|
Far-western Blotting
The far-western blot, or far-western blotting, is a molecular biological method based on the technique of western blot to detect protein-protein interaction ''in vitro''. Whereas western blot uses an antibody probe to detect a protein of interest, far-western blot uses a non-antibody probe which can bind the protein of interest. Thus, whereas western blotting is used for the detection of certain proteins, far-western blotting is employed to detect protein/protein interactions. Method In conventional western blot, gel electrophoresis is used to separate proteins from a sample; these proteins are then transferred to a membrane in a 'blotting' step. In a western blot, specific proteins are then identified using an antibody probe. Far-western blot employs non-antibody proteins to probe the protein of interest on the blot. In this way, binding partners of the probe (or the blotted) protein may be identified. The probe protein is often produced in '' E. coli'' using an expression c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
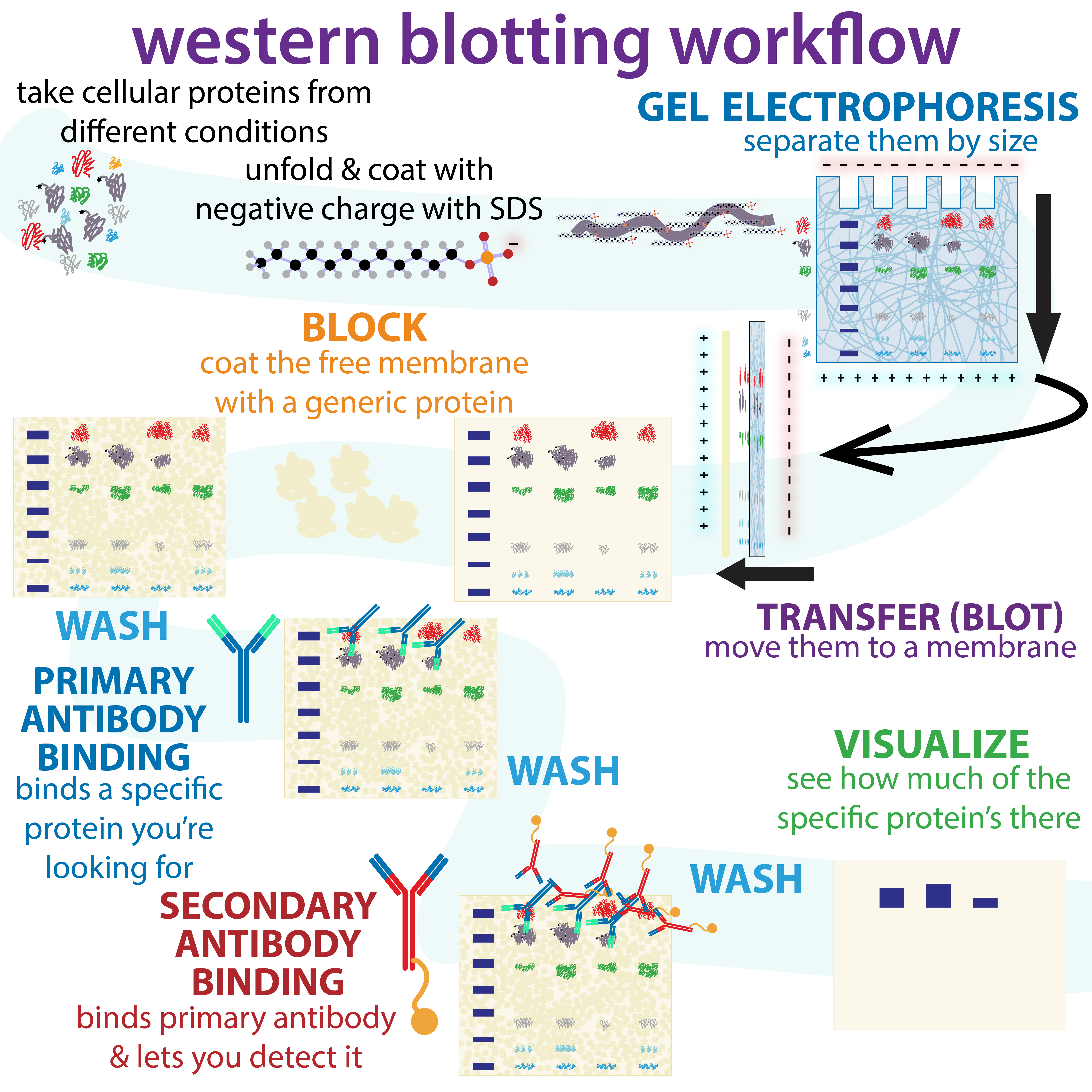
Western Blot
The western blot (sometimes called the protein immunoblot), or western blotting, is a widely used analytical technique in molecular biology and immunogenetics to detect specific proteins in a sample of tissue homogenate or extract. Besides detecting the proteins, this technique is also utilized to visualize, distinguish, and quantify the different proteins in a complicated protein combination. Western blot technique uses three elements to achieve its task of separating a specific protein from a complex: separation by size, transfer of protein to a solid support, and marking target protein using a primary and secondary antibody to visualize. A synthetic or animal-derived antibody (known as the primary antibody) is created that recognizes and binds to a specific target protein. The electrophoresis membrane is washed in a solution containing the primary antibody, before excess antibody is washed off. A secondary antibody is added which recognizes and binds to the primary antibod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blot (biology)
In molecular biology and genetics, a blot is a method of transferring large biomolecules (proteins, DNA or RNA) onto a carrier, such as a membrane composed of nitrocellulose, polyvinylidene fluoride or nylon. In many instances, this is done after a gel electrophoresis, transferring the molecules from the gel onto the Blotting matrix, blotting membrane, and other times adding the samples directly onto the membrane. After the blotting, the transferred molecules are then visualized by colorant staining (for example, silver staining of proteins), autoradiographic visualization of radioactive tracer, radiolabelled molecules (performed before the blot), or specific labelling of some proteins or nucleic acids. The latter is done with antibody, antibodies or hybridization probes that bind only to some molecules of the blot and have an enzyme joined to them. After proper washing, this enzymatic activity (and so, the molecules found in the blot) is visualized by incubation with a proper reag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gel Electrophoresis
Gel electrophoresis is an electrophoresis method for separation and analysis of biomacromolecules (DNA, RNA, proteins, etc.) and their fragments, based on their size and charge through a gel. It is used in clinical chemistry to separate proteins by charge or size (IEF agarose, essentially size independent) and in biochemistry and molecular biology to separate a mixed population of DNA and RNA fragments by length, to estimate the size of DNA and RNA fragments, or to separate proteins by charge. Nucleic acid molecules are separated by applying an electric field to move the negatively charged molecules through a gel matrix of agarose, polyacrylamide, or other substances. Shorter molecules move faster and migrate farther than longer ones because shorter molecules migrate more easily through the pores of the gel. This phenomenon is called sieving. Proteins are separated by the charge in agarose because the pores of the gel are too large to sieve proteins. Gel electrophoresi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antibody
An antibody (Ab) or immunoglobulin (Ig) is a large, Y-shaped protein belonging to the immunoglobulin superfamily which is used by the immune system to identify and neutralize antigens such as pathogenic bacteria, bacteria and viruses, including those that cause disease. Each individual antibody recognizes one or more specific antigens, and antigens of virtually any size and chemical composition can be recognized. Antigen literally means "antibody generator", as it is the presence of an antigen that drives the formation of an antigen-specific antibody. Each of the branching chains comprising the "Y" of an antibody contains a paratope that specifically binds to one particular epitope on an antigen, allowing the two molecules to bind together with precision. Using this mechanism, antibodies can effectively "tag" the antigen (or a microbe or an infected cell bearing such an antigen) for attack by cells of the immune system, or can neutralize it directly (for example, by blocking a p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Escherichia Coli
''Escherichia coli'' ( )Wells, J. C. (2000) Longman Pronunciation Dictionary. Harlow ngland Pearson Education Ltd. is a gram-negative, facultative anaerobic, rod-shaped, coliform bacterium of the genus '' Escherichia'' that is commonly found in the lower intestine of warm-blooded organisms. Most ''E. coli'' strains are part of the normal microbiota of the gut, where they constitute about 0.1%, along with other facultative anaerobes. These bacteria are mostly harmless or even beneficial to humans. For example, some strains of ''E. coli'' benefit their hosts by producing vitamin K2 or by preventing the colonization of the intestine by harmful pathogenic bacteria. These mutually beneficial relationships between ''E. coli'' and humans are a type of mutualistic biological relationship—where both the humans and the ''E. coli'' are benefitting each other. ''E. coli'' is expelled into the environment within fecal matter. The bacterium grows massi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Expression Cloning
Expression cloning is a technique in DNA cloning that uses expression vectors to generate a library of clones, with each clone expressing one protein. This ''expression library'' is then screened for the property of interest and clones of interest are recovered for further analysis. An example would be using an expression library to isolate genes that could confer antibiotic resistance. Expression vectors Expression vectors are a specialized type of cloning vector in which the transcriptional and translational signals needed for the regulation of the gene of interest are included in the cloning vector. The transcriptional and translational signals may be synthetically created to make the expression of the gene of interest easier to regulate. Purpose Usually the ultimate aim of expression cloning is to produce large quantities of specific proteins. To this end, a bacterial expression clone may include a ribosome binding site ( Shine-Dalgarno sequence) to enhance translation of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Affinity Tag
Affinity may refer to: Commerce, finance and law * Affinity (law), kinship by marriage * Affinity analysis, a market research and business management technique * Affinity Credit Union, a Saskatchewan-based credit union * Affinity Equity Partners, an Asian private equity firm * Affinity fraud, a type of scam targeting a specific demographic * Affinity marketing, a method of extending market reach by forming partnerships and cross-selling relationships * Affinity Partners, an American private equity firm Religion and belief * Affinity (canon law), a kinship arising from the sexual intercourse of a man and a woman * Affinity (Christian organisation), network of conservative evangelical churches and Christian agencies * Affinity group, a private, non-commercial and non-governmental organisation formed around a shared interest or goal Science and technology * ''Affinity'', the UK's first road-legal solar car, built by Cambridge University Eco Racing * Affinity (mathematic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyhistidine-tag
A polyhistidine-tag, best known by the trademarked name His-tag, is an amino acid motif in proteins that typically consists of at least six histidine (''His'') residues, often at the N- or C-terminus of the protein. It is also known as a hexa histidine-tag, 6xHis-tag, or His6 tag. The tag was invented by Roche, although the use of histidines and its vectors are distributed by Qiagen. Various purification kits for histidine-tagged proteins are commercially available from multiple companies. The total number of histidine residues may vary in the tag from as low as two, to as high as 10 or more His residues. N- or C-terminal His-tags may also be followed or preceded, respectively, by a suitable amino acid sequence that facilitates removal of the polyhistidine-tag using endopeptidases. This extra sequence is not necessary if exopeptidases are used to remove N-terminal His-tags (e.g., Qiagen TAGZyme). Furthermore, exopeptidase cleavage may solve the unspecific cleavage observed when ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FLAG-tag
FLAG-tag, or FLAG octapeptide, or FLAG epitope, is a peptide protein tag that can be added to a protein using recombinant DNA technology, having the sequence DYKDDDDK (where D=aspartic acid, Y=tyrosine, and K=lysine). It is one of the most specific tags and it is an artificial antigen to which specific, high affinity monoclonal antibodies have been developed and hence can be used for protein purification by affinity chromatography and also can be used for locating proteins within living cells. FLAG-tag has been used to separate recombinant, overexpressed protein from wild-type protein expressed by the host organism. FLAG-tag can also be used in the isolation of protein complexes with multiple subunits, because FLAG-tag's mild purification procedure tends not to disrupt such complexes. FLAG-tag-based purification has been used to obtain proteins of sufficient purity and quality to carry out 3D structure determination by x-ray crystallography. A FLAG-tag can be used in many differen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular Biology Techniques
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms that are held together by attractive forces known as chemical bonds; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions that satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics, organic chemistry, and biochemistry, the distinction from ions is dropped and ''molecule'' is often used when referring to polyatomic ions. A molecule may be homonuclear, that is, it consists of atoms of one chemical element, e.g. two atoms in the oxygen molecule (O2); or it may be heteronuclear, a chemical compound composed of more than one element, e.g. water (two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom; H2O). In the kinetic theory of gases, the term ''molecule'' is often used for any gaseous particle regardless of its composition. This relaxes the requirement that a molecule contains two or more atoms, since the noble gases are individual atoms. Atoms and complexes connected by non-covalent interactions, such as hydrogen bonds or ionic bonds, are typically not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |