|
Falsing
In telecommunications, falsing is a signaling error condition when a signal decoder detects a valid input although the implied protocol function was not intended. This is also known as a false decode. Other forms are referred to as talk-off. Signal detection Signal decoders used in communication systems, such as telephony and two-way radio systems, detect communication protocol states by recognizing a variety of electrical, optical, or acoustic conditions. Misinterpretation of those conditions leads to communication errors. Proper detection of signaling is a compromise between acceptable error rates and cost of implementation. The engineering problem is to produce the simplest circuit that works reliably. A decoder generally tries to filter audio input to strip off every audio component except a sought-after, specific tone. In part, a decoder is a narrow bandpass filter. A signal that gets through the narrow filter is rectified into a DC voltage which is used to switch something ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quik Call I
In a conventional, analog two-way radio system, a standard radio has ''noise squelch'' or ''carrier squelch'', which allows a radio to receive all transmissions. Selective calling is used to address a subset of all two-way radios on a single radio frequency channel. Where more than one user is on the same channel (co-channel users), selective calling can address a subset of all receivers or can direct a call to a single radio. Selective calling features fit into two major categories—''individual calling'' and ''group calling''. Individual calls generally have longer time-constants: it takes more air-time to call an individual radio unit than to call a large group of radios. Selective calling is akin to the use of a lock on a door. A radio with carrier squelch is unlocked and will let any signal in. Selective calling locks out all signals except ones with the correct "key", in this case a specific digital code. Selective calling systems can overlap; e.g. a radio may have CTCSS ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Single-frequency Signaling
In telephony, single-frequency signaling (SF or SF tone) is line signaling in which dial pulses or supervisory signals are conveyed by a single-frequency tone in each direction in the voice-band. SF and similar systems were used in 20th-century carrier systems. An SF signaling unit converts DC signaling (usually, at least in long-distance circuits, E&M signaling) to a format (characterized by the presence or absence of a single voice-frequency tone), which is suitable for transmission over an AC path, ''e.g.'', a carrier system. The SF tone is present in the on-hook or idle state and absent during the seized state. In the seized state, dial pulses are conveyed by bursts of SF tone, corresponding to the interruptions in dc continuity created by a rotary dial or other DC dialing mechanism. The SF tone may occupy a small portion of the user data channel spectrum, ''e.g.,'' 1600 Hz or 2600 Hz (SF "in-band signaling)". There may be a notch filter at the precise SF freque ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CTCSS
In telecommunications, Continuous Tone-Coded Squelch System or CTCSS is one type of in-band signaling that is used to reduce the annoyance of listening to other users on a shared two-way radio communication channel. It is sometimes referred to as tone squelch or PL for Private Line, a trademark of Motorola. It does this by adding a low frequency audio tone to the voice. Where more than one group of users is on the same radio frequency (called ''co-channel users''), CTCSS circuitry mutes those users who are using a different CTCSS tone or no CTCSS. CTCSS tone codes are sometimes referred to as sub-channels, but this is a misnomer because no additional radio channels are created. All users with different CTCSS tones on the same channel are still transmitting on the identical radio frequency, and their transmissions interfere with each other; however; the interference is masked under most conditions. Although it provides some protection against interference, CTCSS does not offer a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
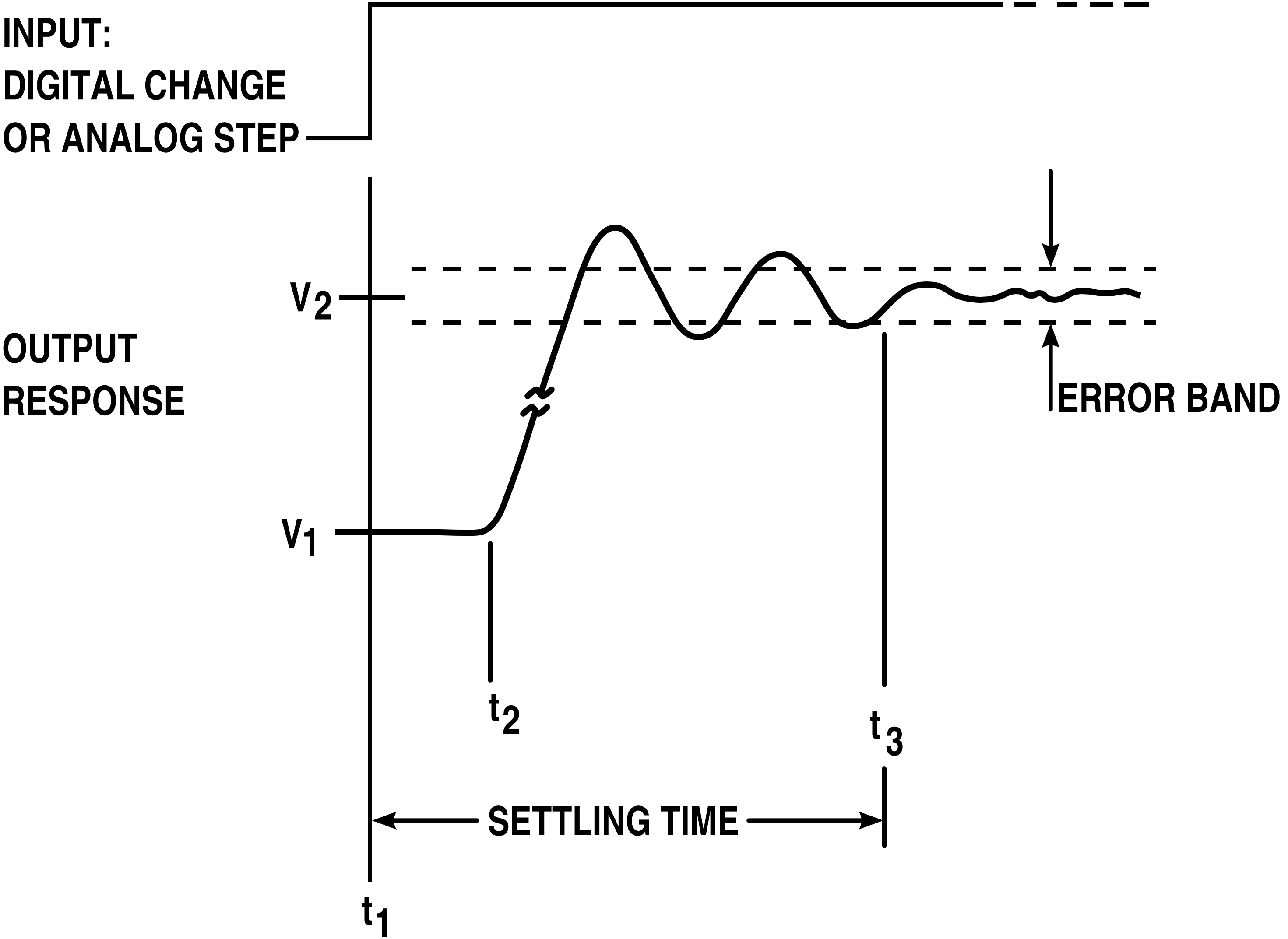
Ringing (signal)
In electronics, signal processing, and video, ringing is oscillation of a signal, particularly in the step response (the response to a sudden change in input). Often ringing is undesirable, but not always, as in the case of resonant inductive coupling. It is also known as hunting. It is also known as ripple, particularly in electricity or in frequency domain response. Electrical circuits In electrical circuits, ringing is an oscillation of a voltage or current. Ringing can be undesirable because it causes extra current to flow, thereby wasting energy and causing extra heating of the components; it can cause unwanted electromagnetic radiation to be emitted; it can increase settling time for the desired final state; and it may cause unwanted triggering of bistable elements in digital circuits. Ringy communications circuits may suffer falsing. Two electrical sources of this ringing are: # A resonant transient response due to undesired parasitic capacitances and inductanc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Selcall
Selcall ( selective calling) is a type of squelch protocol used in radio communications systems, in which transmissions include a brief burst of sequential audio tones. Receivers that are set to respond to the transmitted tone sequence will open their squelch, while others will remain muted. Selcall is a radio signalling protocol mainly in use in Europe, Asia, Australia and New Zealand, and continues to be incorporated in radio equipment marketed in those areas. Details The transmission of a selcall code involves the generation and sequencing of a series of predefined, audible tones. Both the tone frequencies, and sometimes the tone periods, must be known in advance by both the transmitter and the receiver. Each predefined tone represents a single digit. A series of tones therefore represents a series of digits that represents a number. The number encoded in a selcall burst is used to address one or more receivers. If the receiver is programmed to recognise a certain number, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radio Technology
Radio is the technology of communicating using radio waves. Radio waves are electromagnetic waves of frequency between 3 hertz (Hz) and 300 gigahertz (GHz). They are generated by an electronic device called a transmitter connected to an antenna which radiates the waves. They can be received by other antennas connected to a radio receiver; this is the fundamental principle of radio communication. In addition to communication, radio is used for radar, radio navigation, remote control, remote sensing, and other applications. In radio communication, used in radio and television broadcasting, cell phones, two-way radios, wireless networking, and satellite communication, among numerous other uses, radio waves are used to carry information across space from a transmitter to a receiver, by modulating the radio signal (impressing an information signal on the radio wave by varying some aspect of the wave) in the transmitter. In radar, used to locate and track objects like ai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
General Electric
General Electric Company (GE) was an American Multinational corporation, multinational Conglomerate (company), conglomerate founded in 1892, incorporated in the New York (state), state of New York and headquartered in Boston. Over the years, the company had multiple divisions, including GE Aerospace, aerospace, GE Power, energy, GE HealthCare, healthcare, lighting, locomotives, appliances, and GE Capital, finance. In 2020, GE ranked among the Fortune 500, ''Fortune'' 500 as the 33rd largest firm in the United States by gross revenue. In 2023, the company was ranked 64th in the Forbes Global 2000, ''Forbes'' Global 2000. In 2011, GE ranked among the Fortune 20 as the 14th most profitable company, but later very severely underperformed the market (by about 75%) as its profitability collapsed. Two employees of GE—Irving Langmuir (1932) and Ivar Giaever (1973)—have been awarded the Nobel Prize. From 1986 until 2013, GE was the owner of the NBC television network through its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Motorola
Motorola, Inc. () was an American multinational telecommunications company based in Schaumburg, Illinois. It was founded by brothers Paul and Joseph Galvin in 1928 and had been named Motorola since 1947. Many of Motorola's products had been radio-related communication equipment such as two-way radios, consumer walkie-talkies, cellular infrastructure, mobile phones, satellite communicators, pagers, as well as cable modems and semiconductors. After having lost $4.3 billion from 2007 to 2009, Motorola was split into two independent public companies: Motorola Solutions (its legal successor) and Motorola Mobility (spun off), on January 4, 2011. Motorola designed and sold wireless network equipment such as cellular transmission base stations and signal amplifiers. Its business and government customers consisted mainly of wireless voice and broadband systems (used to build private networks), and public safety communications systems like Astro and Dimetra. Motorola's h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Two-out-of-five Code
A two-out-of-five code is a constant-weight code that provides exactly ten possible combinations of two bits, and is thus used for representing the decimal digits using five bits. Each bit is assigned a weight, such that the set bits sum to the desired value, with an exception for zero. According to Federal Standard 1037C: * each decimal digit is represented by a binary numeral consisting of five bits of which two are of one kind, called ''ones'', and three are of the other kind, called ''zeros'', and * the usual weights assigned to the bit positions are 0-1-2-3-6. However, in this scheme, zero is encoded as binary ''01100''; strictly speaking the 0-1-2-3-6 previously claimed is just a mnemonic device. The weights give a unique encoding for most digits, but allow two encodings for 3: 0+3 or 10010 and 1+2 or 01100. The former is used to encode the digit 3, and the latter is used to represent the otherwise unrepresentable zero. The IBM 7070, IBM 7072, and IBM 7074 computers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Logical Conjunction
In logic, mathematics and linguistics, ''and'' (\wedge) is the Truth function, truth-functional operator of conjunction or logical conjunction. The logical connective of this operator is typically represented as \wedge or \& or K (prefix) or \times or \cdot in which \wedge is the most modern and widely used. The ''and'' of a set of operands is true if and only if ''all'' of its operands are true, i.e., A \land B is true if and only if A is true and B is true. An operand of a conjunction is a conjunct. Beyond logic, the term "conjunction" also refers to similar concepts in other fields: * In natural language, the denotation of expressions such as English language, English "Conjunction (grammar), and"; * In programming languages, the Short-circuit evaluation, short-circuit and Control flow, control structure; * In set theory, Intersection (set theory), intersection. * In Lattice (order), lattice theory, logical conjunction (Infimum and supremum, greatest lower bound). Notati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DTMF
Dual-tone multi-frequency (DTMF) signaling is a telecommunication signaling system using the voice-frequency band over telephone lines between telephone equipment and other communications devices and switching centers. DTMF was first developed in the Bell System in the United States, and became known under the trademark Touch-Tone for use in push-button telephones, starting in 1963. The DTMF frequencies are standardized in ITU-T Recommendation Q.23. The signaling system is also known as ''MF4'' in the United Kingdom, as ''MFV'' in Germany, and ''Digitone'' in Canada. Touch-tone dialing with a telephone keypad gradually replaced the use of rotary dials and has become the industry standard in telephony to control equipment and signal user intent. The signaling on trunks in the telephone network uses a different type of multi-frequency signaling. Multifrequency signaling Before the development of DTMF, telephone numbers were dialed with rotary dials for loop-disconnect (LD) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multi-frequency
In telephony, multi-frequency signaling (MF) is a type of signaling that was introduced by the Bell System after World War II. It uses a combination of audible tones for address ( telephone number) transport and supervision signaling on trunk lines between central offices. The signaling is sent '' in-band'' over the same channel as the bearer channel used for voice traffic. Multi-frequency signaling defines electronic signals that consist of a combination of two audible frequencies, usually selected from a set of six frequencies. Over several decades, various types of MF signaling were developed, including national and international varieties. The CCITT standardization process specified the American Bell System version as ''Regional Standard No. 1'', or Signalling System R1, and a corresponding European standard as Signalling System R2. Both were largely replaced by digital systems, such as Signalling System 7, which operate out-of-band on a separate data network. Because o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |