|
Endoplasmic Reticulum Membrane Protein Complex
The endoplasmic reticulum membrane protein complex (EMC) is a putative endoplasmic reticulum-resident membrane protein (co-)chaperone. The EMC is evolutionarily conserved in eukaryotes (animals, plants, and fungi), and its initial appearance might reach back to the last eukaryotic common ancestor (LECA). Many aspects of mEMC biology and molecular function remain to be studied. Composition and structure The EMC consists of up to 10 subunits (EMC1 - EMC4, MMGT1, EMC6 - EMC10), of which only two (EMC8/9) are homologous proteins. Seven out of ten (EMC1, EMC3, EMC4, MMMGT1, EMC6, EMC7, EMC10) subunits are predicted to contain at least one transmembrane domain (TMD), whereas EMC2, EMC8 and EMC9 do not contain any predicted transmembrane domains are herefore likely to interact with the rest of the EMC on the cytosolic face of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). EMC proteins are thought to be present in the mature complex in a 1:1 stoichiometry. Subunit primary structure The majority of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endoplasmic Reticulum
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a part of a transportation system of the eukaryote, eukaryotic cell, and has many other important functions such as protein folding. The word endoplasmic means "within the cytoplasm", and reticulum is Latin for "little net". It is a type of organelle made up of two subunits – rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER), and smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER). The endoplasmic reticulum is found in most eukaryotic cells and forms an interconnected network of flattened, membrane-enclosed sacs known as cisternae (in the RER), and tubular structures in the SER. The membranes of the ER are continuous with the outer nuclear membrane. The endoplasmic reticulum is not found in red blood cells, or spermatozoa. There are two types of ER that share many of the same proteins and engage in certain common activities such as the synthesis of certain lipids and cholesterol. Different types of Cell (biology), cells contain different ratios of the two types of ER dependin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prokaryote
A prokaryote (; less commonly spelled procaryote) is a unicellular organism, single-celled organism whose cell (biology), cell lacks a cell nucleus, nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. The word ''prokaryote'' comes from the Ancient Greek (), meaning 'before', and (), meaning 'nut' or 'kernel'. In the earlier two-empire system arising from the work of Édouard Chatton, prokaryotes were classified within the empire Prokaryota. However, in the three-domain system, based upon molecular phylogenetics, prokaryotes are divided into two domain (biology), domains: Bacteria and Archaea. A third domain, Eukaryote, Eukaryota, consists of organisms with nuclei. Prokaryotes evolution, evolved before eukaryotes, and lack nuclei, mitochondria, and most of the other distinct organelles that characterize the eukaryotic cell. Some unicellular prokaryotes, such as cyanobacteria, form colony (biology), colonies held together by biofilms, and large colonies can create multilayered microbial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphatidylcholine
Phosphatidylcholines (PC) are a class of phospholipids that incorporate choline as a headgroup. They are a major component of biological membranes and can easily be obtained from a variety of readily available sources, such as egg yolk or soybeans, from which they are mechanically or chemically extracted using hexane. They are also a member of the lecithin group of yellow-brownish fatty substances occurring in animal and plant tissues. Dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine (lecithin) is a major component of the pulmonary surfactant, and is often used in the lecithin–sphingomyelin ratio to calculate fetal lung maturity. While phosphatidylcholines are found in all plant and animal cells, they are absent in the membranes of most bacteria, including ''Escherichia coli ''Escherichia coli'' ( )Wells, J. C. (2000) Longman Pronunciation Dictionary. Harlow ngland Pearson Education Ltd. is a gram-negative, facultative anaerobic, rod-shaped, coliform bacterium of the genus '' Esch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mitochondria
A mitochondrion () is an organelle found in the cells of most eukaryotes, such as animals, plants and fungi. Mitochondria have a double membrane structure and use aerobic respiration to generate adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is used throughout the cell as a source of chemical energy. They were discovered by Albert von Kölliker in 1857 in the voluntary muscles of insects. The term ''mitochondrion'', meaning a thread-like granule, was coined by Carl Benda in 1898. The mitochondrion is popularly nicknamed the "powerhouse of the cell", a phrase popularized by Philip Siekevitz in a 1957 ''Scientific American'' article of the same name. Some cells in some multicellular organisms lack mitochondria (for example, mature mammalian red blood cells). The multicellular animal '' Henneguya salminicola'' is known to have retained mitochondrion-related organelles despite a complete loss of their mitochondrial genome. A large number of unicellular organisms, such as microspo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhodopsin
Rhodopsin, also known as visual purple, is a protein encoded by the ''RHO'' gene and a G-protein-coupled receptor (GPCR). It is a light-sensitive receptor protein that triggers visual phototransduction in rod cells. Rhodopsin mediates dim light vision and thus is extremely sensitive to light. When rhodopsin is exposed to light, it immediately photobleaches. In humans, it is fully regenerated in about 30 minutes, after which the rods are more sensitive. Defects in the rhodopsin gene cause eye diseases such as retinitis pigmentosa and congenital stationary night blindness. History Rhodopsin was discovered by Franz Christian Boll in 1876. The name rhodopsin derives from Ancient Greek () for "rose", due to its pinkish color, and () for "sight". It was coined in 1878 by the German physiologist Wilhelm Friedrich Kühne (1837–1900). When George Wald discovered that rhodopsin is a holoprotein, consisting of retinal and an apoprotein, he called it opsin, which tod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hsp90
Hsp90 (heat shock protein 90) is a chaperone (protein), chaperone protein that assists other proteins to protein folding, fold properly, stabilizes proteins against heat stress, and aids in protein degradation. It also stabilizes a number of proteins required for tumor growth, which is why Hsp90 inhibitors are investigated as anti-cancer drugs. Heat shock proteins, as a class, are among the most highly expressed cell (biology), cellular proteins across all species. As their name implies, heat shock proteins protect cells when stressed by elevated temperatures. They account for 1–2% of total protein in unstressed cells. However, when cells are heated, the fraction of heat shock proteins increases to 4–6% of cellular proteins. Heat shock protein 90 (Hsp90) is one of the most common of the heat-related proteins. The "90" comes from the fact that it has a mass of roughly 90 Atomic mass unit, kilodaltons. A 90 kDa protein is considered fairly large for a non-fibrou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
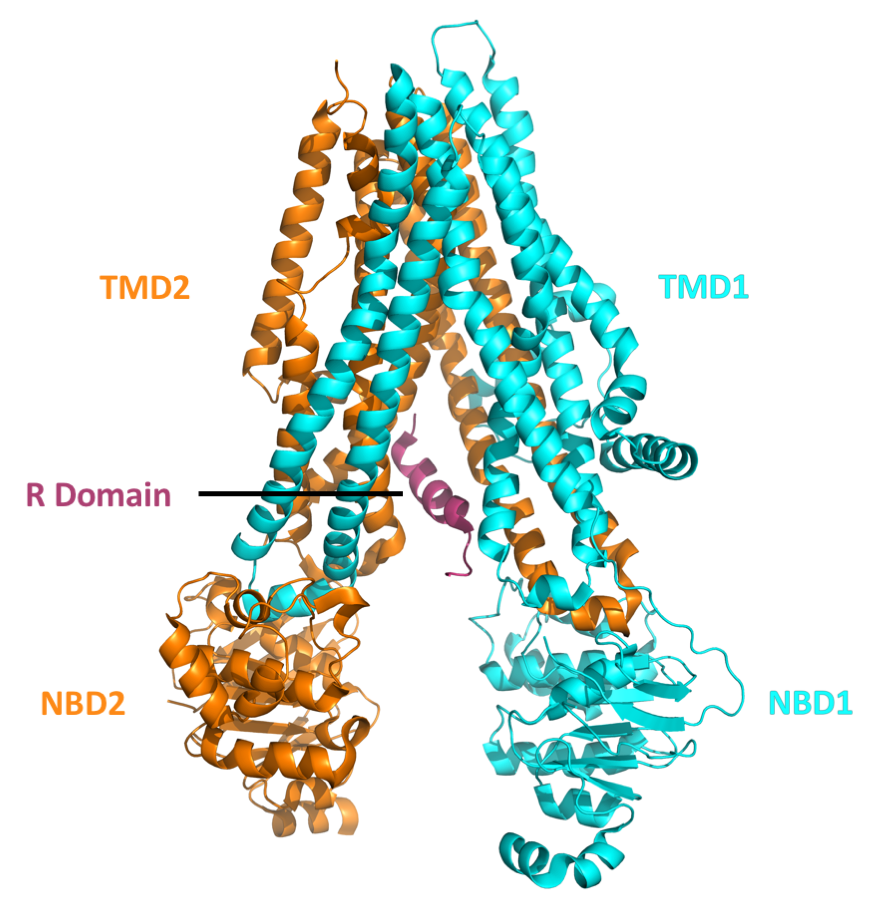
CFTRΔF508
Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) is a membrane protein and anion channel in vertebrates that is encoded by the ''CFTR'' gene. Geneticist Lap-Chee Tsui and his team identified the ''CFTR'' gene in 1989 as the gene linked with CF (cystic fibrosis). The ''CFTR'' gene codes for an ABC transporter-class ion channel protein that conducts chloride and bicarbonate ions across epithelial cell membranes. Mutations of the ''CFTR'' gene affecting anion channel function lead to dysregulation of epithelial lining fluid (mucus) transport in the lung, pancreas and other organs, resulting in cystic fibrosis. Complications include thickened mucus in the lungs with frequent respiratory infections, and pancreatic insufficiency giving rise to malnutrition and diabetes. These conditions lead to chronic disability and reduced life expectancy. In male patients, the progressive obstruction and destruction of the developing vas deferens (spermatic cord) and epididymis appear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DER2
Der or DER may refer to: Places * Darkənd, Azerbaijan * Dearborn (Amtrak station) (station code), in Michigan, US * Der (Sumer), an ancient city located in modern-day Iraq * d'Entrecasteaux Ridge, an oceanic ridge in the south-west Pacific Ocean Science and technology * Derivative chromosome, a structurally rearranged chromosome * Distinguished Encoding Rules, a method for encoding a data object, including public key infrastructure certificates and keys * Distributed Energy Resources * ∂, the partial derivative symbol * Derivation (differential algebra) on an algebra ''A'' over a field ''K'', the space (module) of which is denoted Der''K''(A) * Deep energy retrofit, an energy conservation measure Organizations * Digital Education Revolution, former Australian Government-funded educational reform program * DER rental (Domestic Electric Rentals Ltd), a UK television rentals company * Documentary Educational Resources, a non-profit film producer and distributor Other uses * Def ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Derlin-1
Derlin-1 also known as degradation in endoplasmic reticulum protein 1 is a membrane protein that in humans is encoded by the ''DERL1'' gene. Derlin-1 is located in the membrane of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and is involved in retrotranslocation of specific misfolded proteins and in ER stress. Derlin-1 is widely expressed in thyroid, fat, bone marrow and many other tissues. The protein belongs to the Derlin-family proteins (also called derlins) consisting of derlin-1, derlin-2 and derlin-3 that are components in the endoplasmic reticulum-associated protein degradation (ERAD) pathway. The derlins mediate degradation of misfolded lumenal proteins within ER, and are named ‘der’ for their ‘Degradation in the ER’. Derlin-1 is a mammalian homologue of the yeast '' DER1'' protein, a protein involved in the yeast ERAD pathway. Moreover, derlin-1 is a member of the rhomboid-like clan of polytopic membrane proteins. Overexpression of derlin-1 are associated with many cancers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UBAC2
{{Use dmy dates, date=April 2022 The Union for Bradford and Bingley Staff and Associated Companies (UBAC) was a trade union in the United Kingdom. The union was founded in 1977 as the Bradford and Bingley Staff Association, changing its name in 2001. It represented staff working for Bradford and Bingley and for Alltel Mortgage Solutions, having 2,796 members by 2002. It was a founder member of the Financial Services Staff Federation and of the Alliance for Finance,Gregor Gall, ''Labour unionism in the financial services sector'', p.95 and was affiliated to the Trades Union Congress The Trades Union Congress (TUC) is a national trade union center, national trade union centre, a federation of trade unions that collectively represent most unionised workers in England and Wales. There are 48 affiliated unions with a total of ....Britain's Unions< ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ERAD
Endoplasmic-reticulum-associated protein degradation (ERAD) designates a cellular pathway which targets misfolded proteins of the endoplasmic reticulum for ubiquitination and subsequent degradation by a protein-degrading complex, called the proteasome. Mechanism The process of ERAD can be divided into three steps: Recognition of misfolded or mutated proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum The recognition of misfolded or mutated proteins depends on the detection of substructures within proteins such as exposed hydrophobic regions, unpaired cysteine residues and immature glycans. In mammalian cells for example, there exists a mechanism called glycan processing. In this mechanism, the lectin-type chaperones calnexin/calreticulin (CNX/CRT) provide immature glycoproteins the opportunity to reach their native conformation. They can do this by way of reglucosylating these glycoproteins by an enzyme called UDP-glucose-glycoprotein glucosyltransferase also known as UGGT. Terminal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ER Stress
The unfolded protein response (UPR) is a cellular stress response related to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress. It has been found to be conserved between mammalian species, as well as yeast and worm organisms. The UPR is activated in response to an accumulation of unfolded or misfolded proteins in the lumen of the endoplasmic reticulum. In this scenario, the UPR has three aims: initially to restore normal function of the cell by halting protein translation, degrading misfolded proteins, and activating the signaling pathways that lead to increasing the production of molecular chaperones involved in protein folding. If these objectives are not achieved within a certain time span or the disruption is prolonged, the UPR aims towards apoptosis. Sustained overactivation of the UPR has been implicated in prion diseases as well as several other neurodegenerative diseases, and inhibiting the UPR could become a treatment for those diseases. Diseases amenable to UPR inhibition include Cr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |