|
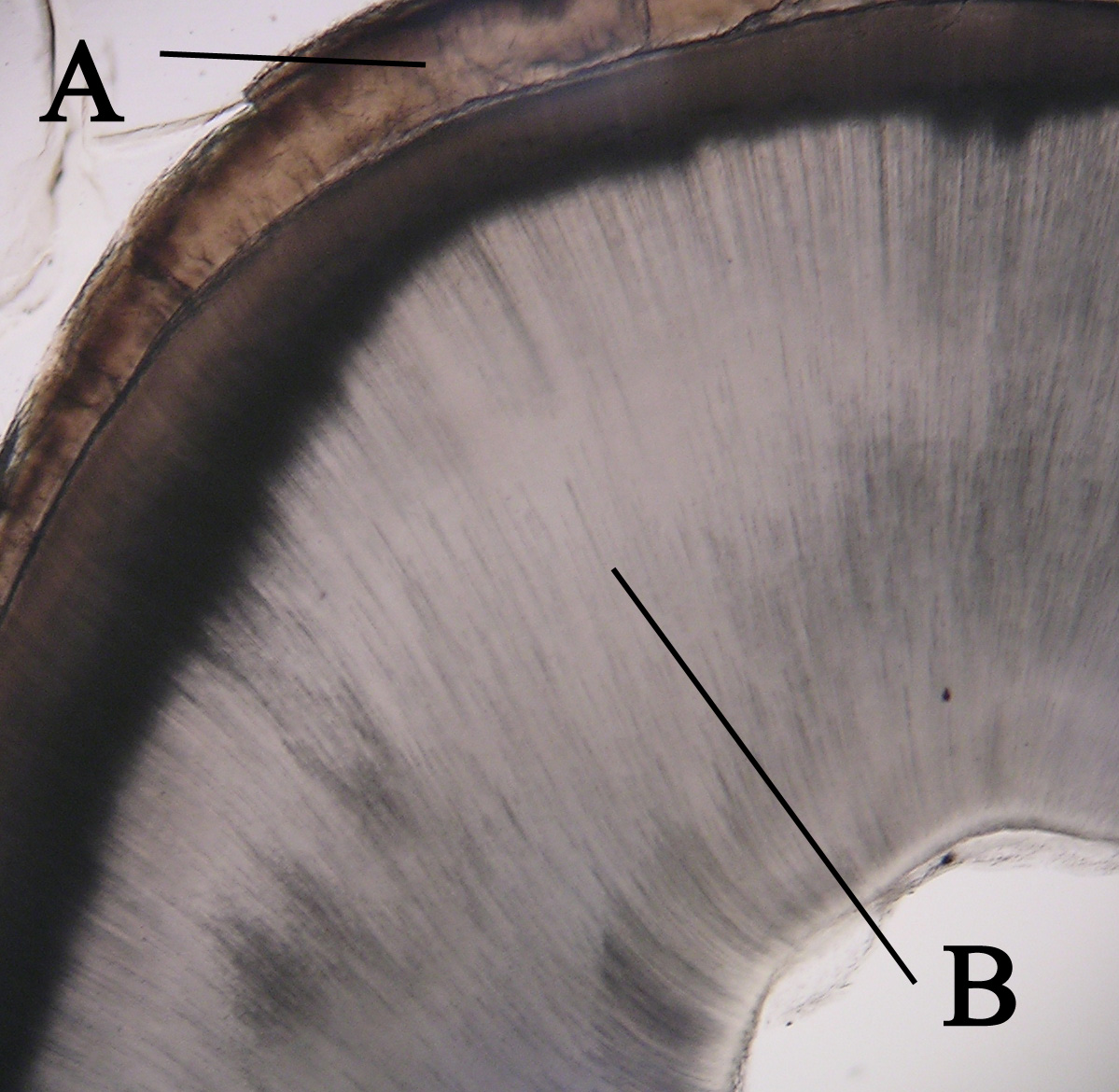
Enamel Spindles
Enamel spindles are "short, linear defects, found at the dentinoenamel junction (DEJ) and extend into the enamel, often being more prevalent at the cusp tips."Histology Course Notes: "Mature Enamel", New Jersey Dental School, 2003-2004, page 2. The DEJ is the interface of the enamel and the underlying dentin. Because they are "formed by entrapment of odontoblast processes between ameloblasts prior to and during amelogenesis Amelogenesis is the process of forming tooth enamel, the hard, protective outer layer of teeth. This process begins during tooth development after the initial formation of dentin ( dentinogenesis), the layer beneath the enamel. The inner enamel e ...," they cannot be found at the enamel surface protruding inward, as enamel lamellae are often located. Enamel spindles are often confused with two other entities: enamel lamellae and enamel tufts. Lamellae are linear enamel defects that extend from the surface of the enamel towards the DEJ, or vice versa. En ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tooth Enamel
Tooth enamel is one of the four major Tissue (biology), tissues that make up the tooth in humans and many animals, including some species of fish. It makes up the normally visible part of the tooth, covering the Crown (tooth), crown. The other major tissues are dentin, cementum, and Pulp (tooth), dental pulp. It is a very hard, white to off-white, highly mineralised substance that acts as a barrier to protect the tooth but can become susceptible to degradation, especially by acids from food and drink. In rare circumstances enamel fails to form, leaving the underlying dentin exposed on the surface. Features Enamel is the hardest substance in the human body and contains the highest percentage of minerals (at 96%),Ross ''et al.'', p. 485 with water and organic material composing the rest.Ten Cate's Oral Histology, Nancy, Elsevier, pp. 70–94 The primary mineral is hydroxyapatite, which is a crystalline calcium phosphate. Enamel is formed on the tooth while the tooth develops wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cusp (dentistry)
A cusp is a pointed, projecting, or elevated feature. In animals, it is usually used to refer to raised points on the crowns of teeth. The concept is also used with regard to the leaflets of the four heart valves. The mitral valve, which has two Heart valve#Structure, cusps, is also known as the bicuspid valve, and the tricuspid valve has three cusps. In humans A cusp is an Commonly used terms of relationship and comparison in dentistry, occlusal or Commonly used terms of relationship and comparison in dentistry, incisal eminence on a tooth. canine tooth, Canine teeth, otherwise known as cuspids, each possess a single cusp, while premolars, otherwise known as bicuspids, possess two each. Molars normally possess either four or five cusps. In certain populations the maxillary molars, especially first molars, will possess a fifth cusp situated on the Commonly used terms of relationship and comparison in dentistry, mesiolingual cusp known as the Cusp of Carabelli. One other variat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interface (chemistry)
In the physical sciences, an interface is the boundary between two spatial regions occupied by different matter, or by matter in different physical states. The interface between matter and air, or matter and vacuum, is called a surface, and studied in surface science. In thermal equilibrium, the regions in contact are called phases, and the interface is called a phase boundary. An example for an interface out of equilibrium is the grain boundary in polycrystalline matter. The importance of the interface depends on the type of system: the bigger the quotient area/volume, the greater the effect the interface will have. Consequently, interfaces are very important in systems with large interface area-to-volume ratios, such as colloids. Interfaces can be flat or curved. For example, oil droplets in a salad dressing are spherical but the interface between water and air in a glass of water is mostly flat. Surface tension is the physical property which rules interface process ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dentin
Dentin ( ) (American English) or dentine ( or ) (British English) () is a calcified tissue (biology), tissue of the body and, along with tooth enamel, enamel, cementum, and pulp (tooth), pulp, is one of the four major components of teeth. It is usually covered by enamel on the crown and cementum on the root and surrounds the entire pulp. By volume, 45% of dentin consists of the mineral hydroxyapatite, 33% is organic material, and 22% is water. Yellow in appearance, it greatly affects the color of a tooth due to the translucency of enamel. Dentin, which is less mineralized and less brittle than enamel, is necessary for the support of enamel. Dentin rates approximately 3 on the Mohs scale of mineral hardness. There are two main characteristics which distinguish dentin from enamel: firstly, dentin forms throughout life; secondly, dentin is sensitive and can become hypersensitive to changes in temperature due to the sensory function of odontoblasts, especially when enamel recedes an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Odontoblast
In vertebrates, an odontoblast is a cell of neural crest origin that is part of the outer surface of the dental pulp, and whose biological function is dentinogenesis, which is the formation of dentin, the substance beneath the tooth enamel on the crown and the cementum on the root. Structure Odontoblasts are large columnar cells, whose cell bodies are arranged along the interface between dentin and pulp, from the crown to the cervix to the root apex in a mature tooth. The cell is rich in endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi complex, especially during primary dentin formation, which allows it to have a high secretory capacity; it first forms the collagenous matrix to form predentin, then mineral levels to form the mature dentin. Odontoblasts form approximately 4 μm of predentin daily during tooth development.Ten Cate's Oral Histology, Nanci, Elsevier, 2013, page 170 During secretion after differentiation from the outer cells of the dental papilla, it is noted that it is polarized s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ameloblast
Ameloblasts are cells present only during tooth development that deposit tooth enamel, which is the hard outermost layer of the tooth forming the surface of the crown. Structure Each ameloblast is a columnar cell approximately 4 micrometers in diameter, 40 micrometers in length and is hexagonal in cross section. The secretory end of the ameloblast ends in a six-sided pyramid-like projection known as the Tomes' process. The angulation of the Tomes' process is significant in the orientation of enamel rods, the basic unit of tooth enamel. Distal terminal bars are junctional complexes that separate the Tomes' processes from ameloblast proper. Development Ameloblasts are derived from oral epithelium tissue of ectodermal origin. Their differentiation from preameloblasts (whose origin is from inner enamel epithelium) is a result of signaling from the ectomesenchymal cells of the dental papilla. Initially the preameloblasts will differentiate into presecretory ameloblasts and then ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amelogenesis
Amelogenesis is the process of forming tooth enamel, the hard, protective outer layer of teeth. This process begins during tooth development after the initial formation of dentin ( dentinogenesis), the layer beneath the enamel. The inner enamel epithelium (IEE), a layer of cells within the developing tooth, plays a crucial role by signaling the differentiation of specialized cells called ameloblasts, which then secrete the proteins and minerals that make up enamel. The formation of dentin is essential for amelogenesis to occur, and a reciprocal signaling process between the developing dentin and the IEE-derived ameloblasts ensures the proper coordination of these two crucial stages of tooth development. Stages Amelogenesis is considered to have three stages. The first stage is known as the inductive stage, the second is the secretory stage, and the third stage is known as the maturation stage. During the inductive stage, ameloblast differentiation from IEE is initiated. Prote ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enamel Lamellae
Enamel lamellae are a type of hypomineralized structure in teeth that extend either from the dentinoenamel junction (DEJ) to the surface of the enamel, or vice versa. In essence, they are prominent linear enamel defects, but are of no clinical consequence.Histology Course Notes: "Mature Enamel", New Jersey Dental School, 2003-2004, page 2. These structures contain proteins, proteoglycans, and lipids. Enamel lamellae should not be confused with two similar entities, '' enamel tufts'' and ''enamel spindles''. Enamel tufts are small branching defects that are found only at the DEJ, and so differ from lamellae which can be facing either direction and are strictly linear. Enamel spindles are also linear defects, but they too can be found only at the DEJ, because they are formed by entrapment of odontoblast processes between ameloblasts prior to and during amelogenesis Amelogenesis is the process of forming tooth enamel, the hard, protective outer layer of teeth. This process begin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enamel Tufts
Enamel tufts are hypomineralized ribbon-like structures that run longitudinally to the tooth axis and extend from the dentinoenamel junction (DEJ) one fifth to a third into the enamel. They are called ''tufts'' due to their wavy look within the enamel microstructure. Biomechanically, enamel tufts are ''closed cracks'' or defects which, in their manner of propagating, act to prevent enamel fractures. This aspect is being studied to see how to make more fracture-resistant materials. However, they can also form without stress during enamel development. Enamel tufts are most common in the enamel of molars of animals that crush hard food objects, such as nuts (crushed by apes) and shellfish (crushed by sea otters). Microstructure Each tuft consists of several unconnected leaves that start near the dentinoenamel junction. These defects as they pass through the enamel rods to the surface become progressively more fragmented and fibrillar. Scanning electron micrography finds that th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dental Enamel
Tooth enamel is one of the four major Tissue (biology), tissues that make up the tooth in humans and many animals, including some species of fish. It makes up the normally visible part of the tooth, covering the Crown (tooth), crown. The other major tissues are dentin, cementum, and Pulp (tooth), dental pulp. It is a very hard, white to off-white, highly mineralised substance that acts as a barrier to protect the tooth but can become susceptible to degradation, especially by acids from food and drink. In rare circumstances enamel fails to form, leaving the underlying dentin exposed on the surface. Features Enamel is the hardest substance in the human body and contains the highest percentage of minerals (at 96%),Ross ''et al.'', p. 485 with water and organic material composing the rest.Ten Cate's Oral Histology, Nancy, Elsevier, pp. 70–94 The primary mineral is hydroxyapatite, which is a crystalline calcium phosphate. Enamel is formed on the tooth while the tooth develops wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |