|
Familial Dysalbuminemic Hyperthyroxinemia
Familial dysalbuminemic hyperthyroxinemia (FDH) rare genetic condition that is a common cause oeuthyroid hyperthyroxinemiaand is associated with mutations in the human serum albumin gene. It is an autosomal dominant condition that is often mistaken for resistance to thyroid hormone (RTH) syndromes or hyperthyroidism. FDH is characterized by high levels of thyroxine (T4) and normal levels of thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH). Due to the mutations in the albumin gene, an abnormal albumin protein binds thyroid hormones with a high affinity than normal. This explains why those with familial dysalbuminemic hyperthyroxinemia have increased T4 levels and normal TSH levels. Signs and symptoms Familial dysalbuminemic hyperthyroxinemia is usually asymptomatic. The clinical features are not specific and vary from patient to patient. In some cases, symptoms such as those seen in hyperthyroidism have been recorded like: palpitations, weight losstremors and anxiety. Cause The mutati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetic Disorder
A genetic disorder is a health problem caused by one or more abnormalities in the genome. It can be caused by a mutation in a single gene (monogenic) or multiple genes (polygenic) or by a chromosome abnormality. Although polygenic disorders are the most common, the term is mostly used when discussing disorders with a single genetic cause, either in a gene or chromosome. The mutation responsible can occur spontaneously before embryonic development (a ''de novo'' mutation), or it can be inherited from two parents who are carriers of a faulty gene ( autosomal recessive inheritance) or from a parent with the disorder (autosomal dominant inheritance). When the genetic disorder is inherited from one or both parents, it is also classified as a hereditary disease. Some disorders are caused by a mutation on the X chromosome and have X-linked inheritance. Very few disorders are inherited on the Y chromosome or mitochondrial DNA (due to their size). There are well over 6,000 known ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bovine Serum Albumin 3v03 Crystal Structure
Bovines (subfamily Bovinae) comprise a diverse group of 10 genera of medium to large-sized ungulates, including cattle, bison, African buffalo, water buffalos, and the four-horned and spiral-horned antelopes. The members of this group are classified into loose tribes rather than formal subgroups, as the evolutionary relationships within the groups are still uncertain. General characteristics include cloven hooves and usually at least one of the sexes of a species having true horns. The largest extant bovine is the gaur. In many countries, bovid milk and meat is used as food by humans. Cattle are kept as livestock almost everywhere except in parts of India and Nepal, where they are considered sacred by most Hindus. Bovids are used as draft animals and as riding animals. Small breeds of domestic bovid, such as the Miniature Zebu, are kept as pets. Bovid leather is durable and flexible and is used to produce a wide range of goods including clothing and bags. Systematics and class ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Denmark
Denmark is a Nordic countries, Nordic country in Northern Europe. It is the metropole and most populous constituent of the Kingdom of Denmark,, . also known as the Danish Realm, a constitutionally unitary state that includes the Autonomous administrative division, autonomous territories of the Faroe Islands and Greenland in the north Atlantic Ocean.* * * Metropolitan Denmark, also called "continental Denmark" or "Denmark proper", consists of the northern Jutland peninsula and an archipelago of 406 islands. It is the southernmost of the Scandinavian countries, lying southwest of Sweden, south of Norway, and north of Germany, with which it shares a short border. Denmark proper is situated between the North Sea to the west and the Baltic Sea to the east.The island of Bornholm is offset to the east of the rest of the country, in the Baltic Sea. The Kingdom of Denmark, including the Faroe Islands and Greenland, has roughly List of islands of Denmark, 1,400 islands greater than in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlantic, North Atlantic, the French West Indies, and List of islands of France, many islands in Oceania and the Indian Ocean, giving it Exclusive economic zone of France, one of the largest discontiguous exclusive economic zones in the world. Metropolitan France shares borders with Belgium and Luxembourg to the north; Germany to the northeast; Switzerland to the east; Italy and Monaco to the southeast; Andorra and Spain to the south; and a maritime border with the United Kingdom to the northwest. Its metropolitan area extends from the Rhine to the Atlantic Ocean and from the Mediterranean Sea to the English Channel and the North Sea. Its Regions of France, eighteen integral regions—five of which are overseas—span a combined area of and hav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Venezuela
Venezuela, officially the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela, is a country on the northern coast of South America, consisting of a continental landmass and many Federal Dependencies of Venezuela, islands and islets in the Caribbean Sea. It comprises an area of , and its population was estimated at 29 million in 2022. The capital and largest urban agglomeration is the city of Caracas. The continental territory is bordered on the north by the Caribbean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean, on the west by Colombia, Brazil on the south, Trinidad and Tobago to the north-east and on the east by Guyana. Venezuela is a presidential republic consisting of States of Venezuela, 23 states, the Venezuelan Capital District, Capital District and Federal Dependencies of Venezuela, federal dependencies covering Venezuela's offshore islands. Venezuela is among the most urbanized countries in Latin America; the vast majority of Venezuelans live in the cities of the north and in the capital. The territory o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hispanic
The term Hispanic () are people, Spanish culture, cultures, or countries related to Spain, the Spanish language, or broadly. In some contexts, Hispanic and Latino Americans, especially within the United States, "Hispanic" is used as an Ethnicity, ethnic or Meta-ethnicity, meta-ethnic term. The term commonly applies to Spaniards and Spanish-speaking (Hispanophone) populations and countries in Hispanic America (the continent) and Hispanic Africa (Equatorial Guinea and the Territorial dispute, disputed territory of Western Sahara), which were formerly part of the Spanish Empire due to colonization mainly between the 16th and 20th centuries. The cultures of Hispanophone countries outside Spain have been influenced as well by the local Pre-Columbian era, pre-Hispanic cultures or other foreign influences. There was also Spanish influence in the former Spanish East Indies, including the Philippines, Marianas, and other nations. However, Spanish is not a predominant language in these ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caucasian Race
The Caucasian race (also Caucasoid, Europid, or Europoid) is an Historical race concepts, obsolete racial classification of humans based on a now-disproven theory of biological race. The ''Caucasian race'' was historically regarded as a biological taxon which, depending on which of the historical race classifications was being used, usually included ancient and modern populations from all or parts of Europe, Western Asia, Central Asia, South Asia, North Africa, and the Horn of Africa. Introduced in the 1780s by members of the Göttingen school of history, the term denoted one of three purported major races of humankind (those three being Caucasoid, Mongoloid, and Negroid). In biological anthropology, ''Caucasoid'' has been used as an umbrella term for Phenotype, phenotypically similar groups from these different regions, with a focus on skeletal anatomy, and especially cranial morphology, without regard to skin tone. Ancient and modern "Caucasoid" populations were thus not exclu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gel Electrophoresis Of Proteins
Protein electrophoresis is a method for analysing the proteins in a fluid or an extract. The electrophoresis may be performed with a small volume of sample in a number of alternative ways with or without a supporting medium, namely agarose or polyacrylamide. Variants of gel electrophoresis include SDS-PAGE, free-flow electrophoresis, electrofocusing, isotachophoresis, affinity electrophoresis, immunoelectrophoresis, counterelectrophoresis, and capillary electrophoresis. Each variant has many subtypes with individual advantages and limitations. Gel electrophoresis is often performed in combination with electroblotting or immunoblotting to give additional information about a specific protein. Denaturing gel methods SDS-PAGE SDS-PAGE, sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, describes a collection of related techniques to separate proteins according to their electrophoretic mobility (a function of the molecular weight of a polypeptide chain) while in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
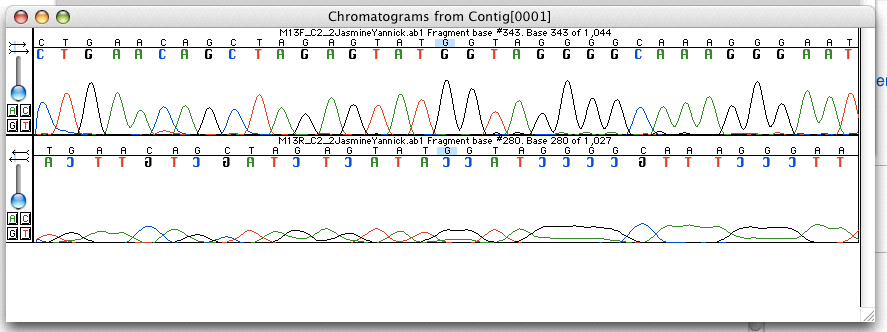
Whole Genome Sequencing
Whole genome sequencing (WGS), also known as full genome sequencing or just genome sequencing, is the process of determining the entirety of the DNA sequence of an organism's genome at a single time. This entails sequencing all of an organism's chromosomal DNA as well as DNA contained in the mitochondrial DNA, mitochondria and, for plants, in the chloroplast. Whole genome sequencing has largely been used as a research tool, but was being introduced to clinics in 2014. In the future of personalized medicine, whole genome sequence data may be an important tool to guide therapeutic intervention. The tool of DNA sequencing, gene sequencing at Single-nucleotide polymorphism, SNP level is also used to pinpoint functional variants from association studies and improve the knowledge available to researchers interested in evolutionary biology, and hence may lay the foundation for predicting disease susceptibility and drug response. Whole genome sequencing should not be confused with DNA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
202403 Protein Gel Electrophoresis Equipment
4 (four) is a number, numeral and digit. It is the natural number following 3 and preceding 5. It is a square number, the smallest semiprime and composite number, and is considered unlucky in many East Asian cultures. Evolution of the Hindu-Arabic digit Brahmic numerals represented 1, 2, and 3 with as many lines. 4 was simplified by joining its four lines into a cross that looks like the modern plus sign. The Shunga would add a horizontal line on top of the digit, and the Kshatrapa and Pallava evolved the digit to a point where the speed of writing was a secondary concern. The Arabs' 4 still had the early concept of the cross, but for the sake of efficiency, was made in one stroke by connecting the "western" end to the "northern" end; the "eastern" end was finished off with a curve. The Europeans dropped the finishing curve and gradually made the digit less cursive, ending up with a digit very close to the original Brahmin cross. While the shape of the character for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Signs And Symptoms
Signs and symptoms are diagnostic indications of an illness, injury, or condition. Signs are objective and externally observable; symptoms are a person's reported subjective experiences. A sign for example may be a higher or lower temperature than normal, raised or lowered blood pressure or an abnormality showing on a medical scan. A symptom is something out of the ordinary that is experienced by an individual such as feeling feverish, a headache or other pains in the body, which occur as the body's immune system fights off an infection. Signs and symptoms Signs A medical sign is an objective observable indication of a disease, injury, or medical condition that may be detected during a physical examination. These signs may be visible, such as a rash or bruise, or otherwise detectable such as by using a stethoscope or taking blood pressure. Medical signs, along with symptoms, help in forming a diagnosis. Some examples of signs are nail clubbing of either the fingernail ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pathophysiology
Pathophysiology (or physiopathology) is a branch of study, at the intersection of pathology and physiology, concerning disordered physiological processes that cause, result from, or are otherwise associated with a disease or injury. Pathology is the medical discipline that describes conditions typically ''observed'' during a disease state, whereas physiology is the biological discipline that describes processes or mechanisms ''operating'' within an organism. Pathology describes the abnormal or undesired condition (symptoms of a disease), whereas pathophysiology seeks to explain the functional changes that are occurring within an individual due to a disease or pathologic state. Etymology The term ''pathophysiology'' comes from the Ancient Greek πάθος (''pathos'') and φυσιολογία (''phisiologia''). History Early Developments The origins of pathophysiology as a distinct field date back to the late 18th century. The first known lectures on the subject were delivered ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |