|
Extravasation (intravenous)
Extravasation is the leakage of intravenously (IV) infused, and potentially damaging, medications into the extravascular tissue around the site of infusion. The leakage can occur through brittle veins in the elderly, through previous venipuncture access, or through direct leakage from wrongly positioned venous access devices. When the leakage is not of harmful consequence it is known as infiltration. Extravasation of medication during intravenous therapy is an adverse event related to therapy that, depending on the medication, amount of exposure, and location, can potentially cause serious injury and permanent harm, such as tissue necrosis. Milder consequences of extravasation include irritation, characterized by symptoms of pain and inflammation, with the clinical signs of warmth, erythema (redness), or tenderness. Medications Complications related to extravasation are possible with any medication. Since vesicants are blistering agents, extravasation may lead to irreversible ti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toxicology
Toxicology is a scientific discipline, overlapping with biology, chemistry, pharmacology, and medicine, that involves the study of the adverse effects of chemical substances on living organisms and the practice of diagnosing and treating exposures to toxins and toxicants. The relationship between dose and its effects on the exposed organism is of high significance in toxicology. Factors that influence chemical toxicity include the dosage, duration of exposure (whether it is acute or chronic), route of exposure, species, age, sex, and environment. Toxicologists are experts on poisons and poisoning. There is a movement for evidence-based toxicology as part of the larger movement towards evidence-based practices. Toxicology is currently contributing to the field of cancer research, since some toxins can be used as drugs for killing tumor cells. One prime example of this is ribosome-inactivating proteins, tested in the treatment of leukemia. The word ''toxicology'' () ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
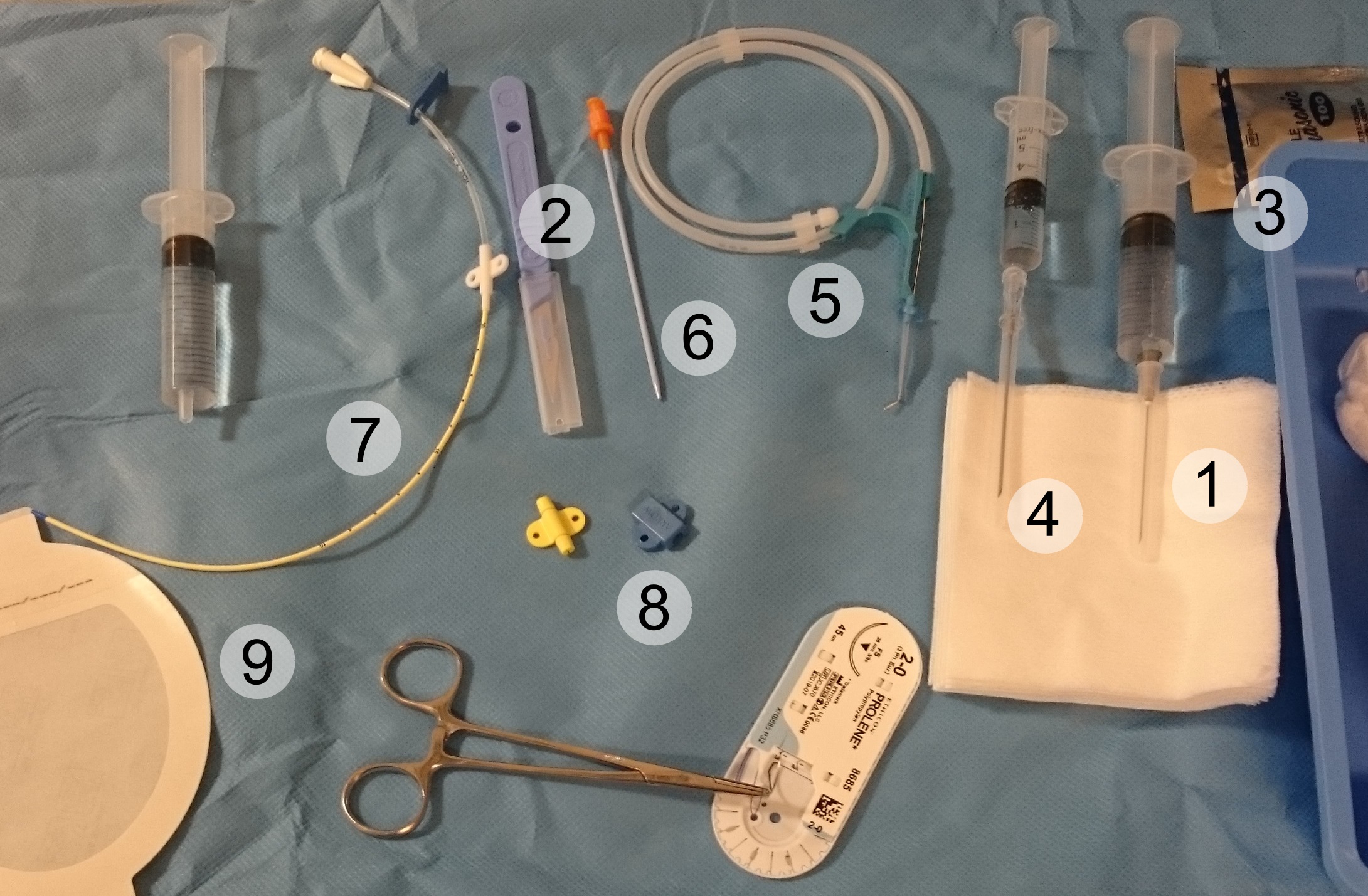
Central Venous Catheter
A central venous catheter (CVC), also known as a central line (c-line), central venous line, or central venous access catheter, is a catheter placed into a large vein. It is a form of venous access. Placement of larger catheters in more centrally located veins is often needed in critically ill patients, or in those requiring prolonged intravenous therapies, for more reliable vascular access. These catheters are commonly placed in veins in the neck (internal jugular vein), chest (subclavian vein or axillary vein), groin (femoral vein), or through veins in the arms (also known as a PICC line, or peripherally inserted central catheters). Central lines are used to administer medication or fluids that are unable to be taken by mouth or would harm a smaller peripheral vein, obtain blood tests (specifically the "central venous oxygen saturation"), administer fluid or blood products for large volume resuscitation, and measure central venous pressure. The catheters used are commonl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paclitaxel
Paclitaxel, sold under the brand name Taxol among others, is a chemotherapy medication used to treat ovarian cancer, esophageal cancer, breast cancer, lung cancer, Kaposi's sarcoma, cervical cancer, and pancreatic cancer. It is administered by intravenous injection. There is also an albumin-bound formulation. Common side effects include hair loss, bone marrow suppression, numbness, allergic reactions, muscle pains, and diarrhea. Other side effects include heart problems, increased risk of infection, and lung inflammation. There are concerns that use during pregnancy may cause birth defects. Paclitaxel is in the taxane family of medications. It works by interference with the normal function of microtubules during cell division. Paclitaxel was isolated in 1971 from the Pacific yew and approved for medical use in 1993. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. It has been made from precursors, and through cell culture. Medical use Paclitaxel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxaliplatin
Oxaliplatin, sold under the brand name Eloxatin among others, is a cancer medication (platinum-based antineoplastic class) used to treat colorectal cancer. It is given by intravenous, infusion into a vein. Common side effects include paresthesia, numbness, feeling tired, nausea, diarrhea, and cytopenia, low blood cell counts. Other serious side effects include allergic reactions. Use in pregnancy is known to harm the baby. Oxaliplatin is in the platinum-based antineoplastic family of medications. It is believed to work by blocking the duplication of DNA. Oxaliplatin was patented in 1976 in Japan and approved for medical use in 1996 in Europe. It is on the 2023 WHO Model List of Essential Medicines, World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. Medical uses Oxaliplatin is used for treatment of colorectal cancer, typically along with folinic acid (leucovorin) and fluorouracil in a combination known as FOLFOX or along with capecitabine in a combination known as CA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mitoxantrone
Mitoxantrone (INN, BAN, USAN; also known as Mitozantrone in Australia; trade name Novantrone) is an anthracenedione antineoplastic agent. Uses Mitoxantrone is used to treat certain types of cancer, mostly acute myeloid leukemia. It improves the survival rate of children suffering from acute lymphoblastic leukemia relapse. The combination of mitoxantrone and prednisone is approved as a second-line treatment for metastatic hormone-refractory prostate cancer. This combination was once the first line of treatment; however, a combination of docetaxel and prednisone improves survival rates and lengthens the disease-free period. Mitoxantrone is also used to treat multiple sclerosis (MS), most notably the subset of the disease known as secondary-progressive MS. In the absence of a cure, mitoxantrone is effective in slowing the progression of secondary-progressive MS and extending the time between relapses in both relapsing-remitting MS and progressive-relapsing MS. Side effects Mit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mitomycin C
Mitomycin C is a mitomycin that is used as a chemotherapy, chemotherapeutic agent by virtue of its antitumour activity. Medical uses It is given intravenously to treat upper gastro-intestinal cancers (e.g. esophageal carcinoma), anal cancers, and breast cancers, as well as by bladder Drug instillation, instillation for superficial bladder cancer, bladder tumours. It is given via intravesical administration for non-muscle invasive bladder cancer. Mitomycin C is also used topically rather than intravenously for eye surgery. Mitomycin C is applied topically to prevent scarring during glaucoma filtering surgery and to prevent haze after photorefractive keratectomy (PRK) or LASIK; mitomycin C has also been shown to reduce fibrosis in strabismus surgery. In April 2020, mitomycin gel, sold under the brand name Jelmyto, was approved in the United States for the treatment of low-grade upper tract urothelial cancer. Urothelial cancer is a cancer of the lining of the urinary system ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mechlorethamine
Chlormethine ( INN, BAN), also known as mechlorethamine ( USAN, USP), mustine, HN2, and (in post-Soviet states) embikhin (эмбихин), is a nitrogen mustard sold under the brand name Mustargen among others. It is the prototype of alkylating agents, a group of anticancer chemotherapeutic drugs. It works by binding to DNA, crosslinking two strands and preventing cell duplication. It binds to the N7 nitrogen on the DNA base guanine. As the chemical is a blister agent, its use is strongly restricted within the Chemical Weapons Convention where it is classified as a Schedule 1 substance. Mechlorethamine belongs to the group of nitrogen mustard alkylating agents. Uses It has been derivatized into the estrogen analogue estramustine phosphate, used to treat prostate cancer. It can also be used in chemical warfare where it has the code-name HN2. This chemical is a form of nitrogen mustard gas and a powerful vesicant. Historically, some uses of mechlorethamine have included lymp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Idarubicin
Idarubicin or 4-demethoxydaunorubicin is an anthracycline antileukemic drug. It inserts itself into DNA and prevents DNA unwinding by interfering with the enzyme topoisomerase II. It is an analog of daunorubicin, but the absence of a methoxy group increases its fat solubility and cellular uptake. Similar to other anthracyclines, it also induces histone eviction from chromatin. It belongs to the family of drugs called antitumor antibiotics. It is currently combined with cytosine arabinoside as a first line treatment of acute myeloid leukemia. It is used for treatment of acute lymphoblastic leukemia and chronic myelogenous leukemia in blast crisis. It is distributed under the trade names Zavedos (UK) and Idamycin (USA). Side effects Diarrhea, stomach cramps, nausea and vomiting Vomiting (also known as emesis, puking and throwing up) is the forceful expulsion of the contents of one's stomach through the mouth and sometimes the nose. Vomiting can be the result of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epirubicin
Epirubicin is an anthracycline drug used for chemotherapy. It can be used in combination with other medications to treat breast cancer in patients who have had surgery to remove the tumor. It is marketed by Pfizer under the trade name Ellence in the US and Pharmorubicin or Epirubicin Ebewe elsewhere. Similarly to other anthracyclines, epirubicin acts by intercalating DNA strands. Intercalation results in complex formation which inhibits DNA and RNA synthesis. It also triggers DNA cleavage by topoisomerase II, resulting in mechanisms that lead to cell death. Binding to cell membranes and plasma proteins may be involved in the compound's cytotoxic effects. Epirubicin also generates free radicals that cause cell and DNA damage. Epirubicin is favoured over doxorubicin, the most popular anthracycline, in some chemotherapy regimens as it appears to cause fewer side-effects. Epirubicin has a different spatial orientation of the hydroxyl group at the 4' carbon of the sugar - it has th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doxorubicin
Doxorubicin, sold under the brand name Adriamycin among others, is a chemotherapy medication used to treat cancer. This includes breast cancer, bladder cancer, Kaposi's sarcoma, lymphoma, and acute lymphocytic leukemia. It is often used together with other chemotherapy agents. Doxorubicin is given by injection into a vein. Common side effects include hair loss, bone marrow suppression, vomiting, rash, and inflammation of the mouth. Other serious side effects may include allergic reactions such as anaphylaxis, heart damage, tissue damage at the site of injection, radiation recall, and treatment-related leukemia. People often experience red discoloration of the urine for a few days. Doxorubicin is in the anthracycline and antitumor antibiotic family of medications. It works in part by interfering with the function of DNA. Doxorubicin was approved for medical use in the United States in 1974. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. Version ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Docetaxel
Docetaxel (DTX or DXL), sold under the brand name Taxotere among others, is a chemotherapy medication used to treat a number of types of cancer. This includes breast cancer, head and neck cancer, stomach cancer, prostate cancer and non-small-cell lung cancer. It may be used by itself or along with other chemotherapy medication. It is given by intravenous infusion, slow injection into a vein. Common side effects include hair loss, cytopenia (low blood cell counts), numbness, shortness of breath, Chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting, nausea, vomiting, and muscle pains. Other severe side effects include allergic reactions and future cancers. Docetaxel induced pneumotoxicity is also a well recognized adverse effect which has to be identified timely and treated after withholding the drug. Side effects are more common in people with liver problems. Use during pregnancy may harm the baby. Docetaxel is in the taxane family of medications. It works by disrupting the normal function o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daunorubicin
Daunorubicin, also known as daunomycin, is a chemotherapy medication used to treat cancer. Specifically it is used for acute myeloid leukemia (AML), acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML), and Kaposi's sarcoma. It is administered by injection into a vein. A liposomal formulation known as liposomal daunorubicin also exists. Common side effects include hair loss, vomiting, bone marrow suppression, and inflammation of the inside of the mouth. Other severe side effects include heart disease and tissue death at the site of injection. Use in pregnancy may harm the fetus. Daunorubicin is in the anthracycline family of medication. It works in part by blocking the function of topoisomerase II. Daunorubicin was approved for medical use in the United States in 1979. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. It was originally isolated from bacteria of the ''Streptomyces'' type. Medical uses It slows or stops the growth of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |