|
Exarchate Of Ravenna
The Exarchate of Ravenna (; ), also known as the Exarchate of Italy, was an administrative district of the Byzantine Empire comprising, between the 6th and 8th centuries, the territories under the jurisdiction of the exarch of Italy (''exarchus Italiae'') resident in Ravenna. The term is used in historiography in a double sense: "exarchate" in the strict sense denotes the territory under the direct jurisdiction of the exarch, i.e. the area of the capital Ravenna, but the term is mainly used to designate all the Byzantine territories in continental and peninsular Italy. According to the legal sources of the time, these territories constituted the so-called ''Provincia Italiae'', on the basis of the fact that they too, until at least the end of the 7th century, fell under the jurisdiction of the exarch and were governed by ''duces'' or ''magistri militum'' under him. The exarchate was established around 584, the year in which the presence of an exarch in Ravenna is attested for th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exarch
An exarch (; from Ancient Greek ἔξαρχος ''exarchos'') was the holder of any of various historical offices, some of them being political or military and others being ecclesiastical. In the late Roman Empire and early Byzantine Empire, an ''exarch'' was a governor of a particular territory. From the end of the 3rd century or early 4th, every Roman diocese was governed by a vicarius, who was titled "exarch" in eastern parts of the Empire, where the Greek language and the use of Greek terminology dominated, even though Latin was the language of the imperial administration from the provincial level up until the 440s (Greek translations were sent out with the official Latin text). In Greek texts, the Latin title is spelled βικάριος (). The office of exarch as a governor with extended political and military authority was later created in the Byzantine Empire, with jurisdiction over a particular territory, usually a frontier region at some distance from the capital Co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
5th Century
The 5th century is the time period from AD 401 (represented by the Roman numerals CDI) through AD 500 (D) in accordance with the Julian calendar. The 5th century is noted for being a period of migration and political instability throughout Eurasia. It saw the collapse of the Western Roman Empire, which came to a formal end in 476 AD. This empire had been ruled by a succession of weak emperors, with the real political might being increasingly concentrated among military leaders. Internal instability allowed a Visigoth army to reach and ransack Rome in 410. Some recovery took place during the following decades, but the Western Empire received another serious blow when a second foreign group, the Vandals, occupied Carthage, capital of an extremely important province in Africa. Attempts to retake the province were interrupted by the invasion of the Huns under Attila. After Attila's defeat, both Eastern and Western empires joined forces for a final assault on Vandal North Africa, bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
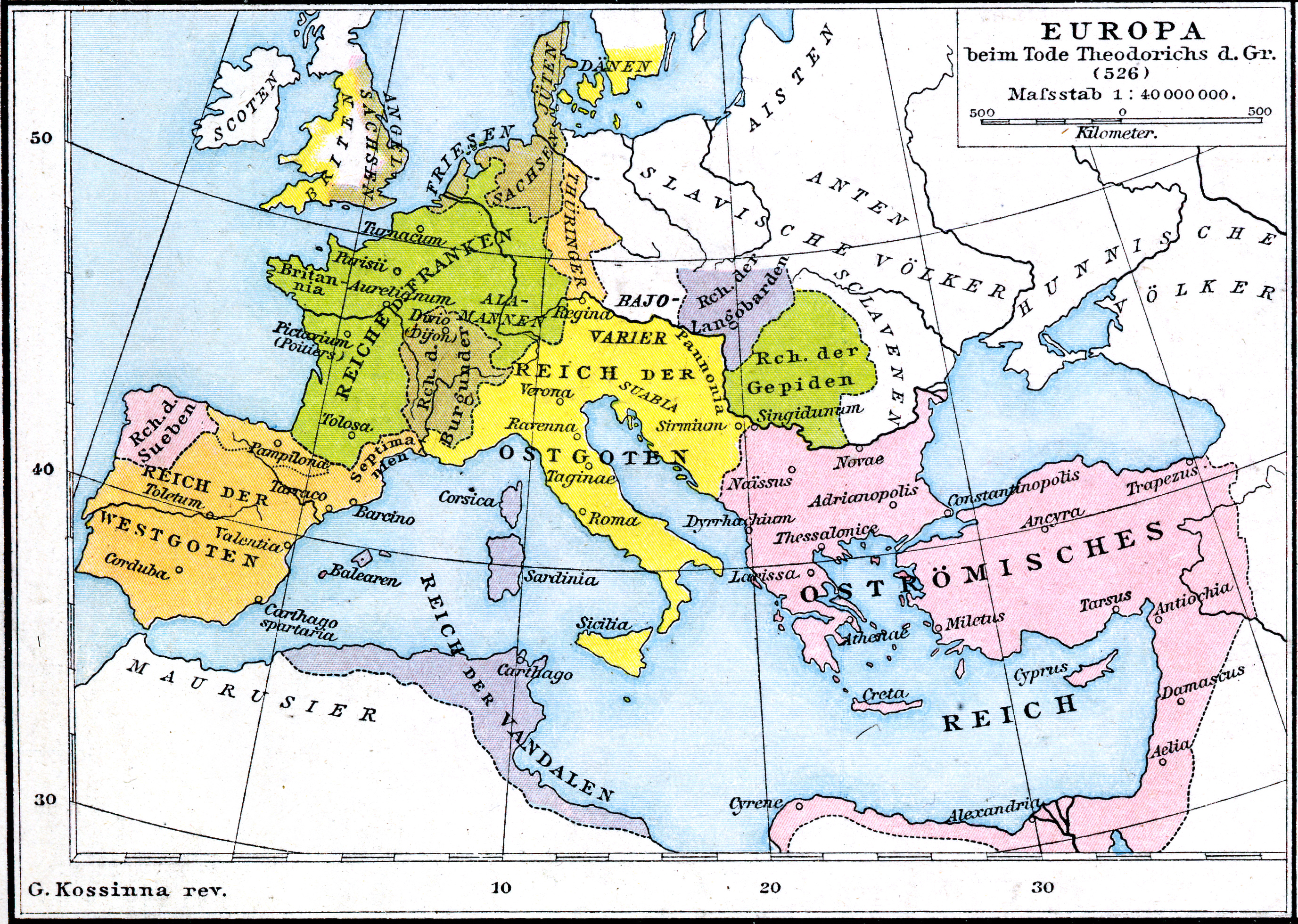
Ostrogothic Kingdom
The Ostrogothic Kingdom, officially the Kingdom of Italy (), was a barbarian kingdom established by the Germanic Ostrogoths that controlled Italian peninsula, Italy and neighbouring areas between 493 and 553. Led by Theodoric the Great, the Ostrogoths killed Odoacer, a Germanic soldier and erstwhile leader of the . Odoacer had previously become the ''de facto'' Kingdom of Odoacer, ruler of Italy following his deposition of Romulus Augustulus, the final emperor of the Western Roman Empire, in 476. Under Theodoric, the Ostrogothic kingdom reached its zenith, stretching from Southern France in the west to Geography of Serbia, Western Serbia in the southeast. Most of the Roman society, social institutions of the Fall of the Western Roman Empire, late Western Roman Empire were preserved during his rule. Theodoric called himself "King of the Goths and Succession of the Roman Empire, Romans" (), demonstrating his desire to be a leader for both peoples. Under Justinian I, the Byzantine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theodoric The Great
Theodoric (or Theoderic) the Great (454 – 30 August 526), also called Theodoric the Amal, was king of the Ostrogoths (475–526), and ruler of the independent Ostrogothic Kingdom of Italy between 493 and 526, regent of the Visigoths (511–526), and a patrician (ancient Rome)#Late Roman and Byzantine period, patrician of the Byzantine Empire#Loss of the Western Roman Empire, Eastern Roman Empire. As ruler of the combined Gothic realms, Theodoric controlled an empire stretching from the Atlantic Ocean to the Adriatic Sea. Though Theodoric himself only used the title 'king' (''rex''), some scholars characterize him as a Roman Emperor#Later assertions to the title, Western Roman emperor in all but name, since he ruled a large part of the former Western Roman Empire described as a ''Res Publica'', had received the former Western imperial regalia from Constantinople in 497 which he used, was referred to by the imperial title ''princeps'' by the Italian aristocracy and exercised imper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ostrogoths
The Ostrogoths () were a Roman-era Germanic peoples, Germanic people. In the 5th century, they followed the Visigoths in creating one of the two great Goths, Gothic kingdoms within the Western Roman Empire, drawing upon the large Gothic populations who had settled in the Balkans in the 4th century. While the Visigoths had formed under the leadership of Alaric I, the new Ostrogothic political entity which came to rule Italy was formed in the Balkans under Theodoric the Great. Theoderic's family, the Amal dynasty, accumulated royal power in Roman Pannonia after the death of Attila, and collapse of his Hunnic empire. Byzantine Empire, Byzantine Zeno (emperor), Emperor Zeno played these Pannonian Goths off against the Thracian Goths to their south. However, instead the two groups united after the death of the Thracian leader Theoderic Strabo and his son Recitach. Zeno then backed Theodoric to invade Italy and replace Odoacer there, whom he had previously supported as its king. In 493, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Romulus Augustulus
Romulus Augustus (after 511), nicknamed Augustulus, was Roman emperor of the Western Roman Empire, West from 31 October 475 until 4 September 476. Romulus was placed on the imperial throne while still a minor by his father Orestes (father of Romulus Augustulus), Orestes, the , for whom he served as little more than a figurehead. After a rule of ten months, the barbarian general Odoacer defeated and killed Orestes and deposed Romulus. As Odoacer did not proclaim any successor, Romulus is typically regarded as the last Western Roman emperor, his deposition marking the Fall of the Western Roman Empire, end of the Western Roman Empire as a political entity. The deposition of Romulus Augustulus is also sometimes used by historians to mark the transition from Classical antiquity, antiquity to the medieval period. Very few records survive of Romulus's reign. There are no known policies, laws or inscriptions of significance of the emperor, which leaves the impression that he was a shado ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turcilingi
The Turcilingi (also spelled Torcilingi or Thorcilingi) were an obscure barbarian people, or possibly a clan or dynasty, who appear in historical sources relating to Middle Danubian peoples who were present in Italy during the reign of Romulus Augustulus (475–76). Their only known leader was Odoacer (Odovacar), but he was described as a ruler of several ethnic groups. Although various origins have been proposed including Hunnic, recent research favors the idea that the Turcilingi might be identical to the Thuringii, who are first mentioned in association with a type of horse, and became politically important only long after the fall of Odoacar. Primary sources The Turcilingi are mentioned in only one independent source: they appear three times in the works of Jordanes, twice in his ''Getica'' and once in his '' Romana''. They are also mentioned once in the ''Historia Langobardorum'' of Paul the Deacon in a passage that is a derivative of Jordanes and once in the ''Historia Mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rugii
The Rugii, Rogi or Rugians (), were one of the smaller Germanic peoples of Late Antiquity who are best known for their short-lived 5th-century kingdom upon the Roman frontier, near present-day Krems an der Donau in Austria. This kingdom, like those of the neighbouring Heruli and Sciri, first appears in records after the death of Attila in 453. The Rugii, Heruli, Sciri and others are believed to have moved into this region from distant homelands under pressure from the Huns, and become part of Attila's Hunnic empire which also moved and came to be based in this region. The Rugii were subsequently part of the alliance which defeated Attila's sons and the Ostrogoths at the Battle of Nedao in 454, giving their kingdom independence. In 469 they were part of a similar alliance who lost to the Ostrogoths at the Battle of Bolia, weakening their kingdom significantly. Many Rugii, once again along with Sciri, Heruli and other Danubians, joined Odoacer in Italy and became part of his k ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sciri
The Sciri, or Scirians, were a Germanic people. They are believed to have spoken an East Germanic language. Their name probably means "the pure ones". The Sciri were mentioned already in the late 3rd century BC as participants in a raid on the city of Olbia (Pontic), Olbia near modern-day Odesa. In the late 4th century they lived somewhere north of the Black Sea and Lower Danube in the vicinity of the Goths. By the early 5th century, the Sciri had been subdued by the Huns, whom they fought under at the Battle of the Catalaunian Plains in 451 AD. After the death of Attila, the Sciri broke free from Hunnic rule at the Battle of Nedao in 454 AD. They subsequently were recorded holding their own kingdom north of the Middle Danube, under the leadership of Edeko and his son Onoulphus. After the destruction of this kingdom by the Ostrogoths in the late 460s AD, Odoacer, another son of Edeko, attained high status within the Roman army in Italy, ruling Sciri, Rugii and other non-Roman pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heruli
The Heruli (also Eluri, Eruli, Herules, Herulians) were one of the smaller Germanic peoples of Late Antiquity, known from records in the third to sixth centuries AD. The best recorded group of Heruli established a kingdom north of the Middle Danube, probably including the area north of present day Vienna. This kingdom was a neighbour to several other small and short-lived kingdoms in the late 5th century AD and early 6th century, including those of the Sciri, Rugii, Danubian Suebi, and Gepids. After the conquest of this Heruli kingdom by the Lombards in 508, splinter groups moved to Sweden, Ostrogothic Italy, and present-day Serbia, which was under Eastern Roman control. The Danubian Heruli are generally equated to the "Elouri" who lived near the Sea of Azov during the late 3rd or early 4th century, and are believed to have migrated westwards. In 267-270 these Elouri took part together with Goths and other eastern European peoples in two massive raids into Roman provinces in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Odoacer
Odoacer ( – 15 March 493 AD), also spelled Odovacer or Odovacar, was a barbarian soldier and statesman from the Middle Danube who deposed the Western Roman child emperor Romulus Augustulus and became the ruler of Italy (476–493). Odoacer's overthrow of Romulus Augustulus is traditionally understood as marking the end of the Western Roman Empire. Although he held power over Italy, he also represented himself as the client of the Eastern Roman Emperor in Constantinople, Zeno. He was referred to not only as a king (), but also as commander (), or using the Roman honorific patrician, granted by Zeno. Odoacer himself used the title of king in the only surviving official document that emanated from his chancery, and it was also used by the consul Basilius. He had the support of the Roman Senate and was able to distribute land to his followers without much opposition. Unrest among his soldiers led to violence in 477–478, but no such disturbances occurred during the later p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Milan
Milan ( , , ; ) is a city in northern Italy, regional capital of Lombardy, the largest city in Italy by urban area and the List of cities in Italy, second-most-populous city proper in Italy after Rome. The city proper has a population of nearly 1.4 million, while its Metropolitan City of Milan, metropolitan city has 3.2 million residents. Within Europe, Milan is the fourth-most-populous List of urban areas in the European Union, urban area of the EU with 6.17 million inhabitants. According to national sources, the population within the wider Milan metropolitan area (also known as Greater Milan) is estimated between 7.5 million and 8.2 million, making it by far the List of metropolitan areas of Italy, largest metropolitan area in Italy and List of metropolitan areas in Europe, one of the largest in the EU.* * * * Milan is the economic capital of Italy, one of the economic capitals of Europe and a global centre for business, fashion and finance. Milan is reco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |