|
Epigenetic Therapy
Epigenetic therapy refers to the use of drugs or other interventions to modify gene expression patterns, potentially treating diseases by targeting epigenetic mechanisms such as DNA methylation and histone modifications. Epigenetics is the study of changes in gene expression that do not arise from alterations in the DNA sequence, resulting in the heritable silencing of genes without changing the coding sequence. Epigenetic therapy involves using drugs or other techniques to influence these epigenetic mechanisms in addressing specific medical conditions. Various diseases, such as diabetes, cancer, heart disease, and mental illnesses, are influenced by epigenetic mechanisms. Emerging areas of epigenetic therapy include its application in heart disease, primarily focusing on tissue regeneration, and in schizophrenia, where the focus lies on alleviating symptoms. Overall, epigenetic therapies aim to target the underlying epigenetic molecular pathways responsible for disease manifest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epigenetic Therapy Diagram
In biology, epigenetics is the study of changes in gene expression that happen without changes to the DNA sequence. The Greek prefix ''epi-'' (ἐπι- "over, outside of, around") in ''epigenetics'' implies features that are "on top of" or "in addition to" the traditional (DNA sequence based) genetic mechanism of inheritance. Epigenetics usually involves a change that is not erased by cell division, and affects the regulation of gene expression. Such effects on cellular and physiological traits may result from environmental factors, or be part of normal development. The term also refers to the mechanism of changes: functionally relevant alterations to the genome that do not involve mutation of the nucleotide sequence. Examples of mechanisms that produce such changes are DNA methylation and histone modification, each of which alters how genes are expressed without altering the underlying DNA sequence. Further, non-coding RNA sequences have been shown to play a key role in the r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hallmarks Of Cancer
The hallmarks of cancer were originally six biological capabilities acquired during the multistep development of human tumors and have since been increased to eight capabilities and two enabling capabilities. The idea was coined by Douglas Hanahan and Robert Weinberg in their paper "The Hallmarks of Cancer" published January 2000 in ''Cell''. These hallmarks constitute an organizing principle for rationalizing the complexities of neoplastic disease. They include sustaining proliferative signaling, evading growth suppressors, resisting cell death, enabling replicative immortality, inducing angiogenesis, and activating invasion and metastasis. Underlying these hallmarks are genome instability, which generates the genetic diversity that expedites their acquisition, and inflammation, which fosters multiple hallmark functions. In addition to cancer cells, tumors exhibit another dimension of complexity: they incorporate a community of recruited, ostensibly normal cells that contribute ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GNAS-AS1
In molecular biology, GNAS antisense RNA (non-protein coding), also known as GNAS-AS1, is a long non-coding RNA.It is antisense to the GNAS gene. It is an imprinted gene, expressed only from the paternal allele, suggesting that it may have a role in suppression of the paternal NESP55 allele encoded by GNAS. See also * Long noncoding RNA Long non-coding RNAs (long ncRNAs, lncRNA) are a type of RNA, generally defined as transcripts more than 200 nucleotides that are not translated into protein. This arbitrary limit distinguishes long ncRNAs from small non-coding RNAs, such as mic ... References Further reading * * * * * * Non-coding RNA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Long Interspersed Nuclear Element
Long interspersed nuclear elements (LINEs) (also known as long interspersed nucleotide elements or long interspersed elements) are a group of non-LTR (long terminal repeat) retrotransposons that are widespread in the genome of many eukaryotes. LINEs contain an internal RNA polymerase, Pol II promoter to initiate Transcription (biology), transcription into Messenger RNA, mRNA, and encode one or two proteins, ORF1 and ORF2. The functional domains present within ORF1 vary greatly among LINEs, but often exhibit RNA/DNA binding activity. ORF2 is essential to successful retrotransposition, and encodes a protein with both reverse transcriptase and endonuclease activity. LINEs are the most abundant transposable element within the human genome, with approximately 20.7% of the sequences identified as being derived from LINEs. The only active lineage of LINE found within humans belongs to the LINE1, LINE-1 class, and is referred to as L1Hs. The human genome contains an estimated 100,000 tru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
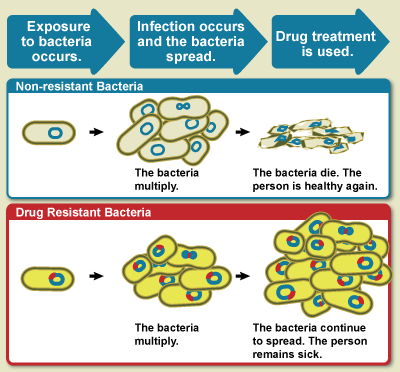
Drug Resistance
Drug resistance is the reduction in effectiveness of a medication such as an antimicrobial or an antineoplastic in treating a disease or condition. The term is used in the context of resistance that pathogens or cancers have "acquired", that is, resistance has evolved. Antimicrobial resistance and antineoplastic resistance challenge clinical care and drive research. When an organism is resistant to more than one drug, it is said to be multidrug-resistant. The development of antibiotic resistance in particular stems from the drugs targeting only specific bacterial molecules (almost always proteins). Because the drug is ''so'' specific, any mutation in these molecules will interfere with or negate its destructive effect, resulting in antibiotic resistance. Furthermore, there is mounting concern over the abuse of antibiotics in the farming of livestock, which in the European Union alone accounts for three times the volume dispensed to humans – leading to development of super-re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MAPK/ERK Pathway
The MAPK/ERK pathway (also known as the Ras-Raf-MEK-ERK pathway) is a chain of proteins in the cell (biology), cell that communicates a signal from a Receptor (biochemistry), receptor on the surface of the cell to the DNA in the nucleus of the cell. The signal starts when a signaling molecule binds to the receptor on the cell surface and ends when the DNA in the nucleus expresses a protein and produces some change in the cell, such as cell division. The pathway includes many proteins, such as mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs), originally called extracellular signal-regulated kinases (ERKs), which communicate by adding phosphate groups to a neighboring protein (Phosphorylation, phosphorylating it), thereby acting as an "on" or "off" switch. When one of the proteins in the pathway is mutated, it can become stuck in the "on" or "off" position, a necessary step in the development of many cancers. In fact, components of the MAPK/ERK pathway were first discovered in cancer cells ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angiogenesis
Angiogenesis is the physiological process through which new blood vessels form from pre-existing vessels, formed in the earlier stage of vasculogenesis. Angiogenesis continues the growth of the vasculature mainly by processes of sprouting and splitting, but processes such as coalescent angiogenesis, vessel elongation and vessel cooption also play a role. Vasculogenesis is the embryonic formation of endothelial cells from mesoderm cell precursors, and from neovascularization, although discussions are not always precise (especially in older texts). The first vessels in the developing embryo form through vasculogenesis, after which angiogenesis is responsible for most, if not all, blood vessel growth during development and in disease. Angiogenesis is a normal and vital process in growth and development, as well as in wound healing and in the formation of granulation tissue. However, it is also a fundamental step in the transition of tumors from a benign state to a malign ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apoptosis
Apoptosis (from ) is a form of programmed cell death that occurs in multicellular organisms and in some eukaryotic, single-celled microorganisms such as yeast. Biochemistry, Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes (Morphology (biology), morphology) and death. These changes include Bleb (cell biology), blebbing, Plasmolysis, cell shrinkage, Karyorrhexis, nuclear fragmentation, Pyknosis, chromatin condensation, Apoptotic DNA fragmentation, DNA fragmentation, and mRNA decay. The average adult human loses 50 to 70 1,000,000,000, billion cells each day due to apoptosis. For the average human child between 8 and 14 years old, each day the approximate loss is 20 to 30 billion cells. In contrast to necrosis, which is a form of traumatic cell death that results from acute cellular injury, apoptosis is a highly regulated and controlled process that confers advantages during an organism's life cycle. For example, the separation of fingers and toes in a developing human embryo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyphenol
Polyphenols () are a large family of naturally occurring phenols. They are abundant in plants and structurally diverse. Polyphenols include phenolic acids, flavonoids, tannic acid, and ellagitannin, some of which have been used historically as dyes and for tanning (leather), tanning garments. Etymology The name derives from the Ancient Greek word (, meaning "many, much") and the word ‘phenol’ which refers to a chemical structure formed by attachment of an aromatic benzenoid (phenyl) ring to a hydroxyl (-OH) group (hence the ''-ol'' suffix). The term "polyphenol" has been in use at least since 1894. Definition Polyphenols are natural products with "one or several hydroxyl groups on aromatic rings", including four principal classes: phenolic acids, flavonoids, stilbenes, and lignans. Flavonoids can be grouped as flavones, flavonols, flavanols, flavanones, isoflavones, proanthocyanidins, and anthocyanins. Particularly abundant flavanoids in foods are catechin (tea, frui ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phytochemical
Phytochemicals are naturally-occurring chemicals present in or extracted from plants. Some phytochemicals are nutrients for the plant, while others are metabolites produced to enhance plant survivability and reproduction. The fields of extracting phytochemicals for manufactured products or applying scientific methods to study phytochemical properties are called ''phytochemistry''. An individual who uses phytochemicals in food chemistry manufacturing or research is a ''phytochemist''. Phytochemicals without a nutrient definition have no confirmed biological activities or proven health benefits when consumed in plant foods. Once phytochemicals in a food enter the digestion process, the fate of individual phytochemicals in the body is unknown due to extensive metabolism of the food in the gastrointestinal tract, producing phytochemical metabolites with different biological properties from those of the parent compound that may have been tested in vitro. Further, the bioavaila ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vorinostat
Vorinostat (International Nonproprietary Name, rINN), also known as suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid (suberic acid, suberoyl+aniline, anilide+hydroxamic acid abbreviated as SAHA), is a member of a larger class of compounds that inhibit histone deacetylases (HDAC). Histone deacetylase inhibitors (HDI) have a broad spectrum of epigenetic activities. Vorinostat is marketed under the name Zolinza ( ) by Merck & Co., Merck for the treatment of cutaneous manifestations in patients with cutaneous T cell lymphoma (CTCL) when the disease persists, gets worse, or comes back during or after two systemic therapies. The compound was developed by Columbia University chemist Ronald Breslow and Memorial Sloan-Kettering researcher Paul Marks (scientist), Paul Marks. Medical uses Vorinostat was the first histone deacetylase inhibitor approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of Cutaneous T-cell lymphoma, CTCL on October 6, 2006. Development In 1966, Charlotte F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |