|
Eflornithine
Eflornithine, sold under the brand name Vaniqa among others, is a medication used to treat African trypanosomiasis (sleeping sickness) and excessive hair growth on the face in women. Specifically it is used for the second stage of sleeping sickness caused by '' T. b. gambiense'' and may be used with nifurtimox. It is taken intravenously (injection into a vein) or topically. It is an ornithine decarboxylase inhibitor. Common side effects when applied as a cream include rash, redness, and burning. Side effects of the injectable form include bone marrow suppression, vomiting, and seizures. It is unclear if it is safe to use during pregnancy or breastfeeding. It is recommended typically for children over the age of 12. Eflornithine was developed in the 1970s and came into medical use in 1990. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. In the United States the injectable form can be obtained from the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
African Trypanosomiasis
African trypanosomiasis is an insect-borne parasitic infection of humans and other animals. Human African trypanosomiasis (HAT), also known as African sleeping sickness or simply sleeping sickness, is caused by the species ''Trypanosoma brucei''. Humans are infected by two types, ''Trypanosoma brucei gambiense'' (TbG) and ''Trypanosoma brucei rhodesiense'' (TbR). TbG causes over 92% of reported cases. Both are usually transmitted by the bite of an infected tsetse fly and are most common in rural areas. Initially, the first stage of the disease is characterized by fevers, headaches, itchiness, and joint pains, beginning one to three weeks after the bite. Weeks to months later, the second stage begins with confusion, poor coordination, numbness, and trouble sleeping. Diagnosis involves detecting the parasite in a blood smear or lymph node fluid. A lumbar puncture is often needed to tell the difference between first- and second-stage disease. Prevention of severe disease in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nifurtimox-eflornithine Combination Treatment
Nifurtimox/eflornithine is a combination of two antiparasitic drugs, nifurtimox and eflornithine, used in the treatment of African trypanosomiasis (sleeping sickness). It was developed by Drugs for Neglected Diseases initiative and partners and is included in the World Health Organization's Model List of Essential Medicines. It is distributed in a kit with material to treat four patients, which weighs 39 kg and has a volume of 170 dm3 , making the transport to remote rural hospitals a logistical challenge. A treatment regimen known as nifurtimox-eflornithine combination treatment (NECT) is used in second stage gambiense African trypanosomiasis throughout Africa where the disease is endemic. The regimen involves slow infusion of 400 mg of eflornithine every 12 hours for 7 days combined with 15 mg/kg of nifurtimox orally three times a day for 10 days. The World Health Organization 2019 guidelines still recommend NECT in cases of advanced disease, but otherwise advise the use of f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nifurtimox
Nifurtimox, sold under the brand name Lampit, is a medication used to treat Chagas disease and sleeping sickness. For sleeping sickness it is used together with eflornithine in nifurtimox-eflornithine combination treatment. In Chagas disease it is a second-line option to benznidazole. It is given by mouth. Common side effects include abdominal pain, headache, nausea, and weight loss. There are concerns from animal studies that it may increase the risk of cancer but these concerns have not been found in human trials. Nifurtimox is not recommended in pregnancy or in those with significant kidney or liver problems. It is a type of nitrofuran. Nifurtimox came into medication use in 1965. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. It is not available commercially in Canada. It was approved for medical use in the United States in August 2020. In regions of the world where the disease is common nifurtimox is provided for free by the World Health Organiz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ornithine Decarboxylase
The enzyme ornithine decarboxylase (, ODC) catalyzes the decarboxylation of ornithine (a product of the urea cycle) to form putrescine. This reaction is the committed step in polyamine synthesis. In humans, this protein has 461 amino acids and forms a homodimer. In humans, ornithine decarboxylase (ODC) is expressed by the gene ''ODC1''. The protein ODC is sometimes referred to as "ODC1" in research pertaining to humans and mice, but certain species such as ''Drosophila'' (''dODC2''), species of Solanaceae plant family (''ODC2''), and the lactic acid bacteria '' Paucilactobacillus wasatchensis'' (''odc2'') have been shown to have a second ODC gene. Reaction mechanism Lysine 69 on ornithine decarboxylase (ODC) binds the cofactor pyridoxal phosphate to form a Schiff base. Ornithine displaces the lysine to form a Schiff base attached to orthonine, which decarboxylates to form a quinoid intermediate. This intermediate rearranges to form a Schiff base attached to putrescine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melarsoprol
Melarsoprol is an arsenic-containing medication used for the treatment of sleeping sickness (African trypanosomiasis). It is specifically used for second-stage disease caused by '' Trypanosoma brucei rhodesiense'' when the central nervous system is involved. For '' Trypanosoma brucei gambiense'', eflornithine or fexinidazole is usually preferred. It is effective in about 95% of people. It is given by injection and is known by patients as "fire in the veins" . Melarsoprol has a high number of side effects. Common side effects include brain dysfunction, numbness, rashes, and kidney and liver problems. About 1–5% of people die during treatment, although this is tolerated due to sleeping sickness itself having a practically 100% mortality rate when untreated. In those with glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency, red blood cell breakdown may occur. It has not been studied in pregnancy. It works by blocking pyruvate kinase, an enzyme required for aerobic metabolism ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hirsutism
Hirsutism is excessive body hair on parts of the body where hair is normally absent or minimal. The word is from early 17th century: from Latin ''hirsutus'' meaning "hairy". It usually refers to a male pattern of hair growth in a female that may be a sign of a more serious medical condition, especially if it develops well after puberty. Cultural stigma against hirsutism can cause much psychological distress and social difficulty. Discrimination based on facial hirsutism often leads to the avoidance of social situations and to symptoms of anxiety and depression. Hirsutism is usually the result of an underlying endocrine imbalance, which may be adrenal, ovarian, or central. It can be caused by increased levels of androgen hormones. The amount and location of the hair is measured by a Ferriman–Gallwey score. It is different from hypertrichosis, which is excessive hair growth anywhere on the body. Treatments may include certain birth control pills, antiandrogens, or ins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WHO Model List Of Essential Medicines
The WHO Model List of Essential Medicines (aka Essential Medicines List or EML), published by the World Health Organization (WHO), contains the medications considered to be most effective and safe to meet the most important needs in a health system. The list is frequently used by countries to help develop their own local lists of essential medicines. , more than 155 countries have created national lists of essential medicines based on the World Health Organization's model list. This includes both Developed country, developed and Developing country, developing countries. The list is divided into core items and complementary items. The core items are deemed to be the most cost-effective options for key health problems and are usable with little additional health care resources. The complementary items either require additional infrastructure such as specially trained health care providers or diagnostic equipment or have a lower cost–benefit ratio. About 25% of items are in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suicide Inhibition
In biochemistry, suicide inhibition, also known as suicide inactivation or mechanism-based inhibition, is an irreversible form of enzyme inhibition that occurs when an enzyme binds a substrate analog and forms an irreversible complex with it through a covalent bond during the normal catalysis reaction. The inhibitor binds to the active site where it is modified by the enzyme to produce a reactive group that reacts irreversibly to form a stable inhibitor-enzyme complex. This usually uses a prosthetic group or a coenzyme, forming electrophilic alpha and beta unsaturated carbonyl compounds and imines. Examples Some clinical examples of suicide inhibitors include: * Disulfiram, which inhibits the acetaldehyde dehydrogenase enzyme. * Aspirin, which inhibits cyclooxygenase 1 and 2 enzymes. * Clavulanic acid, which inhibits β-lactamase: clavulanic acid covalently bonds to a serine residue in the active site of the β-lactamase, restructuring the clavulanic acid molecule, creating a muc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suramin
Suramin is a medication used to treat African sleeping sickness and river blindness. It is the treatment of choice for sleeping sickness without central nervous system involvement. It is given by injection into a vein. Suramin causes a fair number of side effects. Common side effects include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, headache, skin tingling, and weakness. Sore palms of the hands and soles of the feet, trouble seeing, fever, and abdominal pain may also occur. Severe side effects may include low blood pressure, decreased level of consciousness, kidney problems, and low blood cell levels. It is unclear if it is safe when breastfeeding. Suramin was made at least as early as 1916. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. In the United States it can be acquired from the Centers for Disease Control (CDC). In regions of the world where the disease is common suramin is provided for free by the World Health Organization (WHO). Medical uses Suramin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thrombocytopenia
In hematology, thrombocytopenia is a condition characterized by abnormally low levels of platelets (also known as thrombocytes) in the blood. Low levels of platelets in turn may lead to prolonged or excessive bleeding. It is the most common coagulation disorder among intensive care units, intensive care patients and is seen in a fifth of medical patients and a third of surgical patients. A normal human platelet count ranges from 150,000 to 450,000 platelets/microliter (μL) of blood. Values outside this range do not necessarily indicate disease. One common definition of thrombocytopenia requiring emergency treatment is a platelet count below 50,000/μL. Thrombocytopenia can be contrasted with the conditions associated with an abnormally ''high'' level of platelets in the blood – thrombocythemia (when the cause is unknown), and thrombocytosis (when the cause is known). Signs and symptoms Thrombocytopenia usually asymptomatic, has no symptoms and is picked up on a routine comp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
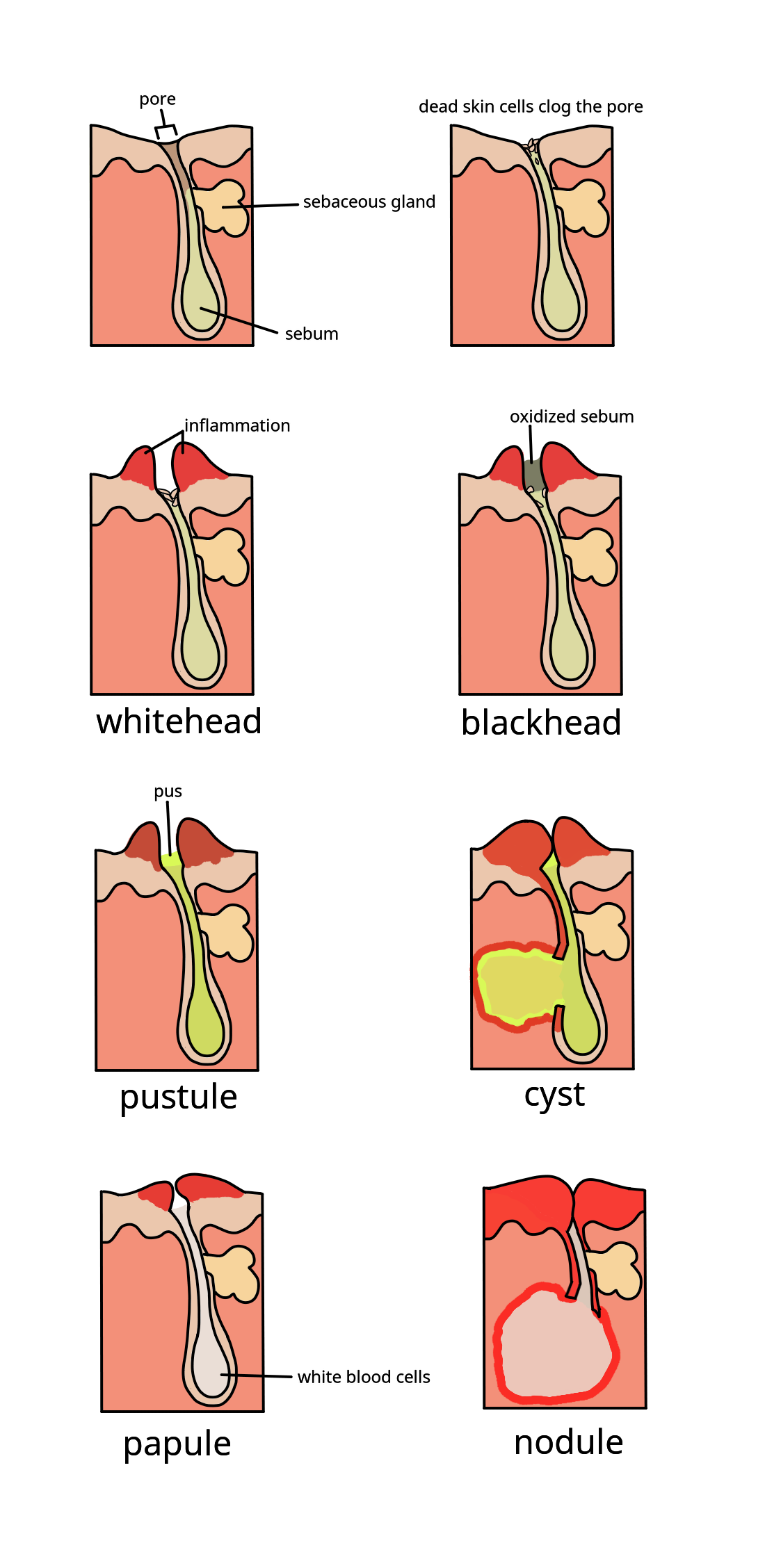
Acne
Acne ( ), also known as ''acne vulgaris'', is a long-term Cutaneous condition, skin condition that occurs when Keratinocyte, dead skin cells and Sebum, oil from the skin clog hair follicles. Typical features of the condition include comedo, blackheads or whiteheads, pimples, oily skin, and possible scarring. It primarily affects skin with a relatively high number of sebaceous gland, oil glands, including the face, upper part of the chest, and back. The resulting appearance can lead to lack of confidence, anxiety (mood), anxiety, reduced self-esteem, and, in extreme cases, clinical depression, depression or suicidal ideations, thoughts of suicide. Susceptibility to acne is primarily genetic in 80% of cases. The roles of diet and cigarette smoking in the condition are unclear, and neither hygiene, cleanliness nor exposure to sunlight are associated with acne. In both sexes, hormones called androgens appear to be part of the underlying mechanism, by causing increased production ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decarboxylation
Decarboxylation is a chemical reaction that removes a carboxyl group and releases carbon dioxide (CO2). Usually, decarboxylation refers to a reaction of carboxylic acids, removing a carbon atom from a carbon chain. The reverse process, which is the first chemical step in photosynthesis, is called carboxylation, the addition of CO2 to a compound. Enzymes that catalyze decarboxylations are called decarboxylases or, the more formal term, carboxy-lyases (Enzyme Commission number, EC number 4.1.1). In organic chemistry The term "decarboxylation" usually means replacement of a carboxyl group () with a hydrogen atom: : Decarboxylation is one of the oldest known organic reactions. It is one of the processes assumed to accompany pyrolysis and destructive distillation. Overall, decarboxylation depends upon stability of the carbanion synthon , although the anion may not be a true chemical intermediate. Typically, carboxylic acids decarboxylate slowly, but carboxylic acids with an α el ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |