|
Ethylenediaminediacetic Acid
Ethylenediaminediacetic acid (EDDA) is the organic compound with the formula C2H4(NHCH2CO2H)2. It is a derivative of two molecules of glycine, wherein the amines are linked. It is a white solid. It is one of several aminopolycarboxylic acids. The conjugate base is a tetradentate ligand. A representative complex is Na o(EDDA)(CO3){{cite book , volume=18 , author=Leon J. Halloran , author2=Arlene L. Gillie , author3=J. Ivan Legg , title=Inorganic Syntheses , chapter=Ethylenediamine- ''N,N'' ′-Diacetic Acid Complexes of Cobalt(III) , pages=103–111, year=1978, doi=10.1002/9780470132494.ch17, isbn=978-0-470-13249-4 Related compounds *ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA), also called EDTA acid, is an aminopolycarboxylic acid with the formula . This white, slightly water-soluble solid is widely used to bind to iron (Fe2+/Fe3+) and calcium ions (Ca2+), forming water-solubl ... References Chelating agents Dicarboxylic acids Tetradentate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organic Compound
Some chemical authorities define an organic compound as a chemical compound that contains a carbon–hydrogen or carbon–carbon bond; others consider an organic compound to be any chemical compound that contains carbon. For example, carbon-containing compounds such as alkanes (e.g. methane ) and its derivatives are universally considered organic, but many others are sometimes considered inorganic, such as certain compounds of carbon with nitrogen and oxygen (e.g. cyanide ion , hydrogen cyanide , chloroformic acid , carbon dioxide , and carbonate ion ). Due to carbon's ability to catenate (form chains with other carbon atoms), millions of organic compounds are known. The study of the properties, reactions, and syntheses of organic compounds comprise the discipline known as organic chemistry. For historical reasons, a few classes of carbon-containing compounds (e.g., carbonate salts and cyanide salts), along with a few other exceptions (e.g., carbon dioxide, and even ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glycine
Glycine (symbol Gly or G; ) is an amino acid that has a single hydrogen atom as its side chain. It is the simplest stable amino acid. Glycine is one of the proteinogenic amino acids. It is encoded by all the codons starting with GG (GGU, GGC, GGA, GGG). Glycine disrupts the formation of alpha-helices in secondary protein structure. Its small side chain causes it to favor random coils instead. Glycine is also an inhibitory neurotransmitter – interference with its release within the spinal cord (such as during a '' Clostridium tetani'' infection) can cause spastic paralysis due to uninhibited muscle contraction. It is the only achiral proteinogenic amino acid. It can fit into both hydrophilic and hydrophobic environments, due to its minimal side chain of only one hydrogen atom. History and etymology Glycine was discovered in 1820 by French chemist Henri Braconnot when he hydrolyzed gelatin by boiling it with sulfuric acid. He originally called it "sugar of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aminopolycarboxylic Acid
left, 120px, a metal complex with the EDTA anion 120px, Aspartic acid is an aminodicarboxylic acid and precursor to other ligands. An aminopolycarboxylic acid (sometimes abbreviated APCA) is a chemical compound containing one or more nitrogen atoms connected through carbon atoms to two or more carboxyl groups. Aminopolycarboxylates that have lost acidic protons form strong complexes with metal ions. This property makes aminopolycarboxylic acids useful complexone in a wide variety of chemical, medical, and environmental applications. Structure The parent of this family of ligands is the amino acid glycine, H2NCH2COOH, in which the amino group, NH2, is separated from the carboxyl group, COOH by a single methylene group, CH2. When the carboxyl group is deprotonated the glycinate ion can function as a bidentate ligand, binding the metal centre through the nitrogen and one of two carboxylate oxygen atoms, to form chelate complexes of metal ions. Replacement of a hydrogen atom on th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conjugate Base
A conjugate acid, within the Brønsted–Lowry acid–base theory, is a chemical compound formed when an acid gives a proton () to a base—in other words, it is a base with a hydrogen ion added to it, as it loses a hydrogen ion in the reverse reaction. On the other hand, a conjugate base is what remains after an acid has donated a proton during a chemical reaction. Hence, a conjugate base is a substance formed by the removal of a proton from an acid, as it can gain a hydrogen ion in the reverse reaction. Because some acids can give multiple protons, the conjugate base of an acid may itself be acidic. In summary, this can be represented as the following chemical reaction: \text + \text \; \ce \; \text + \text Johannes Nicolaus Brønsted and Martin Lowry introduced the Brønsted–Lowry theory, which said that any compound that can give a proton to another compound is an acid, and the compound that receives the proton is a base. A proton is a subatomic particle in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
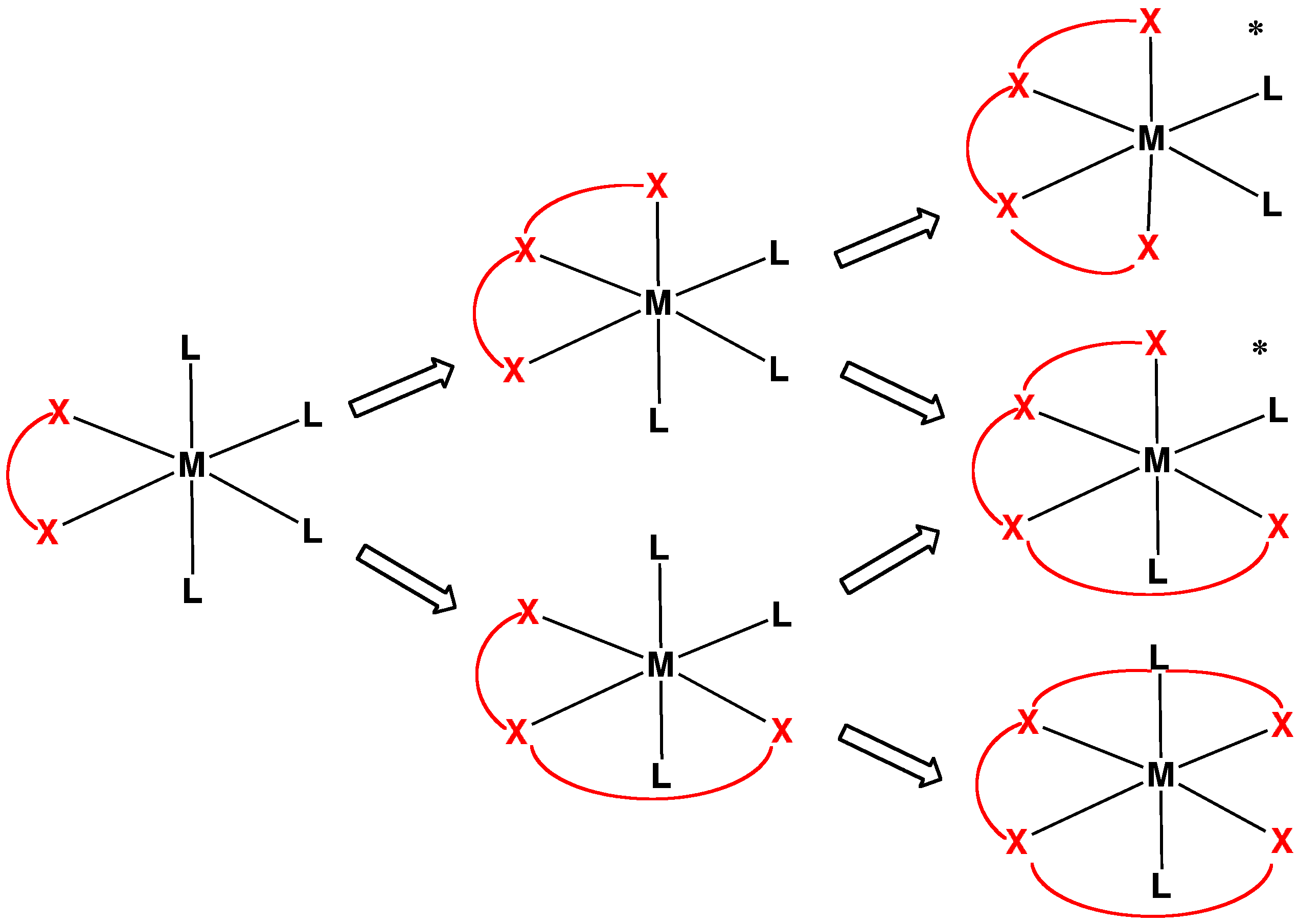
Tetradentate Ligand
In chemistry, tetradentate ligands are ligands that bind four donor atoms to a central atom to form a coordination complex. This number of donor atoms that bind is called denticity and is a method of classifying ligands. Tetradentate ligands are common in nature in the form of chlorophyll, which has a core ligand called chlorin, and heme, which has a core ligand called porphyrin. They are responsible for the colour observed in plants and humans. Phthalocyanine is an artificial macrocyclic tetradentate ligand that is used to make blue and green pigments. Shape Tetradentate ligands can be classified by the topology of the connections between donor atoms. Common forms are linear (also called sequential), ring or tripodal. A tetrapodal ligand that is also tetradentate has four legs with donor atoms and a bridgehead that is not a donor. Upon binding with a central atom, there are several arrangements possible (known as geometric isomers). Linear ligands A linear tetradentate ligand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethylenediaminetetraacetic Acid
Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA), also called EDTA acid, is an aminopolycarboxylic acid with the formula . This white, slightly water-soluble solid is widely used to bind to iron (Fe2+/Fe3+) and calcium ions (Ca2+), forming water-soluble complexes even at neutral pH. It is thus used to dissolve Fe- and Ca-containing scale as well as to deliver iron ions under conditions where its oxides are insoluble. EDTA is available as several salts, notably disodium EDTA, sodium calcium edetate, and tetrasodium EDTA, but these all function similarly. Uses EDTA is widely used in industry. It also has applications in food preservation, medicine, cosmetics, water softening, in laboratories, and other fields. Industrial EDTA is mainly used to sequester (bind or confine) metal ions in aqueous solution. In the textile industry, it prevents metal ion impurities from modifying colours of dyed products. In the pulp and paper industry, EDTA inhibits the ability of metal ions, especiall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chelating Agents
Chelation () is a type of bonding of ions and their molecules to metal ions. It involves the formation or presence of two or more separate coordinate bonds between a polydentate (multiple bonded) ligand and a single central metal atom. These ligands are called chelants, chelators, chelating agents, or sequestering agents. They are usually organic compounds, but this is not a necessity. The word ''chelation'' is derived from Greek χηλή, ''chēlē'', meaning "claw"; the ligands lie around the central atom like the claws of a crab. The term ''chelate'' () was first applied in 1920 by Sir Gilbert T. Morgan and H. D. K. Drew, who stated: "The adjective chelate, derived from the great claw or ''chele'' (Greek) of the crab or other crustaceans, is suggested for the caliperlike groups which function as two associating units and fasten to the central atom so as to produce heterocyclic rings." Chelation is useful in applications such as providing nutritional supplements, in chela ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
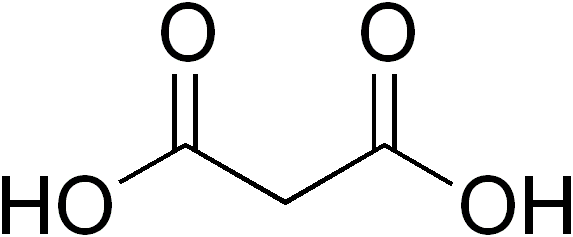
Dicarboxylic Acids
In organic chemistry, a dicarboxylic acid is an organic compound containing two carboxyl groups (). The general molecular formula for dicarboxylic acids can be written as , where R can be aliphatic or Aromatic compound, aromatic.Boy Cornils, Peter Lappe "Dicarboxylic Acids, Aliphatic" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry 2014, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. In general, dicarboxylic acids show similar chemical behavior and reactivity to carboxylic acid, monocarboxylic acids. Dicarboxylic acids are usually colorless solids. A wide variety of dicarboxylic acids are used in industry. Adipic acid, for example, is a precursor to certain kinds of nylon. A wide variety of dicarboxylic acids are found in nature. Aspartic acid and glutamic acid are two amino acids found in all life. Succinic and fumaric acids are essential for metabolism. A large inventory of derivatives are known including many mono- and diesters, amides, etc. Partial list of saturated dicarboxylic acids Some common ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |