|
Enzyme-linked-immuno-sorbent-assays
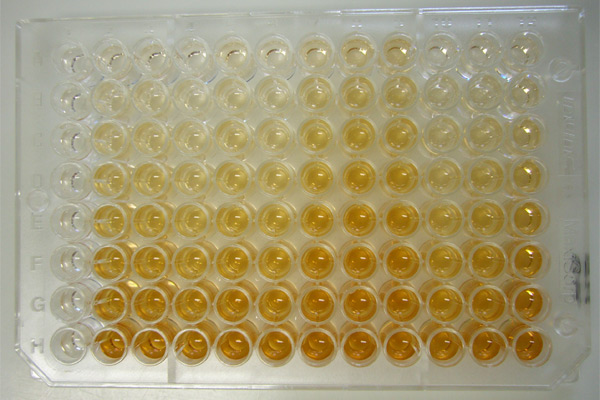
The enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) (, ) is a commonly used analytical biochemistry assay, first described by Eva Engvall and Peter Perlmann in 1971. The assay is a solid-phase type of enzyme immunoassay (EIA) to detect the presence of a ligand (commonly an amino acid) in a liquid sample using antibodies directed against the ligand to be measured. ELISA has been used as a diagnostic tool in medicine, plant pathology, and biotechnology, as well as a quality control check in various industries. In the most simple form of an ELISA, antigens from the sample to be tested are attached to a surface. Then, a matching antibody is applied over the surface so it can bind the antigen. This antibody is linked to an enzyme, and then any unbound antibodies are removed. In the final step, a substance containing the enzyme's substrate is added. If there was binding, the subsequent reaction produces a detectable signal, most commonly a color change. Performing an ELISA involves at le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
3,3',5,5'-Tetramethylbenzidine
3,3′,5,5′-Tetramethylbenzidine or TMB is a chromogenic substrate used in staining procedures in immunohistochemistry as well as being a visualising reagent used in enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA). TMB is a white solid that forms a pale blue-green liquid in solution with ethyl acetate. TMB is degraded by sunlight and by fluorescent lights. Used to detect hematuria as it turns blue in contact with hemoglobin. Enzymatic assay TMB can act as a hydrogen donor for the reduction of hydrogen peroxide to water by peroxidase enzymes such as horseradish peroxidase. The resulting one-electron oxidation product is a diimine-diamine complex, which causes the solution to take on a blue colour, and this colour change can be read on a spectrophotometer at the wavelengths of 370 and 650 nm. The reaction can be halted by addition of acid or another stop reagent. Using sulfuric acid turns TMB yellow, with a Absorption (electromagnetic radiation), peak absorbance of 450 nm. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzyme
An enzyme () is a protein that acts as a biological catalyst by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as product (chemistry), products. Almost all metabolism, metabolic processes in the cell (biology), cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. Metabolic pathways depend upon enzymes to catalyze individual steps. The study of enzymes is called ''enzymology'' and the field of pseudoenzyme, pseudoenzyme analysis recognizes that during evolution, some enzymes have lost the ability to carry out biological catalysis, which is often reflected in their amino acid sequences and unusual 'pseudocatalytic' properties. Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Other biocatalysts include Ribozyme, catalytic RNA molecules, also called ribozymes. They are sometimes descr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immunoassay
An immunoassay (IA) is a biochemical test that measures the presence or concentration of a macromolecule or a small molecule in a solution through the use of an antibody (usually) or an antigen (sometimes). The molecule detected by the immunoassay is often referred to as an "analyte" and is in many cases a protein, although it may be other kinds of molecules, of different sizes and types, as long as the proper antibodies that have the required properties for the assay are developed. Analytes in biological liquids such as blood plasma, serum or urine are frequently measured using immunoassays for medical and research purposes. Immunoassays come in many different formats and variations. Immunoassays may be run in multiple steps with reagents being added and washed away or separated at different points in the assay. Multi-step assays are often called separation immunoassays or heterogeneous immunoassays. Some immunoassays can be carried out simply by mixing the reagents and samples an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ligand Binding Assays
A ligand binding assay (LBA) is an assay, or an analytic procedure, which relies on the binding of ligand (biochemistry), ligand molecules to receptor (biochemistry), receptors, antibody, antibodies or other macromolecules. A detection method is used to determine the presence and amount of the ligand-receptor complexes formed, and this is usually determined Electrochemiluminescence, electrochemically or through a fluorescence detection method. This type of analytic chemistry, analytic test can be used to test for the presence of target molecules in a sample that are known to bind to the receptor. There are numerous types of ligand binding assays, both radiobinding assay, radioactive and non-radioactive.Joseph R. Lakowicz. (1991) Topics in Fluorescence Spectroscopy: Biochemical applications. Some newer types are called "mix-and-measure" assays because they require fewer steps to complete, for example foregoing the removal of unbound reagents. Ligand binding assays are used primarily ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spectrophotometry
Spectrophotometry is a branch of electromagnetic spectroscopy concerned with the quantitative measurement of the reflection or transmission properties of a material as a function of wavelength. Spectrophotometry uses photometers, known as spectrophotometers, that can measure the intensity of a light beam at different wavelengths. Although spectrophotometry is most commonly applied to ultraviolet, Visible spectrum, visible, and infrared radiation, modern spectrophotometers can interrogate wide swaths of the electromagnetic spectrum, including x-ray, ultraviolet, Visible spectrum, visible, infrared, or microwave wavelengths. Overview Spectrophotometry is a tool that hinges on the quantitative analysis of molecules depending on how much light is absorbed by colored compounds. Important features of spectrophotometers are spectral bandwidth (the range of colors it can transmit through the test sample), the percentage of sample transmission, the logarithmic range of sample absorptio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reflectometry
Reflectometry is a general term for the use of the reflection of waves or pulses at surfaces and interfaces to detect or characterize objects, sometimes to detect anomalies as in fault detection and medical diagnosis. There are many different forms of reflectometry. They can be classified in several ways: by the used radiation (electromagnetic, ultrasound, particle beams), by the geometry of wave propagation (unguided versus wave guides or cables), by the involved length scales (wavelength and penetration depth in relation to size of the investigated object), by the method of measurement (continuous versus pulsed, polarization resolved, ...), and by the application domain. Radiation sources *Electromagnetic radiation of widely varying wavelength is used in many different forms of reflectometry: ** Radar: Reflections of radiofrequency pulses are used to detect the presence and to measure the location and speed of objects such as aircraft, missiles, ships, vehicles. ** Lidar: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Analysis
Analysis (: analyses) is the process of breaking a complex topic or substance into smaller parts in order to gain a better understanding of it. The technique has been applied in the study of mathematics and logic since before Aristotle (384–322 BC), though ''analysis'' as a formal concept is a relatively recent development. The word comes from the Ancient Greek (''analysis'', "a breaking-up" or "an untying" from ''ana-'' "up, throughout" and ''lysis'' "a loosening"). From it also comes the word's plural, ''analyses''. As a formal concept, the method has variously been ascribed to René Descartes ('' Discourse on the Method''), and Galileo Galilei. It has also been ascribed to Isaac Newton, in the form of a practical method of physical discovery (which he did not name). The converse of analysis is synthesis: putting the pieces back together again in a new or different whole. Science and technology Chemistry The field of chemistry uses analysis in three ways: to i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Analyte
An analyte, component (in clinical chemistry), titrand (in titrations), or chemical species is a substance or chemical constituent that is of interest in an analytical procedure. The remainder of the sample is called the matrix. The procedure of analysis measures the analyte's chemical or physical properties, thus establishing its identity or concentration in the sample. See also *Analytical chemistry * Standard solution *Immunoassay An immunoassay (IA) is a biochemical test that measures the presence or concentration of a macromolecule or a small molecule in a solution through the use of an antibody (usually) or an antigen (sometimes). The molecule detected by the immunoassay ... * Magnetic immunoassay References Analytical chemistry {{Analytical-chemistry-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antigen-antibody Interaction
Antigen-antibody interaction, or antigen-antibody reaction, is a specific chemical interaction between antibodies produced by B cells of the white blood cells and antigens during immune reaction. The antigens and antibodies combine by a process called agglutination. It is the fundamental reaction in the body by which the body is protected from complex foreign molecules, such as pathogens and their chemical toxins. In the blood, the antigens are specifically and with high affinity bound by antibodies to form an antigen-antibody complex. The immune complex is then transported to cellular systems where it can be destroyed or deactivated. The first correct description of the antigen-antibody reaction was given by Richard J. Goldberg at the University of Wisconsin in 1952. It came to be known as "Goldberg's theory" (of antigen-antibody reaction). There are several types of antibodies and antigens, and each antibody is capable of binding only to a specific antigen. The specificity of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ligand Binding Assay
A ligand binding assay (LBA) is an assay, or an analytic procedure, which relies on the binding of ligand molecules to receptors, antibodies or other macromolecules. A detection method is used to determine the presence and amount of the ligand-receptor complexes formed, and this is usually determined electrochemically or through a fluorescence detection method. This type of analytic test can be used to test for the presence of target molecules in a sample that are known to bind to the receptor. There are numerous types of ligand binding assays, both radioactive and non-radioactive.Joseph R. Lakowicz. (1991) Topics in Fluorescence Spectroscopy: Biochemical applications. Some newer types are called "mix-and-measure" assays because they require fewer steps to complete, for example foregoing the removal of unbound reagents. Ligand binding assays are used primarily in pharmacology for various demands. Specifically, despite the human body's endogenous receptors, hormones, and other n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Signal (information Theory)
A signal is both the process and the result of Signal transmission, transmission of data over some transmission media, media accomplished by embedding some variation. Signals are important in multiple subject fields including signal processing, information theory and biology. In signal processing, a signal is a function that conveys information about a phenomenon. Any quantity that can vary over space or time can be used as a signal to share messages between observers. The ''IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing'' includes audio signal, audio, video, speech, image, sonar, and radar as examples of signals. A signal may also be defined as observable change in a quantity over space or time (a time series), even if it does not carry information. In nature, signals can be actions done by an organism to alert other organisms, ranging from the release of plant chemicals to warn nearby plants of a predator, to sounds or motions made by animals to alert other animals of food. Signa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Substrate (biochemistry)
In chemistry, the term substrate is highly context-dependent. Broadly speaking, it can refer either to a chemical species being observed in a chemical reaction, or to a surface on which other chemical reactions or microscopy are performed. In the former sense, a reagent is added to the ''substrate'' to generate a product through a chemical reaction. The term is used in a similar sense in synthetic and organic chemistry, where the substrate is the chemical of interest that is being modified. In biochemistry, an enzyme substrate is the material upon which an enzyme acts. When referring to Le Chatelier's principle, the substrate is the reagent whose concentration is changed. ;Spontaneous reaction : :*Where S is substrate and P is product. ;Catalysed reaction : :*Where S is substrate, P is product and C is catalyst. In the latter sense, it may refer to a surface on which other chemical reactions are performed or play a supporting role in a variety of spectroscopic and mic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |