|
Electronic Centralised Aircraft Monitor
An electronic centralised aircraft monitoring (ECAM) or electronic centralized aircraft monitoring is a system on Airbus aircraft that monitor aircraft functions and relays them to the pilots. It also produces messages detailing failures and in certain cases, lists procedures to undertake to correct the problem. History ECAM is similar to other systems, known as Engine Indicating and Crew Alerting System (EICAS), used by Boeing, Bombardier Inc., Bombardier, COMAC, Dornier Flugzeugwerke, Dornier, Embraer, Saab AB, Saab, and Xi'an Aircraft Industrial Corporation, Xi'an, ''Centralized Fault Detection System'' (CFDS) on McDonnell Douglas, or ''Engine Warning Display'' (EWD) on ATR (aircraft manufacturer), ATR, which display data concerning aircraft systems and also failures. Airbus developed ECAM, such that it not only provided the features of EICAS, but also displayed corrective action to be taken by the pilot, as well as system limitations after the failures. Using a colour-cod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ECAM Airbus
ECAM may refer to: * Electronic centralised aircraft monitor, a system that monitors aircraft functions and relays them to the pilots * ''Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine'', a medical journal * École Catholique des Arts et Métiers, an engineering school in Lyon, France * ECAM Rennes - Louis de Broglie, an engineering school in Rennes, France * The Madrid Film School (), a film school in Madrid, Spain See also * {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cockpit
A cockpit or flight deck is the area, on the front part of an aircraft, spacecraft, or submersible, from which a pilot controls the vehicle. The cockpit of an aircraft contains flight instruments on an instrument panel, and the controls that enable the pilot to fly the aircraft. In most airliners, a door separates the cockpit from the aircraft cabin. After the September 11, 2001 attacks, all major airlines fortified their cockpits against access by hijackers. Etymology The word cockpit seems to have been used as a nautical term in the 17th century, without reference to cock fighting. It referred to an area in the rear of a ship where the cockswain's station was located, the cockswain being the pilot of a smaller "boat" that could be dispatched from the ship to board another ship or to bring people ashore. The word "cockswain" in turn derives from the old English terms for "boat-servant" (''coque'' is the French word for "shell"; and ''swain'' was old English for boy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avionics
Avionics (a portmanteau of ''aviation'' and ''electronics'') are the Electronics, electronic systems used on aircraft. Avionic systems include communications, Air navigation, navigation, the display and management of multiple systems, and the hundreds of systems that are fitted to aircraft to perform individual functions. These can be as simple as a searchlight for a police helicopter or as complicated as the tactical system for an airborne early warning platform. History The term "avionics" was coined in 1949 by Philip J. Klass, senior editor at ''Aviation Week & Space Technology'' magazine as a portmanteau of "aviation electronics". Radio communication was first used in aircraft just prior to World War I. The first Airborne radio relay, airborne radios were in zeppelins, but the military sparked development of light radio sets that could be carried by heavier-than-air craft, so that aerial reconnaissance biplanes could report their observations immediately in case they we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aircraft Instruments
Flight instruments are the instruments in the cockpit of an aircraft that provide the pilot with data about the flight situation of that aircraft, such as altitude, airspeed, Variometer, vertical speed, heading and much more other crucial information in flight. They improve safety by allowing the pilot to fly the aircraft in level flight, and make turns, without a reference outside the aircraft such as the horizon. Visual flight rules (VFR) require an airspeed indicator, an altimeter, and a compass or other suitable magnetic direction indicator. Instrument flight rules (IFR) additionally require a gyroscopic pitch-bank (artificial horizon), direction (directional gyro) and rate of turn indicator, plus a slip-skid indicator, adjustable altimeter, and a clock. Flight into instrument meteorological conditions (IMC) require radio navigation instruments for precise takeoffs and landings. The term is sometimes used loosely as a synonym for cockpit, cockpit instruments as a whole, in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electronic Flight Instrument System
In aviation, an electronic flight instrument system (EFIS) is a flight instrument display system in an aircraft cockpit that displays flight data electronically rather than electromechanically. An EFIS normally consists of a primary flight display (PFD), multi-function display (MFD), and an engine indicating and crew alerting system (EICAS) display. Early EFIS models used cathode-ray tube (CRT) displays, but liquid crystal displays (LCD) are now more common. The complex electromechanical attitude director indicator (ADI) and horizontal situation indicator (HSI) were the first candidates for replacement by EFIS. Now, however, few flight deck instruments cannot be replaced by an electronic display. Display units Primary flight display (PFD) On the flight deck, the display units are the most obvious parts of an EFIS system, and are the features that lead to the term ''glass cockpit''. The display unit that replaces the artificial horizon is called the primary flight di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glass Cockpit
A glass cockpit is an aircraft cockpit that features an array of electronic (digital) flight instrument display device, displays, typically large liquid-crystal display, LCD screens, rather than traditional Analog device, analog dials and gauges. While a traditional cockpit relies on numerous mechanical gauges (nicknamed "steam gauges") to display information, a glass cockpit uses several multi-function displays and a primary flight display driven by flight management systems, that can be adjusted to show flight information as needed. This simplifies aircraft operation and navigation and allows aviator, pilots to focus only on the most pertinent information. They are also popular with airline companies as they usually eliminate the need for a flight engineer, saving costs. In recent years the technology has also become widely available in small aircraft. As aircraft displays have modernized, the sensors that feed them have modernized as well. Traditional gyroscope, gyroscopic fli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Airbus A380
The Airbus A380 is a very large wide-body airliner, developed and produced by Airbus until 2021. It is the world's largest passenger airliner and the only full-length double-deck jet airliner. Airbus studies started in 1988, and the project was announced in 1990 to challenge the dominance of the Boeing 747 in the long-haul market. The then-designated A3XX project was presented in 1994 and Airbus launched the €–billion ($10.7–billion) A380 programme on 19 December 2000. The first prototype was unveiled in Toulouse, France on 18 January 2005, commencing its first flight on 27 April 2005. It then obtained its type certificate from the European Aviation Safety Agency (EASA) and the US Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) on 12 December 2006. Due to difficulties with the electrical wiring, the initial production was delayed by two years and the development costs almost doubled. It was first delivered to Singapore Airlines on 15 October 2007 and entered service on 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Airbus A350
The Airbus A350 is a flight length, long-range, wide-body twin-engine airliner developed and produced by Airbus. The initial A350 design proposed in 2004, in response to the Boeing 787 Dreamliner, would have been a development of the Airbus A330 with composite wings, advanced winglets, and new efficient engines. Due to inadequate market support, Airbus switched in 2006 to a clean-sheet "XWB" (eXtra Wide Body) design, powered by two Rolls-Royce Trent XWB high bypass turbofan engines. The prototype first flew on 14 June 2013 from Toulouse, France. Type certification from the European Aviation Safety Agency (EASA) was obtained in September 2014, followed by certification from the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) two months later. The A350 is the first Airbus aircraft largely made of carbon-fibre-reinforced polymers. The fuselage is designed around a 3-3-3 nine-across economy cross-section, an increase from the eight-across A330/A340 2-4-2 configuration. It has a common t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
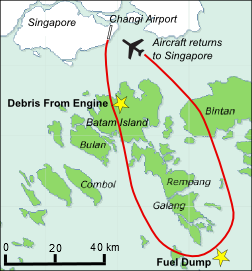
Qantas Flight 32
Qantas Flight 32 was a regularly scheduled passenger flight from London to Sydney via Singapore. On 4 November 2010, the aircraft operating the route, an Airbus A380, suffered an Turbine engine failure#Contained and uncontained failures, uncontained failure in one of its four Rolls-Royce Trent 900 engines. The failure occurred over the Riau Islands, Indonesia, four minutes after takeoff from Changi Airport, Singapore Changi Airport. After Holding (aeronautics), holding for almost two hours to assess the situation, the aircraft made a successful emergency landing at Changi. No injuries occurred to the passengers, crew, or people on the ground, despite debris from the aircraft falling onto houses in Batam. On inspection, a turbine disc in the aircraft's Aircraft engine#Engine position numbering, number-two engine (on the port and starboard, port side nearer the fuselage) was found to have disintegrated, causing extensive damage to the nacelle, wing, fuel system, landing gear, fli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Airbus A220
The Airbus A220 is a family of five-abreast narrow-body airliners by Airbus Canada Limited Partnership (ACLP). It was originally developed by Bombardier Aviation and had two years in service as the Bombardier CSeries. The program was launched on 13 July 2008. The smaller A220-100 (formerly CS100) Maiden flight, first flew on 16 September 2013, received an initial type certificate from Transport Canada on 18 December 2015, and entered service on 15 July 2016 with launch operator Swiss Global Air Lines. The longer A220-300 (formerly CS300) first flew on 27 February 2015, received an initial type certificate on 11 July 2016, and entered service with airBaltic on 14 December 2016. Both launch operators recorded better-than-expected fuel burn and dispatch reliability, as well as positive feedback from passengers and crew. In July 2018, the aircraft was rebranded as the A220 after Airbus acquired a majority stake in the programme through a joint venture that became ACLP in June 20 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Airbus A310
The Airbus A310 is a wide-body aircraft, Aircraft design process, designed and manufactured by Airbus Industrie GIE, then a consortium of European aerospace manufacturers. Airbus had identified a demand for an aircraft smaller than the Airbus A300, A300, the first Twinjet, twin-jet wide-body. On 7 July 1978, the A310 (initially the A300B10) was launched with orders from Swissair and Lufthansa. On 3 April 1982, the first prototype conducted its maiden flight, and the A310 received its type certificate on 11 March 1983. Keeping the same eight-abreast cross-section, the A310 is shorter than the initial A300 variants, and has a smaller wing, down from . The A310 introduced a two-crew glass cockpit, later adopted for the A300-600 with a common type rating. It was powered by the same General Electric CF6-80 or Pratt & Whitney JT9D then PW4000 turbofan jet engines. It can seat 220 passengers in two classes, or 240 in all-economy, and has a flying range up to . It has overwing exits ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Airbus A300-600
The Airbus A300 is Airbus' first production aircraft and the world's first twin-engine, double-aisle (wide-body) airliner. It was developed by ''Airbus Industrie GIE'', now merged into Airbus SE, and manufactured from 1971 to 2007. In September 1967, aircraft manufacturers in France, West Germany and the United Kingdom signed an initial memorandum of understanding to collaborate to develop an innovative large airliner. The French and West Germans reached a firm agreement on 29 May 1969, after the British withdrew from the project on 10 April 1969. A new collaborative aerospace company, ''Airbus Industrie GIE'', was formally created on 18 December 1970 to develop and produce it. The A300 prototype first flew on 28 October 1972. The first twin-engine widebody airliner, the A300 typically seats 247 passengers in two classes over a range of 5,375 to 7,500 km (2,900 to 4,050 nmi; ). Initial variants are powered by General Electric CF6-50 or Pratt & Whitney JT9D turb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |