|
Ergonovine
Ergonovine, also known as ergometrine and lysergic acid propanolamide, is a medication used to cause contractions of the uterus to treat heavy vaginal bleeding after childbirth. It can be used either by mouth, by injection into a muscle, or injection into a vein. Common side effects include high blood pressure, vomiting, seizures, headache, and low blood pressure. Other serious side effects include ergotism. Ergonovine was discovered in 1932. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. Ergonovine is controlled in some countries because it can be used to make the psychedelic drug lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD). It is also known to produce psychedelic effects itself at high doses. Medical uses Ergonovine has a medical use in obstetrics to facilitate delivery of the placenta and to prevent bleeding after childbirth by causing smooth muscle tissue in the blood vessel walls to narrow, thereby reducing blood flow. It is usually combined with oxytoci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uterotonic
A uterotonic, also known as an oxytocic or ecbolic, is a type of medication used to induce contraction or greater tonicity of the uterus. Uterotonics are used both to induce labor and to reduce postpartum hemorrhage. Labor induction in the third trimester of pregnancy may be required due to medical necessity, or may be desired for social reasons. Generally, labor induction is indicated when the risk of carrying the pregnancy outweighs the risk of delivering. These reason include, but are not limited to, pregnancies that are prolonged, prelabor rupture of the fetal membranes, and concerns about the health and safety of the mother and/or child. There are multiple techniques available to stimulate uterine contractions including mechanical, pharmacological, and alternative medicine methods to initiate contractions prior to spontaneous onset of labor. Postpartum hemorrhage, also known as PPH, is defined as a loss of 500 mL or greater of blood within 24 hours after giving birth. It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psychedelic Drug
Psychedelics are a subclass of hallucinogenic drugs whose primary effect is to trigger non-ordinary mental states (known as psychedelic experiences or "trips") and a perceived "expansion of consciousness". Also referred to as classic hallucinogens or serotonergic hallucinogens, the term ''psychedelic'' is sometimes used more broadly to include various other types of hallucinogens as well, such as those which are atypical or adjacent to psychedelia like salvia and MDMA, respectively. Classic psychedelics generally cause specific psychological, visual, and auditory changes, and oftentimes a substantially altered state of consciousness. They have had the largest influence on science and culture, and include mescaline, LSD, psilocybin, and DMT. There are a large number of both naturally occurring and synthetic serotonergic psychedelics. Most psychedelic drugs fall into one of the three families of chemical compounds: tryptamines, phenethylamines, or lysergamides. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lysergic Acid Diethylamide
Lysergic acid diethylamide, commonly known as LSD (from German ; often referred to as acid or lucy), is a Semisynthesis, semisynthetic, Hallucinogen, hallucinogenic compound derived from ergot, known for its powerful psychological effects and Serotonin, serotonergic activity. It was historically significant in psychiatry and 1960s counterculture; it is currently legally restricted but experiencing renewed scientific interest and increasing use. When taken orally, LSD has an onset of action within 0.4 to 1.0 hours (range: 0.1–1.8 hours) and a duration of effect lasting 7 to 12 hours (range: 4–22 hours). It is commonly administered via tabs of Blotting paper, blotter paper. LSD is extremely potent, with noticeable effects at doses as low as 20 Microgram, micrograms and is sometimes taken in much smaller amounts for microdosing. Yet no fatal human overdoses have been documented. LSD is mainly used recreationally or for spiritual purposes. LSD can cause mystical experiences. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oral Administration
Oral administration is a route of administration whereby a substance is taken through the Human mouth, mouth, swallowed, and then processed via the digestive system. This is a common route of administration for many medications. Oral administration can be easier and less painful than other routes of administration, such as Injection (medicine), injection. However, the onset of action is relatively low, and the effectiveness is reduced if it is not absorbed properly in the digestive system, or if it is broken down by digestive enzymes before it can reach the bloodstream. Some medications may cause gastrointestinal side effects, such as nausea or vomiting, when taken orally. Oral administration can also only be applied to conscious patients, and patients able to swallow. Terminology ''Per os'' (; ''P.O.'') is an adverbial phrase meaning literally from Latin "through the mouth" or "by mouth". The expression is used in medicine to describe a treatment that is taken orally (but not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seizure
A seizure is a sudden, brief disruption of brain activity caused by abnormal, excessive, or synchronous neuronal firing. Depending on the regions of the brain involved, seizures can lead to changes in movement, sensation, behavior, awareness, or consciousness. Symptoms vary widely. Some seizures involve subtle changes, such as brief lapses in attention or awareness (as seen in absence seizures), while others cause generalized convulsions with loss of consciousness ( tonic–clonic seizures). Most seizures last less than two minutes and are followed by a postictal period of confusion, fatigue, or other symptoms. A seizure lasting longer than five minutes is a medical emergency known as status epilepticus. Seizures are classified as provoked, when triggered by a known cause such as fever, head trauma, or metabolic imbalance, or unprovoked, when no immediate trigger is identified. Recurrent unprovoked seizures define the neurological condition epilepsy. Clinical features Seizur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blood Vessel
Blood vessels are the tubular structures of a circulatory system that transport blood throughout many Animal, animals’ bodies. Blood vessels transport blood cells, nutrients, and oxygen to most of the Tissue (biology), tissues of a Body (biology), body. They also take waste and carbon dioxide away from the tissues. Some tissues such as cartilage, epithelium, and the lens (anatomy), lens and cornea of the eye are not supplied with blood vessels and are termed ''avascular''. There are five types of blood vessels: the arteries, which carry the blood away from the heart; the arterioles; the capillaries, where the exchange of water and chemicals between the blood and the tissues occurs; the venules; and the veins, which carry blood from the capillaries back towards the heart. The word ''vascular'', is derived from the Latin ''vas'', meaning ''vessel'', and is mostly used in relation to blood vessels. Etymology * artery – late Middle English; from Latin ''arteria'', from Gree ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
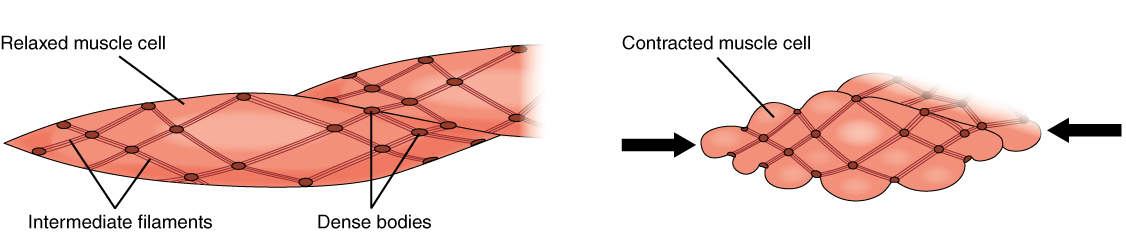
Smooth Muscle
Smooth muscle is one of the three major types of vertebrate muscle tissue, the others being skeletal and cardiac muscle. It can also be found in invertebrates and is controlled by the autonomic nervous system. It is non- striated, so-called because it has no sarcomeres and therefore no striations (''bands'' or ''stripes''). It can be divided into two subgroups, ''single-unit'' and ''multi-unit'' smooth muscle. Within single-unit muscle, the whole bundle or sheet of smooth muscle cells contracts as a syncytium. Smooth muscle is found in the walls of hollow organs, including the stomach, intestines, bladder and uterus. In the walls of blood vessels, and lymph vessels, (excluding blood and lymph capillaries) it is known as vascular smooth muscle. There is smooth muscle in the tracts of the respiratory, urinary, and reproductive systems. In the eyes, the ciliary muscles, iris dilator muscle, and iris sphincter muscle are types of smooth muscles. The iris dilator and s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Childbirth
Childbirth, also known as labour, parturition and delivery, is the completion of pregnancy, where one or more Fetus, fetuses exits the Womb, internal environment of the mother via vaginal delivery or caesarean section and becomes a newborn to the world. In 2019, there were about 140.11 million human births globally. In Developed country, developed countries, most deliveries occur in hospitals, while in Developing country, developing countries most are home births. The most common childbirth method worldwide is vaginal delivery. It involves four stages of labour: the cervical effacement, shortening and Cervical dilation, opening of the cervix during the first stage, descent and birth of the baby during the second, the delivery of the placenta during the third, and the recovery of the mother and infant during the fourth stage, which is referred to as the Postpartum period, postpartum. The first stage is characterised by abdominal cramping or also back pain in the case of B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bleeding
Bleeding, hemorrhage, haemorrhage or blood loss, is blood escaping from the circulatory system from damaged blood vessels. Bleeding can occur internally, or externally either through a natural opening such as the mouth, nose, ear, urethra, vagina, or anus, or through a puncture in the skin. Hypovolemia is a massive decrease in blood volume, and death by excessive loss of blood is referred to as exsanguination. Typically, a healthy person can endure a loss of 10–15% of the total blood volume without serious medical difficulties (by comparison, blood donation typically takes 8–10% of the donor's blood volume). The stopping or controlling of bleeding is called hemostasis and is an important part of both first aid and surgery. Types * Upper head ** Intracranial hemorrhage — bleeding in the skull. ** Cerebral hemorrhage — a type of intracranial hemorrhage, bleeding within the brain tissue itself. ** Intracerebral hemorrhage — bleeding in the brain caused by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Placenta
The placenta (: placentas or placentae) is a temporary embryonic and later fetal organ that begins developing from the blastocyst shortly after implantation. It plays critical roles in facilitating nutrient, gas, and waste exchange between the physically separate maternal and fetal circulations, and is an important endocrine organ, producing hormones that regulate both maternal and fetal physiology during pregnancy. The placenta connects to the fetus via the umbilical cord, and on the opposite aspect to the maternal uterus in a species-dependent manner. In humans, a thin layer of maternal decidual ( endometrial) tissue comes away with the placenta when it is expelled from the uterus following birth (sometimes incorrectly referred to as the 'maternal part' of the placenta). Placentas are a defining characteristic of placental mammals, but are also found in marsupials and some non-mammals with varying levels of development. Mammalian placentas probably first evolved abou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Obstetrics
Obstetrics is the field of study concentrated on pregnancy, childbirth and the postpartum period. As a medical specialty, obstetrics is combined with gynecology under the discipline known as obstetrics and gynecology (OB/GYN), which is a surgical field. Main areas Prenatal care Prenatal care is important in screening for various complications of pregnancy. This includes routine office visits with physical exams and routine lab tests along with telehealth care for women with low-risk pregnancies: Image:Ultrasound_image_of_a_fetus.jpg, 3D ultrasound of fetus (about 14 weeks gestational age) Image:Sucking his thumb and waving.jpg, Fetus at 17 weeks Image:3dultrasound 20 weeks.jpg, Fetus at 20 weeks First trimester Routine tests in the first trimester of pregnancy generally include: * Complete blood count * Blood type ** Rh-negative antenatal patients should receive RhoGAM at 28 weeks to prevent Rh disease. * Indirect Coombs test (AGT) to assess risk of hem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Controlled Substance
A controlled substance is generally a drug or chemical whose manufacture, possession and use is regulated by a government, such as illicitly used drugs or prescription medications that are designated by law. Some treaties, notably the Single Convention on Narcotic Drugs, the Convention on Psychotropic Substances, and the United Nations Convention Against Illicit Traffic in Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances, provide internationally agreed-upon "schedules" of controlled substances, which have been incorporated into national laws; however, national laws usually significantly expand on these international conventions. Some precursor chemicals used for the production of illegal drugs are also controlled substances in many countries, even though they may lack the pharmacological effects of the drugs themselves. Substances are classified according to schedules and consist primarily of potentially psychoactive substances and anabolic steroids. The controlled substanc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |