|
End Stage Pulmonary Disease
End stage pulmonary disease (ESPD) is the result of chronic progressive lung diseases like COPD, idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, or systemic progressive diseases that affect the lungs such as cystic fibrosis or granulomatosis with polyangiitis. It is defined as when the lungs can no longer or barely remove enough carbon dioxide or supply enough oxygen to meet the body's basic needs. Treatment incorporates a lung transplant Lung transplantation, or pulmonary transplantation, is a surgical procedure in which one or both lungs are replaced by lungs from a donor. Donor lungs can be retrieved from a living or deceased donor. A living donor can only donate one Lobes of t .... References Lung disorders Organ failure {{respiratory-disease-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Journal Of Palliative Nursing
The ''International Journal of Palliative Nursing'' is a monthly peer-reviewed medical journal covering palliative care nursing. It was established in 1995 and is published by the Mark Allen Group. The editor-in-chief is Brian Nyatanga (of the University of Worcester). The journal is abstracted and indexed in CINAHL, Emerging Sources Citation Index, MEDLINE/PubMed, and Scopus Scopus is a scientific abstract and citation database, launched by the academic publisher Elsevier as a competitor to older Web of Science in 2004. The ensuing competition between the two databases has been characterized as "intense" and is c .... References External links * Anesthesiology and palliative medicine journals Academic journals established in 1995 Monthly journals English-language journals {{med-journal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
COPD
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a type of progressive lung disease characterized by chronic respiratory symptoms and airflow limitation. GOLD defines COPD as a heterogeneous lung condition characterized by chronic respiratory symptoms (shortness of breath, cough, sputum production or exacerbations) due to abnormalities of the airways (bronchitis, bronchiolitis) or alveoli (emphysema) that cause persistent, often progressive, airflow obstruction. The main symptoms of COPD include shortness of breath and a cough, which may or may not produce mucus. COPD progressively worsens, with everyday activities such as walking or dressing becoming difficult. While COPD is incurable, it is preventable and treatable. The two most common types of COPD are emphysema and chronic bronchitis and have been the two classic COPD phenotypes. However, this basic dogma has been challenged as varying degrees of co-existing emphysema, chronic bronchitis, and potentially significant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis
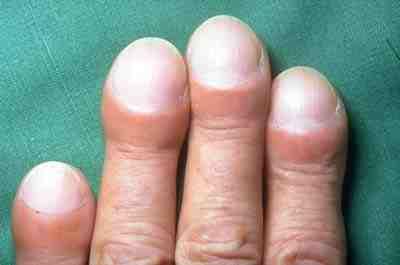
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) synonymous with cryptogenic fibrosing alveolitis is a rare, progressive illness of the respiratory system, characterized by the thickening and stiffening of lung tissue, associated with the formation of scar tissue. It is a type of chronic pulmonary fibrosis characterized by a progressive and irreversible decline in lung function. The tissue in the lungs becomes thick and stiff, which affects the tissue that surrounds the air sacs in the lungs. Symptoms typically include gradual onset of dypsnea, shortness of breath and a dry cough. Other changes may include feeling tired, and nail clubbing, clubbing abnormally large and dome shaped finger and toenails. Complications may include pulmonary hypertension, heart failure, pneumonia or pulmonary embolism. The cause is unknown, hence the term Idiopathic disease, idiopathic. Risk factors include cigarette smoking, gastroesophageal reflux disease, certain viral infections, and genetic predisposition ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cystic Fibrosis
Cystic fibrosis (CF) is a genetic disorder inherited in an autosomal recessive manner that impairs the normal clearance of Sputum, mucus from the lungs, which facilitates the colonization and infection of the lungs by bacteria, notably ''Staphylococcus aureus''. CF is a rare genetic disorder that affects mostly the lungs, but also the pancreas, liver, kidneys, and intestine. The hallmark feature of CF is the accumulation of thick mucus in different organs. Long-term issues include Shortness of breath, difficulty breathing and coughing up mucus as a result of frequent pneumonia, lung infections. Other signs and symptoms may include Sinusitis, sinus infections, failure to thrive, poor growth, Steatorrhea, fatty stool, Nail clubbing, clubbing of the fingers and toes, and infertility in most males. Different people may have different degrees of symptoms. Cystic fibrosis is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner. It is caused by the presence of mutations in both copies (alleles) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Granulomatosis With Polyangiitis
Granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA), formerly known as Wegener's granulomatosis (WG), after Nazi German physician Friedrich Wegener, is a rare, long-term, systemic disorder that involves the formation of granulomas and vasculitis, inflammation of blood vessels (vasculitis). It is an autoimmune disease and a form of vasculitis that affects small- and medium-sized vessels in many organs, but most commonly affects the upper respiratory tract, lungs, and kidneys. The signs and symptoms of GPA are highly varied and reflect which organs are supplied by the affected blood vessels. Typical signs and symptoms include epistaxis, nosebleeds, stuffy nose and crustiness of nasal secretions, and uveitis, inflammation of the uveal layer of the eye. Damage to the heart, lungs, and kidneys can be fatal. The cause of GPA is unknown. Genetics have a role in GPA, though the risk of inheritance appears to be low. GPA treatment depends on the severity of the disease. Severe disease is typically ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lung Transplantation
Lung transplantation, or pulmonary transplantation, is a surgical procedure in which one or both lungs are replaced by lungs from a donor. Donor lungs can be retrieved from a living or deceased donor. A living donor can only donate one lung lobe. With some lung diseases, a recipient may only need to receive a single lung. With other lung diseases such as cystic fibrosis, it is imperative that a recipient receive two lungs. While lung transplants carry certain associated risks, they can also extend life expectancy and enhance the quality of life for those with end stage pulmonary disease. Qualifying conditions Lung transplantation is the therapeutic measure of last resort for patients with end-stage lung disease who have exhausted all other available treatments without improvement. A variety of conditions may make such surgery necessary. The most common indications for a lung transplant are pulmonary fibrosis, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), cystic fibrosis, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lung Disorders
Respiratory diseases, or lung diseases, are pathological conditions affecting the organs and tissues that make gas exchange difficult in air-breathing animals. They include conditions of the respiratory tract including the trachea, bronchi, bronchioles, alveoli, pleurae, pleural cavity, the nerves and muscles of respiration. Respiratory diseases range from mild and self-limiting, such as the common cold, influenza, and pharyngitis to life-threatening diseases such as bacterial pneumonia, pulmonary embolism, tuberculosis, acute asthma, lung cancer, and severe acute respiratory syndromes, such as COVID-19. Respiratory diseases can be classified in many different ways, including by the organ or tissue involved, by the type and pattern of associated signs and symptoms, or by the cause of the disease. The study of respiratory disease is known as pulmonology. A physician who specializes in respiratory disease is known as a pulmonologist, a chest medicine specialist, a respira ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |