|
Energy In The Netherlands
Energy in the Netherlands describes energy and electricity production, consumption and import in the Netherlands. Electricity sector in the Netherlands is the main article of electricity in the Netherlands. In 2020 the Netherlands was reliant on fossil fuel for energy needs, especially natural gas, however the plan is to bring renewable power up to 70% of the electricity needs of the Netherlands by 2030. Subsidies and declining costs for renewables (primarily wind and solar) have boosted their use in the Netherlands; renewable energy provided 40% of Dutch electricity production in 2022, up from 12% in 2012 and 4% in 2002. Energy statistics Energy plans The Netherlands has set a target of 70% of electricity from renewable sources (mainly solar and wind power) by 2030. Transition away from natural gas To reduce its greenhouse emissions, the government of the Netherlands is subsidizing a transition away from natural gas for all homes in the country by 2050. In Amsterdam, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CO2 Emissions Netherlands
CO or variants may refer to: Chemistry * Carbon monoxide (CO), a colorless, odorless, and tasteless gas * Carbonyl group, composed of a carbon atom double-bonded to an oxygen atom: C=O * Cobalt, a chemical element, symbol Co Computing and telecommunications * .co (second-level domain), the Internet second-level domain meaning "commercial" * .co, the Internet country code top-level domain (ccTLD) for Colombia * Commitment ordering (CO), a concurrency control technique for databases * Telephone exchange, or central office (CO) Mathematics * Cofunction, or Co, in trigonometry * Cuboctahedron, a uniform polyhedron People * Nguyễn Hữu Có (1925–2012), Vietnamese general * Conrado Co (born 1940), Filipino badminton player * Alfredo Co (born 1949), Filipino Sinologist * Atoy Co (born 1951), Filipino actor and basketball coach * Leonard Co (1953–2010), Filipino botanist * Nando Có (born 1973), Bissau-Guinean footballer * Kenedy Có (born 1998), Bissau-Guinean footb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World Energy Resources And Consumption
World energy supply and consumption refers to the global supply of energy resources and its consumption. The system of global energy supply consists of the energy development, refinement, and trade of energy. Energy supplies may exist in various forms such as ''raw resources'' or ''more processed and refined'' forms of energy. The raw energy resources include for example coal, unprocessed oil and gas, uranium. In comparison, the refined forms of energy include for example refined oil that becomes fuel and electricity. Energy resources may be used in various different ways, depending on the specific resource (e.g. coal), and intended end use (industrial, residential, etc.). Energy production and consumption play a significant role in the global economy. It is needed in industry and global transportation. The total energy supply chain, from production to final consumption, involves many activities that cause a loss of useful energy. As of 2022, energy consumption is still a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electricity Generation
Electricity generation is the process of generating electric power from sources of primary energy. For electric utility, utilities in the electric power industry, it is the stage prior to its Electricity delivery, delivery (Electric power transmission, transmission, Electric power distribution, distribution, etc.) to end users or its Grid energy storage, storage, using for example, the Pumped-storage hydroelectricity, pumped-storage method. Consumable electricity is not freely available in nature, so it must be "produced", transforming other forms of energy to electricity. Production is carried out in power stations, also called "power plants". Electricity is most often generated at a power plant by electromechanical electric generator, generators, primarily driven by heat engines fueled by combustion or nuclear fission, but also by other means such as the kinetic energy of flowing water and wind. Other energy sources include solar photovoltaics and geothermal power. There are ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Netherlands
, Terminology of the Low Countries, informally Holland, is a country in Northwestern Europe, with Caribbean Netherlands, overseas territories in the Caribbean. It is the largest of the four constituent countries of the Kingdom of the Netherlands. The Netherlands consists of Provinces of the Netherlands, twelve provinces; it borders Germany to the east and Belgium to the south, with a North Sea coastline to the north and west. It shares Maritime boundary, maritime borders with the United Kingdom, Germany, and Belgium. The official language is Dutch language, Dutch, with West Frisian language, West Frisian as a secondary official language in the province of Friesland. Dutch, English_language, English, and Papiamento are official in the Caribbean Netherlands, Caribbean territories. The people who are from the Netherlands is often referred to as Dutch people, Dutch Ethnicity, Ethnicity group, not to be confused by the language. ''Netherlands'' literally means "lower countries" i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electricity Sector In The Netherlands
The total electricity consumption of the Netherlands in 2021 was 117 terawatt-hours (TWh). The consumption grew from 7 TWh in 1950 by an average of 4.5% per year. In 2021, fossil fuels, such as natural gas and coal, accounted for around 62% of the total electricity produced. Renewable energy sources, such as biomass, wind power, and solar power, produce 38% of the total electricity. One nuclear plant in Borssele is responsible for around 3% of total generation. More than 75% of electricity is produced centrally by thermal and nuclear units. From 2005 to 2008, the Netherlands imported 13-15% of its electricity. After 2008, however, the share of electricity imported decreased drastically, meaning that in 2009, the Netherlands became a net exporter of electricity. That was until 2011, when the electricity import balance increased sharply. This development continued in 2012 and 2013. A 2010 amount of 56.1 PJ almost doubled in 2015 to 110.7. The cause of the increase in electricity i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
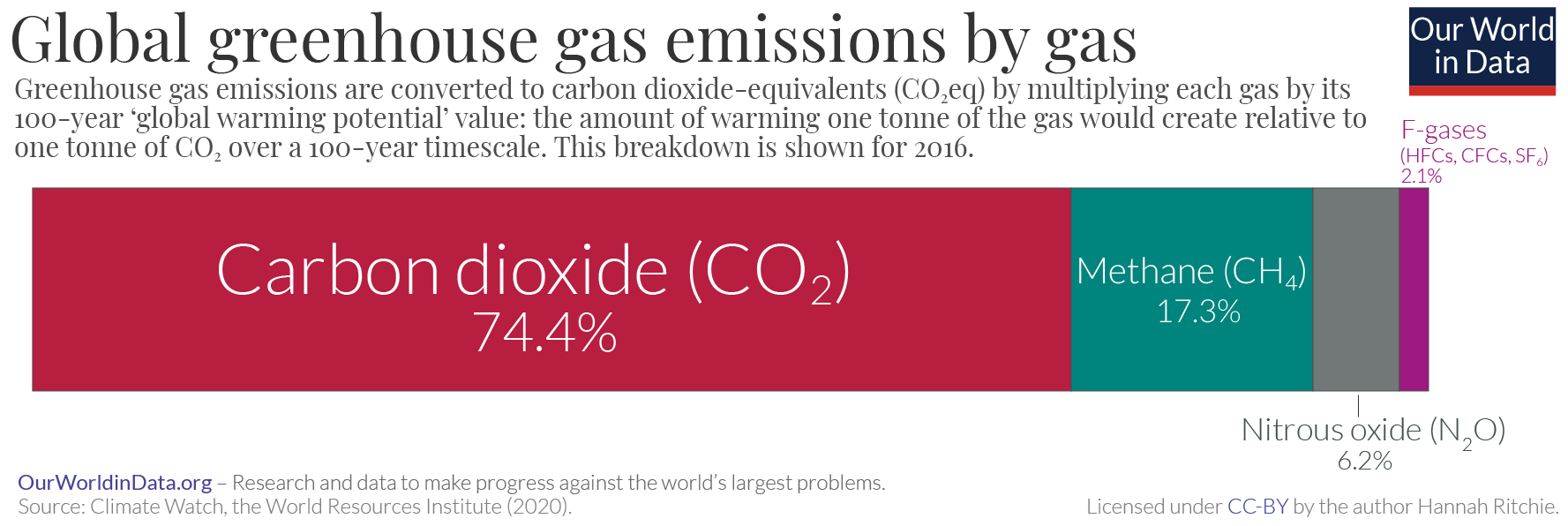
Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions from human activities intensify the greenhouse effect. This contributes to climate change. Carbon dioxide (), from burning fossil fuels such as coal, petroleum, oil, and natural gas, is the main cause of climate change. The top contributors to greenhouse gas emissions, largest annual emissions are from China followed by the United States. The United States has List of countries by greenhouse gas emissions per capita, higher emissions per capita. The main producers fueling the emissions globally are Big Oil, large oil and gas companies. Emissions from human activities have increased Carbon dioxide in Earth's atmosphere, atmospheric carbon dioxide by about 50% over pre-industrial levels. The growing levels of emissions have varied, but have been consistent among all greenhouse gases. Emissions in the 2010s averaged 56 billion tons a year, higher than any decade before. Total cumulative emissions from 1870 to 2022 were 703 (2575 ), of which 484±20 (177 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electric Stove
An electric stove, electric cooker or electric range is a stove with an integrated electrical heating device to cook and bake. Electric stoves became popular as replacements for solid-fuel (wood or coal) stoves which required more labor to operate and maintain. Some modern stoves come in a unit with built-in extractor hoods. The stove's one or more "burners" (heating elements) may be controlled by a rotary switch with a finite number of positions; or may have an " infinite switch" called a ''simmerstat'' that allows constant variability between minimum and maximum heat settings. Some stove burners and controls incorporate thermostats. History Early patents On September 20, 1859, George B. Simpson was awarded US patent #25532 for an 'electro-heater' surface heated by a platinum-wire coil powered by batteries. In his words, useful to "warm rooms, boil water, cook victuals...". Canadian inventor Thomas Ahearn filed patent #39916 in 1892 for an "Electric Oven," a device he p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
District Heating
District heating (also known as heat networks) is a system for distributing heat generated in a centralized location through a system of insulated pipes for residential and commercial heating requirements such as space heater, space heating and water heating. The heat is often obtained from a cogeneration plant burning fossil fuels or biomass, but heating plant, heat-only boiler stations, geothermal heating, heat pumps and central solar heating are also used, as well as heat waste from factories and nuclear power electricity generation. District heating plants can provide higher efficiencies and better pollution control than localized boilers. According to some research, district heating with combined heat and power (CHPDH) is the cheapest method of cutting carbon emissions, and has one of the lowest carbon footprints of all fossil generation plants. District heating is ranked number 27 in Drawdown (climate), Project Drawdown's 100 solutions to climate change, global warming. His ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waste Incineration
Incineration is a waste treatment process that involves the combustion of substances contained in waste materials. Industrial plants for waste incineration are commonly referred to as waste-to-energy facilities. Incineration and other high-temperature waste treatment systems are described as "thermal treatment". Incineration of waste materials converts the waste into ash, flue gas and heat. The ash is mostly formed by the inorganic constituents of the waste and may take the form of solid lumps or particulates carried by the flue gas. The flue gases must be cleaned of gaseous and particulate pollutants before they are dispersed into the atmosphere. In some cases, the heat that is generated by incineration can be used to generate electric power. Incineration with energy recovery is one of several waste-to-energy technologies such as gasification, pyrolysis and anaerobic digestion. While incineration and gasification technologies are similar in principle, the energy produced ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geothermal Energy
Geothermal energy is thermal energy extracted from the crust (geology), crust. It combines energy from the formation of the planet and from radioactive decay. Geothermal energy has been exploited as a source of heat and/or electric power for millennia. Geothermal heating, using water from hot springs, for example, has been used for bathing since Paleolithic times and for space heating since Roman times. Geothermal power (generation of electricity from geothermal energy), has been used since the 20th century. Unlike wind and solar energy, geothermal plants produce power at a constant rate, without regard to weather conditions. Geothermal resources are theoretically more than adequate to supply humanity's energy needs. Most extraction occurs in areas near tectonic plate boundaries. The cost of generating geothermal power decreased by 25% during the 1980s and 1990s. Technological advances continued to reduce costs and thereby expand the amount of viable resources. In 2021, the US ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Data Center
A data center is a building, a dedicated space within a building, or a group of buildings used to house computer systems and associated components, such as telecommunications and storage systems. Since IT operations are crucial for business continuity, it generally includes redundant or backup components and infrastructure for power supply, data communication connections, environmental controls (e.g., air conditioning, fire suppression), and various security devices. A large data center is an industrial-scale operation using as much electricity as a medium town. Estimated global data center electricity consumption in 2022 was 240–340 TWh, or roughly 1–1.3% of global electricity demand. This excludes energy used for cryptocurrency mining, which was estimated to be around 110 TWh in 2022, or another 0.4% of global electricity demand. The IEA projects that data center electric use could double between 2022 and 2026. High demand for electricity from data centers, incl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |