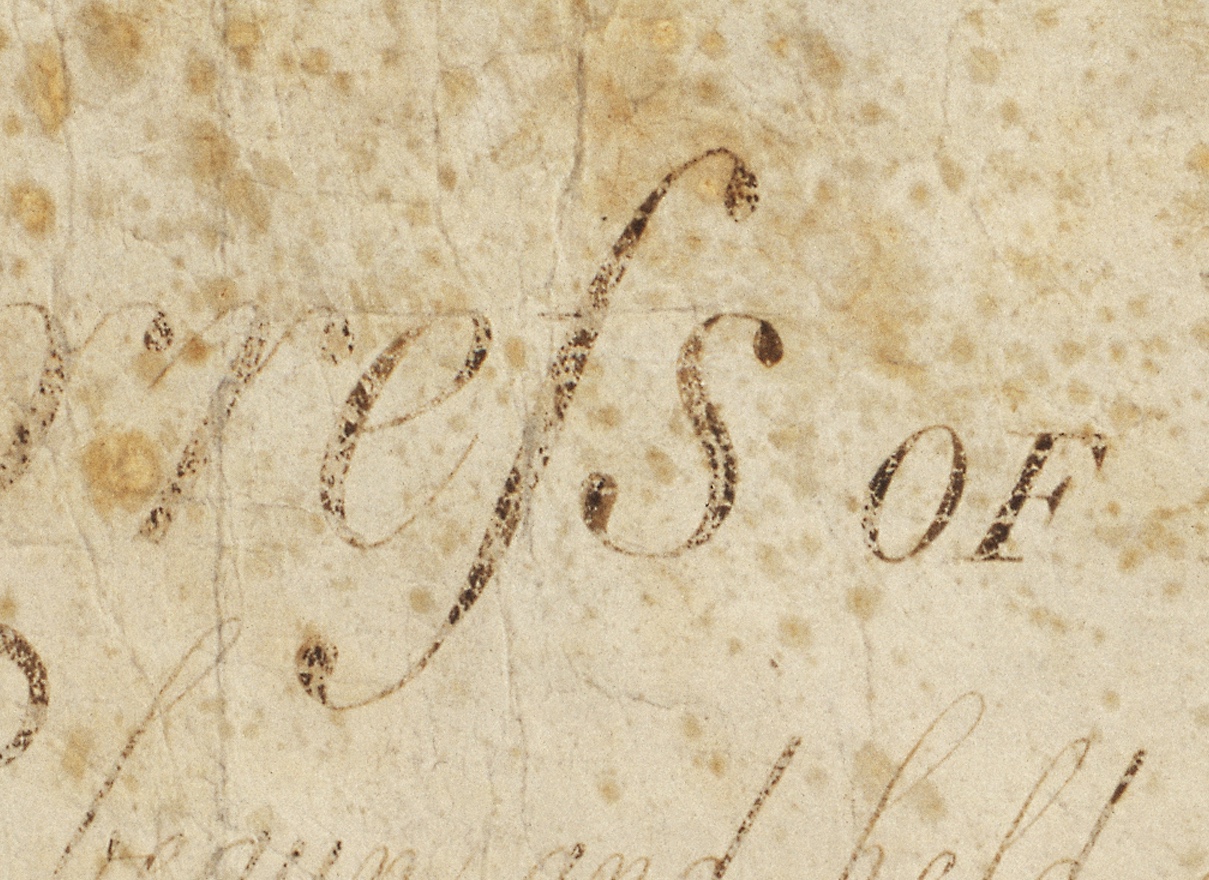|
Etymology Of Assam
Though the precise Etymology of Assam, a state in India is unclear—there is general agreement that it is related to the Ahom people."Ahoms also gave Assam and its language their name (''Ahom'' and the modern ''ɒχɒm'' 'Assam' come from an attested earlier form ''asam'', ''acam'', probably from a Burmese corruption of the word ''Shan/Shyam'', cf. ''Siam'': Kakati 1962; 1-4)." Whatever the source of the English name, ''Assam'' is itself an anglicization. Scholarly views John Peter Wade (1805) called the Ahom kingdom, that commenced on the Konder Chokey, "Kingdom of Assam"."The Kingdom of Assam, where it is entered from Bengal, commences on the north of the Berhampooter, at the Khonder Chokey, nearly opposite to the picturesque estate of the late Mr Raush at Goalpara; and at the Nagrabaree Hill on the South", Wade, Dr John Peter, (1805)A Geographical Sketch of Assam in Asiatic Annual Register, reprinted Some have speculated that the Bodo word "Ha-com" meaning low land was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Etymology
Etymology ( ) is the study of the origin and evolution of words—including their constituent units of sound and meaning—across time. In the 21st century a subfield within linguistics, etymology has become a more rigorously scientific study. Most directly tied to historical linguistics, philology, and semiotics, it additionally draws upon comparative semantics, morphology, pragmatics, and phonetics in order to attempt a comprehensive and chronological catalogue of all meanings and changes that a word (and its related parts) carries throughout its history. The origin of any particular word is also known as its ''etymology''. For languages with a long written history, etymologists make use of texts, particularly texts about the language itself, to gather knowledge about how words were used during earlier periods, how they developed in meaning and form, or when and how they entered the language. Etymologists also apply the methods of comparative linguistics to reconstruct in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Srimanta Sankardeva
Srimanta Sankardev (, ; 1449–1568) was a 15th–16th century Assamese polymath; a saint-scholar, poet, playwright, dancer, actor, musician, artist social-religious reformer and a figure of importance in the cultural and religious history of the Bhakti movement in Assam. He is credited with building on past cultural relics and devising new forms of music ( Borgeet), theatrical performance ( Ankia Naat, Bhaona), dance ( Sattriya), literary language ( Brajavali). Besides, he has left a literary oeuvre of trans-created scriptures ( Bhagavat of Sankardev), poetry and theological works written in Sanskrit, Assamese and Brajavali. The Bhagavatic religious movement he started, Ekasarana Dharma and also called Neo-Vaishnavite movement, influenced two medieval kingdoms – Koch and the Ahom kingdom – and the assembly of devotees he initiated evolved over time into monastic centers called Sattras, which continue to be important socio-religious institutions in Assam and to a l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaty Of Yandabo
The Treaty of Yandabo ( ) was the peace treaty that ended the First Anglo-Burmese War. The treaty was signed on 24February 1826, nearly two years after the war formally broke out on 5March 1824, by General Sir Archibald Campbell on the British side, and the Governor of Legaing Maha Min Hla Kyaw Htin from the Burmese side, without any due permission and consent of the Ahom kingdom, Kachari kingdom or the other territories covered in the treaty. With the British army at Yandabo village, only from the capital Ava, the Burmese were forced to accept the British terms without discussion. According to the treaty, the Burmese agreed to: * Cede to the British- Assam, Manipur, Rakhine (Arakan), and the Tanintharyi (Tenasserim) coast. * Cease all interference in Cachar region of Assam and the Jaintia Hills district. * Pay an indemnity of one million pounds sterling in four installments. * Allow an exchange of diplomatic representatives between Ava and Calcutta. * Sign a commercial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Long S
The long s, , also known as the medial ''s'' or initial ''s'', is an Archaism, archaic form of the lowercase letter , found mostly in works from the late 8th to early 19th centuries. It replaced one or both of the letters ''s'' in a double-''s'' sequence (e.g., "ſinfulneſs" for "sinfulness" and "poſſeſs" or "poſseſs" for "possess", but never "poſſeſſ"). The modern letterform is known as the "short", "terminal", or "round" ''s''. In typography, the long ''s'' is known as a type of swash letter, commonly referred to as a "swash ''s''". The long ''s'' is the basis of the first half of the grapheme of the German alphabet Orthographic ligature, ligature letter , ( or , 'sharp ''s'''). As with other letters, the long ''s'' may have a variant appearance depending on typeface: , , , . Rules English This list of rules for the long ''s'' is not exhaustive, and it applies only to books printed during the 17th to early 19th centuries in English-speaking countries. Similar r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean-Baptiste Tavernier
Jean-Baptiste Tavernier (1605–1689) was a 17th-century French gem merchant and traveler. Tavernier, a private individual and merchant traveling at his own expense, covered, by his own account, 60,000 leagues in making six voyages to Persia and India between the years 1630 and 1668. In 1675, Tavernier, at the behest of his patron Louis XIV, known as the Sun King, published ''Les Six Voyages de Jean-Baptiste Tavernier'' (''Six Voyages'', 1676). Tavernier is best known for his 1666 discovery or purchase of the 116-carat Tavernier Blue diamond that he subsequently sold to Louis XIV of France in 1668 for 120,000 livres, the equivalent of 172,000 ounces of pure gold, and a letter of ennoblement. In 1669, Tavernier purchased for 60,000 livres the Seigneury (fief) of Aubonne, located in the Duchy of Savoy near the city of Geneva, and became Baron of Aubonne. Tavernier's writings show that he was a keen observer and a remarkable cultural anthropologist. His ''Six Voyages'' became ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mir Jumla II
Mir Jumla II (12 February 1591 – 30 March 1663), or Amir Jumla, also known as Ardistānī Mir Muhammad, was a military general, wealthy diamond trader, a ''Vizier'' of Golconda sultanate, and later a prominent subahdar of Bengal under the Mughal Emperor Aurangzeb. Mir Jumla was a powerful politician that played important role in northern and Peninsular region of India during the reign of Shah Jahan to Aurangzeb, where he encountered multiple European nation companies interest in India, such as Danish East India Company, East India Company, Dutch East India Company, and Portuguese East India Company. He commanded the vast merchant fleets enterprise which sailed throughout Surat, Thatta, Rakhine State, Arakan, Ayuthya, Balasore, Aceh, Melaka, Johore, Bantam (city), Bantam, Makassar, Ceylon, Bandar Abbas, Mecca, Jeddah, Basra, Aden, Masqat, Mocha, Yemen, Mocha and the Maldives. The most important aspect of Mir Jumla's rule in Bengal was his Mir Jumla's invasion of Assam, n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Long S
The long s, , also known as the medial ''s'' or initial ''s'', is an Archaism, archaic form of the lowercase letter , found mostly in works from the late 8th to early 19th centuries. It replaced one or both of the letters ''s'' in a double-''s'' sequence (e.g., "ſinfulneſs" for "sinfulness" and "poſſeſs" or "poſseſs" for "possess", but never "poſſeſſ"). The modern letterform is known as the "short", "terminal", or "round" ''s''. In typography, the long ''s'' is known as a type of swash letter, commonly referred to as a "swash ''s''". The long ''s'' is the basis of the first half of the grapheme of the German alphabet Orthographic ligature, ligature letter , ( or , 'sharp ''s'''). As with other letters, the long ''s'' may have a variant appearance depending on typeface: , , , . Rules English This list of rules for the long ''s'' is not exhaustive, and it applies only to books printed during the 17th to early 19th centuries in English-speaking countries. Similar r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ahom Language
Ahom or Tai-Ahom (Ahom:𑜁𑜪𑜨 𑜄𑜩 𑜒𑜑𑜪𑜨 or 𑜁𑜨𑜉𑜫 𑜄𑜩 𑜒𑜑𑜪𑜨; ) is a dormant, Southwestern Tai language formerly spoken by the Ahom people. It's currently undergoing a revival and mainly used in religious and educational purposes. Ahom language was the state language of Ahom kingdom. It was relatively free of both Mon-Khmer and Indo-Aryan influences and has a written tradition dating back to the 13th century. The Ahom people established the Ahom kingdom and ruled parts of the Brahmaputra river valley in the present day Indian state of Assam between the 13th and the 18th centuries. The language was the court language of the kingdom, until it began to be replaced by the Assamese language in the 17th century. Since the early 18th century, there have been no native speakers of the language, though extensive manuscripts in the language still exist today. The tonal system of the language is entirely lost. The language was only par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ahom Script
The Ahom script or Tai Ahom Script is an abugida that is used to write the Ahom language, a dormant Tai language undergoing revival spoken by the Ahom people till the late 18th-century, who established the Ahom kingdom and ruled the eastern part of the Brahmaputra valley between the 13th and the 18th centuries.Diller, A. (1993). Tai Languages. In ''International Encyclopedia of Linguistics'' (Vol. 4, pp. 128-131). Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press. The old Ahom language today survives in the numerous manuscripts written in this script currently in institutional and private possession. History It is believed that the Ahom people adopted their script from either Old Mon or Old Burmese, in Upper Myanmar before migrating to the Brahmaputra Valley in the 13th century. This is supported based on similar shapes of characters between Ahom and Old Mon and Old Burmese scripts. It is clear, however, that the script and language would have changed during the few hundred years it was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bhagavat Of Sankardeva
The Bhagavat of Sankardev is the Assamese adaptation of the Bhagavata Purana made by Srimanta Sankardev in 15th-16th century in the regions that form present-day Assam and Cooch Behar. Though the major portions of the work was transcreated by Sankardev, a few other writers from that period contributed to the remaining sections. This book is revered and forms the central religious text for the followers of Sankardev (Ekasarana Dharma). The text is not a literal translation from the original Sanskrit into the vernacular but it is an adaptation to the local milieu in language and content. Sankardev's transcreation Srimanta Sankardev transcreated the different sections of the original Bhagavata Purana at different times of his life. They are: In the Bara Bhuyan territory # Book VI (''Ajamilopakhayana'' part) # Book VIII (''Amrta-manthana'' part): Sankardev omits the first and the last chapters of the original twenty-four chapters, and narrates four stories from the rest (''Gaje ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Assamese Language
Assamese () or Asamiya ( ) is an Indo-Aryan language spoken mainly in the north-eastern Indian state of Assam, where it is an official language. It has long served as a ''lingua franca'' in parts of Northeast India."Axomiya is the major language spoken in Assam, and serves almost as a lingua franca among the different speech communities in the whole area." It has over 15 million native speakers and 8.3 million second language, second language speakers according to ''Ethnologue''. Nefamese, an Assamese-based pidgin in Arunachal Pradesh, was used as a lingua franca till it was replaced by Hindi language, Hindi; and Nagamese Creole, Nagamese, an Assamese-based Creole language, continues to be widely used in Nagaland. The Kamtapuri language of Rangpur division of Bangladesh and the Cooch Behar district, Cooch Behar and Jalpaiguri district, Jalpaiguri districts of India is linguistically closer to Assamese, though the speakers identify with the Bengali culture and the literary lan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suhungmung
Suhungmung (), or Dihingia Roja was one of the most prominent Ahom Kings who ruled at the cusp of Assam's medieval history. His reign broke from the early Ahom rule and established a multi-ethnic polity in his kingdom. Under him the Ahom Kingdom expanded greatly for the first time since Sukaphaa, at the cost of the Chutia and the Dimasa kingdoms. He also successfully defended his kingdom against Muslim invasions, first by a general called Bar Ujjir and another by Turbak Khan. During his time, the Khen dynasty collapsed and the Koch dynasty ascended in the Kamata kingdom. His general, Ton-kham, pursued the Muslims up to the Karatoya river, the western boundary of the erstwhile Kamarupa Kingdom, the farthest west an Ahom military force had ventured in its entire six hundred years of rule. He was the first Ahom king to adopt a Hindu title, Swarganarayana, indicating a move towards an inclusive polity; and Ahom kings came to be known as the ''Swargadeo'' (literal meani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |