|
Farebox Recovery
The farebox recovery ratio (also called fare recovery ratio, fare recovery rate or other terms) of a passenger transportation system is the fraction of operating expenses which are met by the fares paid by passengers. It is computed by dividing the system's total fare revenue by its total operating expenses. Fare structures There are generally two types of fare structures: a simple, flat rate fare structure (pay a fixed fare regardless of time of day and/or travel distance) or a complex, variable rate fare structure (pay a variable fare depending on time of day and/or travel distance). A variable fare structure is typically associated with a higher recovery ratio, though it may simply be the case that such systems are implemented only on more profitable networks or modes such as commuter rail. Variable-rate fares require a higher initial investment in fare ticketing technologies such as the use of contactless smart cards, turnstiles or fare gates, automated ticket machine A ti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Farebox
A fare is the fee paid by a passenger for use of a public transport system: rail, bus, taxi, etc. In the case of air transport, the term airfare is often used. Fare structure is the system set up to determine how much is to be paid by various passengers using a transit vehicle at any given time. A linked trip is a trip from the origin to the destination on the transit system. Even if a passenger must make several transfers during a journey, the trip is counted as one linked trip on the system. Uses The fare paid is a contribution to the operational costs of the transport system involved, either partial (as is frequently the case with publicly supported systems) or total. The portion of operating costs covered by fares - the farebox recovery ratio - typically varies from 30%-60% in North America and Europe, with some rail systems in Asia over 100%. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
JR Shikoku
The , commonly known as , is the smallest of the seven constituent companies of the Japan Railways Group (JR Group). It operates of intercity and local rail services in the four Prefectures of Japan, prefectures on the island of Shikoku in Japan. The company has its headquarters in Takamatsu, Kagawa. ." Shikoku Railway Company. Retrieved on March 27, 2010. Lines  In 1988 JR Shikoku, unlike other JR companies, discontinued the classification of its rail lines as either main, secondary, or branch lines. Prior to the change, the Dosan, Kōtoku, Tokushima, and Yosan Lines had all been main line ...
In 1988 JR Shikoku, unlike other JR companies, discontinued the classification of its rail lines as either main, secondary, or branch lines. Prior to the change, the Dosan, Kōtoku, Tokushima, and Yosan Lines had all been main line ...
[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kintetsu Railway
, referred to as and officially Kinki-Nippon Railway, is a Japanese passenger railway company, managing infrastructure and operating passenger train service. Its railway system is the largest in Japan, excluding Japan Railways Group. The railway network connects Osaka, Nara, Nara, Nara, Kyoto, Nagoya, Tsu, Mie, Tsu, Ise, Mie, Ise, and Yoshino, Nara, Yoshino. Kintetsu Railway Co., Ltd. is a wholly owned subsidiary of Kintetsu Group Holdings Co., Ltd. History On September 16, 1910, was founded and renamed a month after. Osaka Electric Tramway completed Ikoma Tunnel and started operating a line between Osaka and Nara (present-day Nara Line (Kintetsu), Nara Line) on April 30, 1914. The modern Kashihara, Osaka, and Shigi lines were completed in the 1920s, followed by the Kyoto Line (a cooperative venture with Keihan Electric Railway). Daiki founded in 1927, which consolidated on September 15, 1936. In 1938, Daiki teamed up with its subsidiary to operate the first private rail ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nagoya Municipal Subway
The , also referred to as simply the Nagoya Subway, is a rapid transit system serving Nagoya, the capital of Aichi Prefecture in Japan. It consists of six lines that cover of route and serve 87 stations. Approximately 90% of the subway's total track length is underground. The subway system is owned and operated by the Nagoya City Transportation Bureau and, like other large Japanese cities including Tokyo and Osaka, is heavily complemented by suburban rail, together forming an extensive network of 47 lines in and around Greater Nagoya. Of them, the subway lines represent 38% of Greater Nagoya's total rail ridership of 3 million passengers a day. In 2002, the system introduced Hatchii as its official mascot. __TOC__ Lines and infrastructure The six lines that comprise the Nagoya subway network are, for the most part, independent. However, Meikō Line services partially interline with the Meijō Line, and the operations of both lines are combined. Therefore, there are in fact ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meitetsu
, publicly trading as , is a private railway company operating around Aichi Prefecture and Gifu Prefecture of Japan. Some of the more famous trains operated by Meitetsu include the '' Panorama Car'' and the '' Panorama Car Super'', both of which offer views through their wide front windows. While the ''Panorama Super'' train is used extensively for the railroad's limited express service, the older and more energy-consuming ''Panorama Car'' train has been retired, the last run being on 27 December 2008. In the Tōkai region around Nagoya, it is a central firm of the Meitetsu Group, which is involved in transport, retail trade, service industry, and real estate, among other industries. As of March 2023, Meitetsu operated of track, 275 stations, and 1,076 train cars, being one of the largest private railway companies in Japan. History Meitetsu was founded on June 25, 1894, as the Aichi Horsecar Company. Over time, Meitetsu has acquired many small railway and interurban c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yokohama Municipal Subway
is the rapid transit network in the city of Yokohama, Japan, south of Tokyo in Kanagawa Prefecture. It is operated by Yokohama City Transportation Bureau as two lines, though three continuous lines exist. Lines The Yokohama Municipal Subway consists of three lines: Line 1, Line 3 and 4. Line 1 and 3 are operated as a single line, nicknamed the Yokohama Municipal Subway Blue Line, Blue Line. Line 4 is nicknamed the Yokohama Municipal Subway Green Line, Green Line. Upon the addition to the network of this line on March 30, 2008, the Blue Line and Green Line monikers came into official use. Transfer between the Blue and Green Line is possible at Center-Kita Station, Center-Kita and Center-Minami Stations. Feeder bus services from western Kawasaki, Kanagawa, Kawasaki City area run to Azamino Station. The "missing" Line 2 was planned to run from Kanagawa-Shinmachi Station via Yokohama Station to Byobugaura Station. The line was previously considered as a bypass line fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toei Subway
The is one of two subway systems in Tokyo, Japan, the other being the Tokyo Metro. The Toei Subway lines were originally licensed to the Teito Rapid Transit Authority (the predecessor of Tokyo Metro) but were constructed by the Tokyo Metropolitan Government following transfers of the licenses for each line. The subway has run at a financial loss for most of its history due to high construction expenses, particularly for the Toei Ōedo Line , Oedo Line. However, it reported its first net profit of ¥3.13bn in FY2006. The Toei Subway is operated by the Tokyo Metropolitan Bureau of Transportation. Tokyo Metro and Toei trains form completely separate networks. While users of prepaid rail passes can freely interchange between the two networks, regular ticket holders must purchase a second ticket, or a special transfer ticket, to change from a Toei line to a Tokyo Metro line and vice versa. The sole exceptions are on the segment of the Toei Mita Line between Meguro and Shirokane-Takana ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tokyo Metropolitan Bureau Of Transportation
The , also known as Toei Transportation, Toei Transport, or simply , is a bureau of the Tokyo Metropolitan Government which operates public transport services in Tokyo. Among its services, the Toei Subway is one of two rapid transit systems which make up the Tokyo subway system, the other being Tokyo Metro. Toei Subway Toei Subway operates 4 rapid transit (subway) lines which complement the 9 lines operated by Tokyo Metro. Tokyo Sakura Tram Tokyo Sakura Tram (the public name of the ''Toden Arakawa Line,'' the sole remaining line of Tokyo's once-extensive streetcar system) is a 30-station hybrid light rail/tram line. Nippori-Toneri Liner Nippori-Toneri Liner is a 13-station, long automated guideway transit system which commened operation on March 30, 2008. Ueno Zoo Monorail (Closed) Ueno Zoo Monorail was a long suspended monorail inside the grounds of Ueno Zoo which commenced operation on December 17, 1957. Operation was suspended on October 31, 2019, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
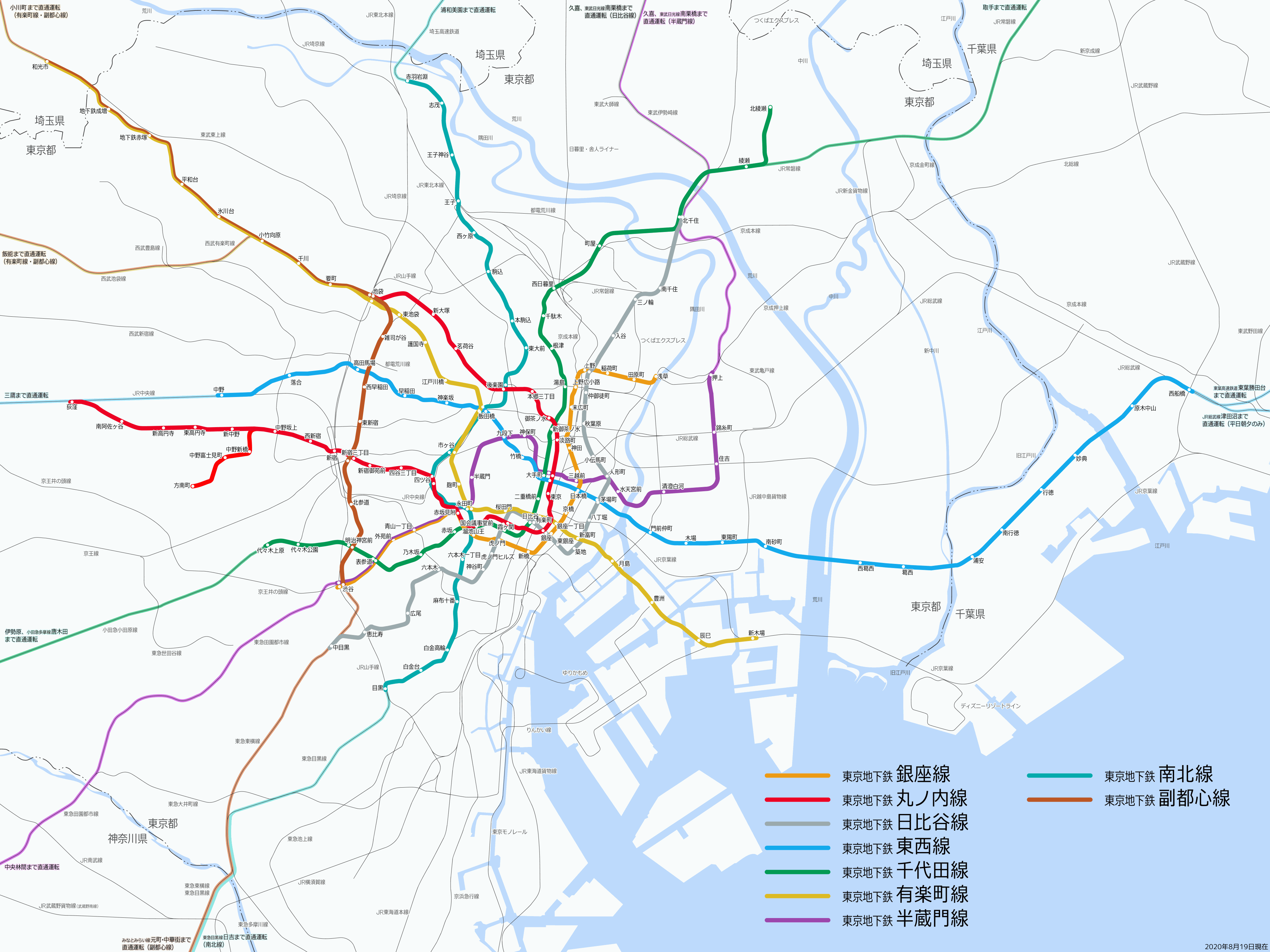
Tokyo Metro
The Tokyo Metro () is a major rapid transit system in Tokyo, Japan, operated by the #Organization, Tokyo Metro Co. With an average daily ridership of 6.52 million passengers (as of 2023), the Tokyo Metro is the larger of the Tokyo subway, two subway operators in the city, the other being the Toei Subway, with 2.85 million average daily rides. Organization Tokyo Metro is operated by , a joint-stock company jointly owned by the Government of Japan and the Tokyo Metropolitan Government. The company, founded as a part of then-Prime Minister Junichiro Koizumi's policy of converting statutory corporations into Joint-stock company, joint-stock companies, replaced the , commonly known as Eidan or TRTA, on April 1, 2004. TRTA was administered by the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport (Japan), Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport, and jointly funded by the national and metropolitan governments. It was formed in 1941 as a part-nationalization of the Tokyo Undergrou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sendai Subway
The is a rapid transit system in Sendai, Japan. It is operated by the Sendai City Transportation Bureau. The subway consists of two lines, the north-south Namboku Line, which opened in July 1987, and the east-west Tozai Line, which opened in December 2015. The subway was damaged in the 11 March 2011 Tohoku earthquake and tsunami Eleven or 11 may refer to: *11 (number) * One of the years 11 BC, AD 11, 1911, 2011 Literature * ''Eleven'' (novel), a 2006 novel by British author David Llewellyn *''Eleven'', a 1970 collection of short stories by Patricia Highsmith *''Eleven'' ... and shut down. It reopened on 29 April 2011. Lines Rolling stock * Sendai Subway 1000 series 4-car EMUs (Namboku Line, since July 1987) * Sendai Subway 2000 series 4-car EMUs (Tozai Line, since December 2015) * Sendai Subway 3000 series 4-car EMUs (Namboku Line, since 24 October 2024) Network Map References External links Official website (in English) Sendai Subway – official websit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hakodate Streetcar
The is a public transport authority in Hakodate, Hokkaido, Hakodate, Japan. The bureau currently operates only trams, although until 1 April 2003 it also ran a number of bus routes. The , a private horsecar operating company, opened Hakodate's first tram line in 1897. It was the first tram in Japan to be located north of Tokyo. The network was electrified in 1913. Following several changes of ownership, the Hakodate City Government finally took over control of the lines in 1943. Hakodate City Tram There were once twelve routes operating on six lines with a total length of 17.9 km. However, declining ridership led to closure of parts of the network in 1978, 1992, and 1993. The current network consists of two routes operating on four lines with a total length of 10.9 km. *Lines: Officially, there are four lines: **Hakodate City Tram Main Line, Main Line (本線): Hakodate-Dokku-mae — Jūjigai — Hakodate-Ekimae **Hakodate City Tram Yunokawa Line, Yunokawa Li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sapporo Streetcar
The is a tram loop located in Sapporo, Hokkaidō, Japan. It is operated by the Sapporo City Transportation Bureau. The system is often referred to as simply . The first section of the network opened in 1909 as the ; it was electrified in 1918. The city transportation bureau took over the network in 1927. Since 2020, it has been managed by a subsidiary company, . Lines and routes At its peak in 1958, the network was in length with 11 lines and 7 routes. However, the network shrank due to increased automobile ownership and the opening of the Sapporo Municipal Subway. After the closures in the 1970s, three lines remained. They were collectively called the or simply the , since the lines covered an incomplete city center route. *: Nishi-Yon-Chōme – Nishi-Jūgo-Chōme *: Nishi-Jūgo-Chōme – Chūō-Toshokan-Mae *: Chūō-Toshokan-Mae – Susukino The lines were combined into a single circle route following the opening of the between Susukino and Nishi-Yo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |