|
Extremotroph
An extremotroph (from Latin ' meaning "extreme" and Greek ' () meaning "food") is an organism that feeds on matter that is not typically considered to be food to most life on Earth. "These anthropocentric definitions that we make of extremophily and extremotrophy focus on a single environmental extreme but many extremophiles may fall into multiple categories, for example, organisms living inside hot rocks deep under the Earth's surface." Examples *''Pestalotiopsis microspora'': plastic eater *''Halomonas titanicae'': metal eater *''Geotrichum candidum'': compact disk eater *''Aspergillus fumigatus'': printed circuit board eater *''Deinococcus radiodurans'': radioactive waste eater *Actinobacteria from arid and desert habitats *Cold-tolerant cyanobacteria found in polar ice shelves Industrial uses Extremotrophs are used as bioremediation and biodegradation agents. See also *Chemotroph *Extremophile *Heterotroph *Lithoautotroph A lithoautotroph is an organism that derive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extremophile
An extremophile () is an organism that is able to live (or in some cases thrive) in extreme environments, i.e., environments with conditions approaching or stretching the limits of what known life can adapt to, such as extreme temperature, pressure, radiation, salinity, or pH level. Since the definition of an extreme environment is relative to an arbitrarily defined standard, often an anthropocentric one, these organisms can be considered Dominance (ecology), ecologically dominant in the evolutionary history of the planet. Dating back to more than 40 million years ago, extremophiles have continued to thrive in the most extreme conditions, making them one of the most abundant lifeforms. The study of extremophiles has expanded human knowledge of the limits of life, and informs speculation about extraterrestrial life. Extremophiles are also of interest because of their potential for bioremediation of environments made hazardous to humans due to pollution or contamination. Character ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anthropocentrism
Anthropocentrism ( ) is the belief that human beings are the central or most important entity on the planet. The term can be used interchangeably with humanocentrism, and some refer to the concept as human supremacy or human exceptionalism. From an anthropocentric perspective, humankind is seen as separate from nature and superior to it, and other entities (animals, plants, minerals, etc.) are viewed as resources for humans to use. It is possible to distinguish between at least three types of anthropocentrism: perceptual anthropocentrism (which "characterizes paradigms informed by sense-data from human sensory organs"); descriptive anthropocentrism (which "characterizes paradigms that begin from, center upon, or are ordered around ''Homo sapiens'' / ‘the human'"); and normative anthropocentrism (which "characterizes paradigms that make assumptions or assertions about the superiority of ''Homo sapiens'', its capacities, the primacy of its values, rits position in the universe" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pestalotiopsis Microspora
''Pestalotiopsis microspora'' is a species of endophytic fungus capable of breaking down and digesting polyurethane. Originally identified in 1880 in fallen foliage of common ivy (''Hedera helix'') in Buenos Aires, it also causes leaf spot in Hypericum 'Hidcote' ('' Hypericum patulum'') shrubs in Japan. However, its polyurethane degradation activity was discovered only in the 2010s in two distinct ''P. microspora'' strains isolated from plant stems in the Yasuni National Forest within the Ecuadorian Amazon rainforest by a group of student researchers led by molecular biochemistry professor Scott Strobel as part of Yale's annual Rainforest Expedition and Laboratory. It is the first fungus species found to be able to subsist on polyurethane in anaerobic conditions. This makes the fungus a potential candidate for bioremediation projects involving large quantities of plastic. ''Pestalotiopsis microspora'' was originally described from Buenos Aires, Argentina in 1880 by mycolo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Halomonas Titanicae
''Halomonas titanicae'' is a gram-negative, halophilic species of bacteria which was isolated in 2010 from rusticles recovered from the wreck of the RMS ''Titanic''. It has been estimated by Henrietta Mann, one of the researchers that first isolated it, that the action of microbes like ''H. titanicae'' may bring about the total deterioration of the ''Titanic'' by 2030. While the bacteria have been identified as a potential danger to oil rigs and other man-made objects in the deep sea, they also have the potential to be used in bioremediation to accelerate the decomposition of shipwrecks littering the ocean floor. Cell morphology ''Halomonas titanicae'' is a gram-negative, rod-shaped bacterium that produces peritrichous flagella. It is catalase and oxidase positive. It has been found to form biofilms and some strains are capable of oxidation of thiosulfate, which is regulated by quorum sensing. It is able to withstand high osmotic pressure due to producing molecules like ect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geotrichum Candidum
''Geotrichum candidum'' is a fungus which is a member of the human microbiome, notably associated with skin, sputum, and faeces where it occurs in 25–30% of specimens. It is common in soil and has been isolated from soil collected around the world, in all continents. ''G. candidum'' is the causative agent of the human disease geotrichosis and the plant disease sour rot which infects citrus fruits, tomatoes, carrots, and other vegetables. It can affect harvested fruit of durians such as ''Durio graveolens''. ''G. candidum'' is used widely in the production of certain dairy products including rind cheeses such as Camembert, Saint-Nectaire, Reblochon, and others. The fungus can also be found in a Nordic countries, Nordic yogurt-like product known as viili where it is responsible for the product's velvety texture. In a 2001 study, ''G. candidum'' was found to consume the polycarbonate found in Compact disc, CDs. History Taxonomy The genus ''Geotrichum'' was described by Johann ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aspergillus Fumigatus
''Aspergillus fumigatus'' is a species of fungus in the genus ''Aspergillus'', and is one of the most common ''Aspergillus'' species to cause disease in individuals with an immunodeficiency. ''Aspergillus fumigatus'', a saprotroph widespread in nature, is typically found in soil and decaying organic matter, such as compost heaps, where it plays an essential role in carbon and nitrogen recycling. Colonies of the fungus produce from conidiophores; thousands of minute grey-green conidia (2–3 μm) which readily become airborne. For many years, ''A. fumigatus'' was thought to only reproduce asexually, as neither mating nor meiosis had ever been observed. In 2008, ''A. fumigatus'' was shown to possess a fully functional sexual reproductive cycle, 145 years after its original description by Fresenius. Although ''A. fumigatus'' occurs in areas with widely different climates and environments, it displays low genetic variation and a lack of population genetic differentiation on a global s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Printed Circuit Board
A printed circuit board (PCB), also called printed wiring board (PWB), is a Lamination, laminated sandwich structure of electrical conduction, conductive and Insulator (electricity), insulating layers, each with a pattern of traces, planes and other features (similar to wires on a flat surface) Chemical milling, etched from one or more sheet layers of copper laminated onto or between sheet layers of a non-conductive substrate. PCBs are used to connect or Electrical wiring, "wire" Electronic component, components to one another in an electronic circuit. Electrical components may be fixed to conductive pads on the outer layers, generally by soldering, which both electrically connects and mechanically fastens the components to the board. Another manufacturing process adds Via (electronics), vias, metal-lined drilled holes that enable electrical interconnections between conductive layers, to boards with more than a single side. Printed circuit boards are used in nearly all e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deinococcus Radiodurans
''Deinococcus radiodurans'' is a bacterium, an extremophile and one of the most radiation-resistant organisms known. It can survive cold, dehydration, vacuum, and acid, and therefore is known as a polyextremophile. ''The Guinness Book Of World Records'' listed it in January 1998 as the world's most radiation-resistant bacterium or lifeform. Several bacteria of comparable radioresistance are known, including some species of the genus '' Chroococcidiopsis'' (phylum cyanobacteria) and some species of '' Rubrobacter'' (phylum Actinomycetota); among the archaea, the species '' Thermococcus gammatolerans'' shows comparable radioresistance. Name and classification The name ''Deinococcus radiodurans'' derives from the Ancient Greek δεινός () and κόκκος () meaning "terrible grain/berry" and the Latin and , meaning "radiation-surviving". The species was formerly called ''Micrococcus radiodurans''. As a consequence of its hardiness, it has been nicknamed “Conan the Bacteri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Actinobacteria
The Actinomycetota (or Actinobacteria) are a diverse phylum of Gram-positive bacteria with high GC content. They can be terrestrial or aquatic. They are of great importance to land flora because of their contributions to soil systems. In soil they help to decompose the organic matter of dead organisms so the molecules can be taken up anew by plants. While this role is also played by fungi, Actinomycetota are much smaller and likely do not occupy the same ecological niche. In this role the colonies often grow extensive mycelia, as fungi do, and the name of an important order of the phylum, Actinomycetales (the actinomycetes), reflects that they were long believed to be fungi. Some soil actinomycetota (such as '' Frankia'') live symbiotically with the plants whose roots pervade the soil, fixing nitrogen for the plants in exchange for access to some of the plant's saccharides. Other species, such as many members of the genus ''Mycobacterium'', are important pathogens. Beyond the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyanobacteria
Cyanobacteria ( ) are a group of autotrophic gram-negative bacteria that can obtain biological energy via oxygenic photosynthesis. The name "cyanobacteria" () refers to their bluish green (cyan) color, which forms the basis of cyanobacteria's informal common name, blue-green algae. Cyanobacteria are probably the most numerous taxon to have ever existed on Earth and the first organisms known to have produced oxygen, having appeared in the middle Archean eon and apparently originated in a freshwater or terrestrial environment. Their photopigments can absorb the red- and blue-spectrum frequencies of sunlight (thus reflecting a greenish color) to split water molecules into hydrogen ions and oxygen. The hydrogen ions are used to react with carbon dioxide to produce complex organic compounds such as carbohydrates (a process known as carbon fixation), and the oxygen is released as a byproduct. By continuously producing and releasing oxygen over billions of years, cyanobacte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
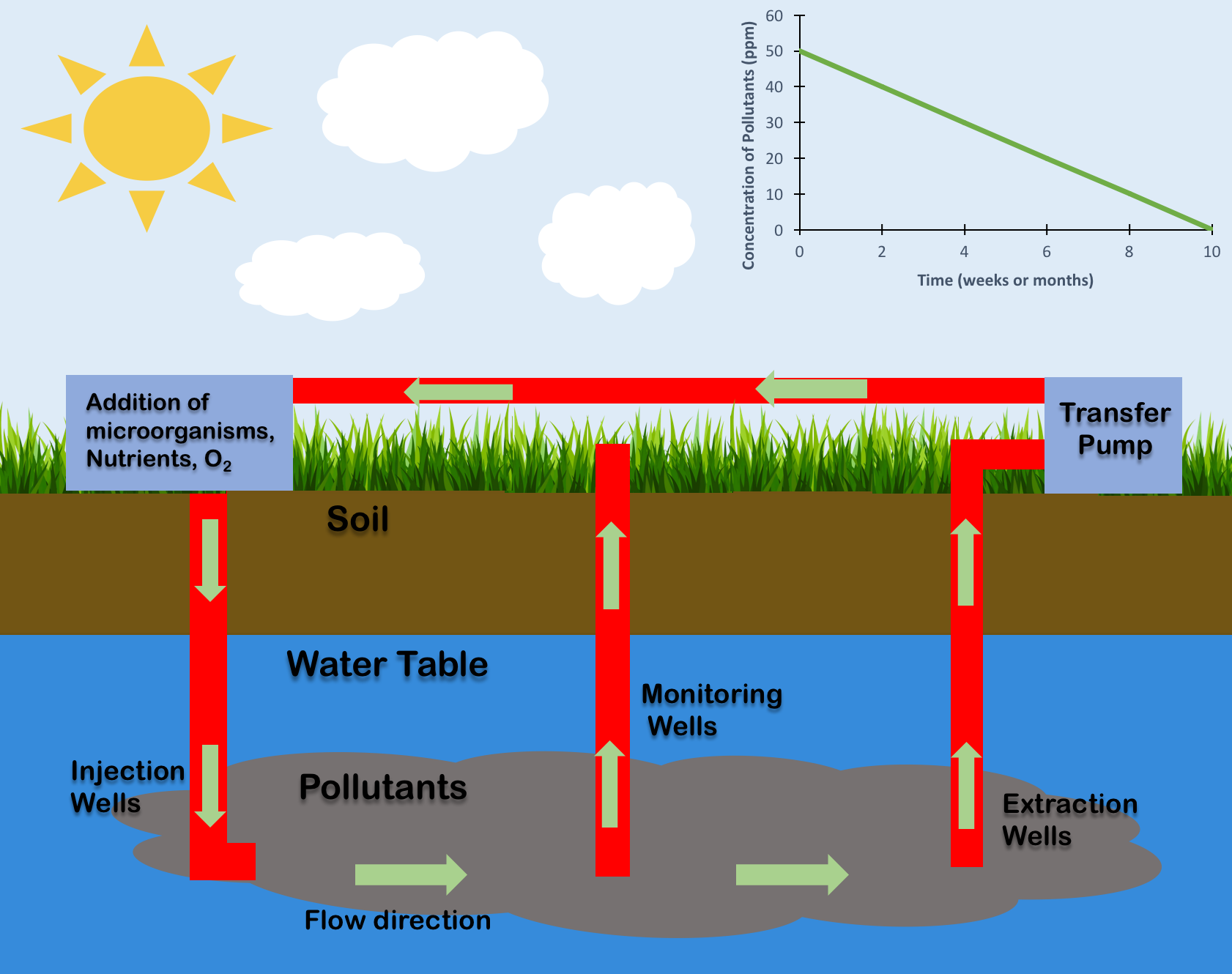
Bioremediation
Bioremediation broadly refers to any process wherein a biological system (typically bacteria, microalgae, fungi in mycoremediation, and plants in phytoremediation), living or dead, is employed for removing environmental pollutants from air, water, soil, fuel gasses, industrial effluents etc., in natural or artificial settings. The natural ability of organisms to adsorb, accumulate, and degrade common and emerging pollutants has attracted the use of biological resources in treatment of contaminated environment. In comparison to conventional physicochemical treatment methods bioremediation may offer advantages as it aims to be sustainable, eco-friendly, cheap, and scalable. This technology is rarely implemented however because it is slow or inefficient. Most bioremediation is inadvertent, involving native organisms. Research on bioremediation is heavily focused on stimulating the process by inoculation of a polluted site with organisms or supplying nutrients to promote their growt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biodegradation
Biodegradation is the breakdown of organic matter by microorganisms, such as bacteria and fungi. It is generally assumed to be a natural process, which differentiates it from composting. Composting is a human-driven process in which biodegradation occurs under a specific set of circumstances. The process of biodegradation is threefold: first an object undergoes biodeterioration, which is the mechanical weakening of its structure; then follows biofragmentation, which is the breakdown of materials by microorganisms; and finally assimilation, which is the incorporation of the old material into new cells. In practice, almost all chemical compounds and materials are subject to biodegradation, the key element being time. Things like vegetables may degrade within days, while glass and some plastics take many millennia to decompose. A standard for biodegradability used by the European Union is that greater than 90% of the original material must be converted into , water and minerals b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |