph
Hemolymph, or haemolymph, is a fluid, similar to the blood in invertebrates, that circulates in the inside of the arthropod's body, remaining in direct contact with the animal's tissues. It is composed of a fluid plasma in which hemolymph cells called hemocytes are dispersed. In addition to hemocytes, the plasma also contains many chemicals. It is the major tissue type of the open circulatory system characteristic of arthropods (for example, arachnids, crustaceans and insects). In addition, some non-arthropods such as mollusks possess a hemolymphatic circulatory system. Oxygen-transport systems were long thought unnecessary in insects, but ancestral and functional hemocyanin has been found in the hemolymph. Insect "blood" generally does not carry hemoglobin, although hemoglobin may be present in the tracheal system instead and play some role in respiration. Method of transport In the grasshopper, the closed portion of the system consists of tubular hearts and an ao ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trachea
The trachea (: tracheae or tracheas), also known as the windpipe, is a cartilaginous tube that connects the larynx to the bronchi of the lungs, allowing the passage of air, and so is present in almost all animals' lungs. The trachea extends from the larynx and branches into the two primary bronchi. At the top of the trachea, the cricoid cartilage attaches it to the larynx. The trachea is formed by a number of horseshoe-shaped rings, joined together vertically by overlying annular ligaments of trachea, ligaments, and by the trachealis muscle at their ends. The epiglottis closes the opening to the larynx during swallowing. The trachea begins to form in the second month of embryo development, becoming longer and more fixed in its position over time. Its epithelium is lined with columnar epithelium, column-shaped cells that have hair-like extensions called cilia, with scattered goblet cells that produce protective mucins. The trachea can be affected by inflammation or infection, usua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hemocoel
In vertebrates, the circulatory system is a organ system, system of organs that includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood which is circulated throughout the body. It includes the cardiovascular system, or vascular system, that consists of the heart and blood vessels (from Greek meaning ''heart'', and Latin meaning ''vessels''). The circulatory system has two divisions, a systemic circulation, systemic circulation or circuit, and a pulmonary circulation, pulmonary circulation or circuit. Some sources use the terms ''cardiovascular system'' and ''vascular system'' interchangeably with ''circulatory system''. The network of blood vessels are the great vessels of the heart including large elastic arteries, and large veins; other arteries, smaller arterioles, capillaries that join with venules (small veins), and other veins. The Closed circulatory system, circulatory system is closed in vertebrates, which means that the blood never leaves the network of blood vessels. Many in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesoderm
The mesoderm is the middle layer of the three germ layers that develops during gastrulation in the very early development of the embryo of most animals. The outer layer is the ectoderm, and the inner layer is the endoderm.Langman's Medical Embryology, 11th edition. 2010. The mesoderm forms mesenchyme, mesothelium and coelomocytes. Mesothelium lines coeloms. Mesoderm forms the muscles in a process known as myogenesis, septa (cross-wise partitions) and mesenteries (length-wise partitions); and forms part of the gonads (the rest being the gametes). Myogenesis is specifically a function of mesenchyme. The mesoderm differentiates from the rest of the embryo through intercellular signaling, after which the mesoderm is polarized by an organizing center. The position of the organizing center is in turn determined by the regions in which beta-catenin is protected from degradation by GSK-3. Beta-catenin acts as a co-factor that alters the activity of the transcription facto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lipid
Lipids are a broad group of organic compounds which include fats, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins (such as vitamins A, D, E and K), monoglycerides, diglycerides, phospholipids, and others. The functions of lipids include storing energy, signaling, and acting as structural components of cell membranes. Lipids have applications in the cosmetic and food industries, and in nanotechnology. Lipids are broadly defined as hydrophobic or amphiphilic small molecules; the amphiphilic nature of some lipids allows them to form structures such as vesicles, multilamellar/ unilamellar liposomes, or membranes in an aqueous environment. Biological lipids originate entirely or in part from two distinct types of biochemical subunits or "building-blocks": ketoacyl and isoprene groups. Using this approach, lipids may be divided into eight categories: fatty acyls, glycerolipids, glycerophospholipids, sphingolipids, saccharolipids, and polyketides (derived from condensatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |