|
Effect Of Taxes And Subsidies On Price
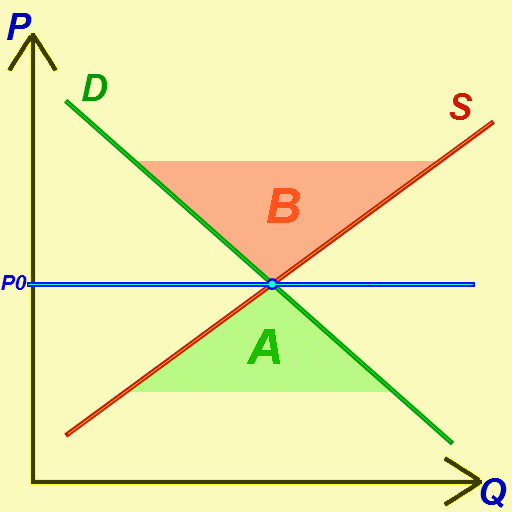
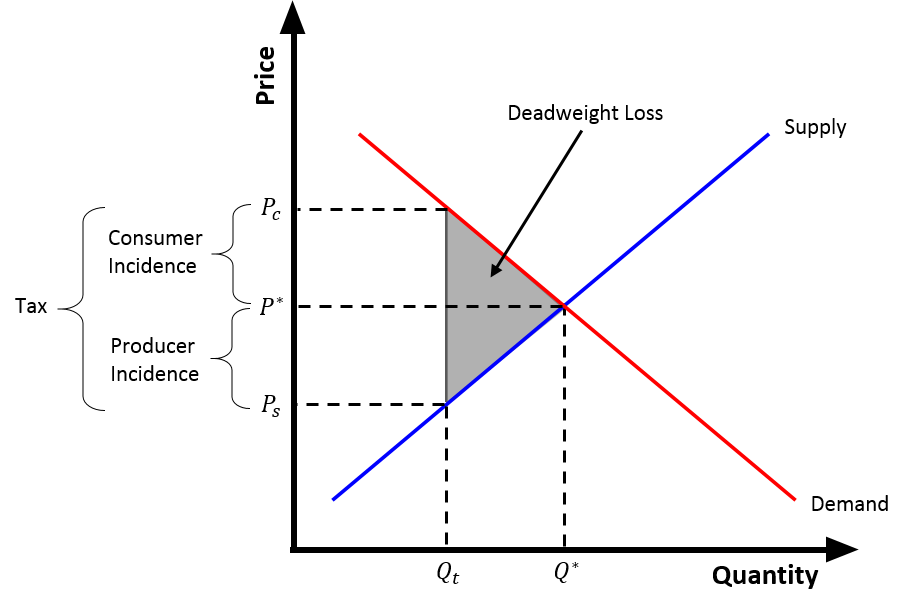
Taxes and subsidies change the price of goods and, as a result, the quantity consumed. There is a difference between an ad valorem tax and a specific tax or subsidy in the way it is applied to the price of the good. In the end levying a tax moves the market to a new equilibrium where the price of a good paid by buyers increases and the proportion of the price received by sellers decreases. The incidence of a tax does not depend on whether the buyers or sellers are taxed since taxes levied on sellers are likely to be met by raising the price charged to buyers. Most of the burden of a tax falls on the less elastic side of the market because of a lower ability to respond to the tax by changing the quantity sold or bought. Introduction of a subsidy, on the other hand, may either lowers the price of production which encourages firms to produce more, or lowers the price paid by buyers, encouraging higher sales volume. Such a policy is beneficial both to sellers and buyers. Specific tax ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subsidy
A subsidy, subvention or government incentive is a type of government expenditure for individuals and households, as well as businesses with the aim of stabilizing the economy. It ensures that individuals and households are viable by having access to essential goods and services while giving businesses the opportunity to stay afloat and/or competitive. Subsidies not only promote long term economic stability but also help governments to respond to economic shocks during a recession or in response to unforeseen shocks, such as the COVID-19 pandemic. Subsidies take various forms— such as direct government expenditures, tax incentives, soft loans, price support, and government provision of goods and services. For instance, the government may distribute direct payment subsidies to individuals and households during an economic downturn in order to help its citizens pay their bills and to stimulate economic activity. Here, subsidies act as an effective financial aid issued when t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ad Valorem Tax
An ''ad valorem'' tax (Latin for "according to value") is a tax whose amount is based on the value of a transaction or of a property. It is typically imposed at the time of a transaction, as in the case of a sales tax or value-added tax (VAT). An ''ad valorem'' tax may also be imposed annually, as in the case of a real or personal property tax, or in connection with another significant event (e.g. inheritance tax, expatriation tax, or tariff). In some countries, a stamp duty is imposed as an ''ad valorem'' tax. Operation All ad valorem taxes are collected according to the determined value of the taxed item. In the most common application of ad valorem taxes, namely municipal property taxes, public tax assessors regularly assess the property owner's real estate in order to determine its current value. The determined value of the property is used to calculate the annual tax collected by the municipality or any other government entity upon the property owner. Ad valorem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Specific Tax
A per unit tax, or specific tax, is a tax A tax is a mandatory financial charge or levy imposed on an individual or legal entity by a governmental organization to support government spending and public expenditures collectively or to regulate and reduce negative externalities. Tax co ... that is defined as a fixed amount for each unit of a good or service sold, such as cents per kilogram. It is thus proportional to the particular quantity of a product sold, regardless of its price. Excise taxes, for instance, fall into this tax category. By contrast, an ad valorem tax is a charge based on a fixed percentage of the product value. Per unit taxes have administrative advantages when it is easy to measure quantities of the product or service being sold. Effect on supply curve Any tax will raise cost of production hence shift the supply curve to the left. In the case of specific tax, the shift will be purely parallel because the amount of tax is the same at all prices. That am ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supply And Demand
In microeconomics, supply and demand is an economic model of price determination in a Market (economics), market. It postulates that, Ceteris_paribus#Applications, holding all else equal, the unit price for a particular Good (economics), good or other traded item in a perfect competition, perfectly competitive market, will vary until it settles at the market clearing, market-clearing price, where the quantity demanded equals the quantity supplied such that an economic equilibrium is achieved for price and quantity transacted. The concept of supply and demand forms the theoretical basis of modern economics. In situations where a firm has market power, its decision on how much output to bring to market influences the market price, in violation of perfect competition. There, a more complicated model should be used; for example, an oligopoly or product differentiation, differentiated-product model. Likewise, where a buyer has market power, models such as monopsony will be more a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Economic Equilibrium
In economics, economic equilibrium is a situation in which the economic forces of supply and demand are balanced, meaning that economic variables will no longer change. Market equilibrium in this case is a condition where a market price is established through competition such that the amount of goods or services sought by buyers is equal to the amount of goods or services produced by sellers. This price is often called the competitive price or market clearing price and will tend not to change unless demand or supply changes, and quantity is called the "competitive quantity" or market clearing quantity. Understanding economic equilibrium An economic equilibrium is a situation when the economic agent cannot change the situation by adopting any strategy. The concept has been borrowed from the physical sciences. Take a system where physical forces are balanced for instance.This economically interpreted means no further change ensues. Properties of equilibrium Three basic prope ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tax Supply And Demand
A tax is a mandatory financial charge or levy imposed on an individual or legal entity by a governmental organization to support government spending and public expenditures collectively or to regulate and reduce negative externalities. Tax compliance refers to policy actions and individual behavior aimed at ensuring that taxpayers are paying the right amount of tax at the right time and securing the correct tax allowances and tax relief. The first known taxation occurred in Ancient Egypt around 3000–2800 BC. Taxes consist of direct or indirect taxes and may be paid in money or as labor equivalent. All countries have a tax system in place to pay for public, common societal, or agreed national needs and for the functions of government. Some countries levy a flat percentage rate of taxation on personal annual income, but most scale taxes are progressive based on brackets of yearly income amounts. Most countries charge a tax on an individual's income and corporate income. Countr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Excess Burden Of Taxation
In economics, the excess burden of taxation is one of the economic losses that society suffers as the result of taxes or subsidies. Economic theory posits that distortions change the amount and type of economic behavior from that which would occur in a free market without the tax. Excess burdens can be measured using the average cost of funds or the marginal cost of funds (MCF). Excess burdens were first discussed by Adam Smith. An equivalent kind of inefficiency can also be caused by subsidies (which technically can be viewed as taxes with negative rates). Economic losses due to taxes have been evaluated to be as low as 2.5 cents per dollar of revenue, and as high as 30 cents per dollar of revenue (on average), and even much higher at the margins. Measures of the excess burden The cost of a distortion is usually measured as the amount that would have to be paid to the people affected by its supply, the greater the excess burden. The second is the tax rate: as a general ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tax Incidence
In economics, tax incidence or tax burden is the effect of a particular tax on the distribution of economic welfare. Economists distinguish between the entities who ultimately bear the tax burden and those on whom the tax is initially imposed. The tax burden measures the true economic effect of the tax, measured by the difference between real incomes or utilities before and after imposing the tax, and taking into account how the tax causes prices to change. For example, if a 10% tax is imposed on sellers of butter, but the market price rises 8% as a result, most of the tax burden is on buyers, not sellers. The concept of tax incidence was initially brought to economists' attention by the French Physiocrats, in particular François Quesnay, who argued that the incidence of all taxation falls ultimately on landowners and is at the expense of land rent. Tax incidence is said to "fall" upon the group that ultimately bears the burden of, or ultimately suffers a loss from, the tax. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pricing
Pricing is the Business process, process whereby a business sets and displays the price at which it will sell its products and services and may be part of the business's marketing plan. In setting prices, the business will take into account the price at which it could acquire the goods, the manufacturing cost, the marketplace, competition, market condition, brand, and quality of the product. Pricing is a fundamental aspect of product management and is one of the four Ps of the marketing mix, the other three aspects being product, promotion, and Distribution (business), place. Price is the only revenue generating element among the four Ps, the rest being cost center (business), cost centers. However, the other Ps of marketing will contribute to decreasing price elasticity and so enable price increases to drive greater revenue and profits. Pricing can be a manual or automatic process of applying prices to purchase and sales orders, based on factors such as a fixed amount, quantit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taxation And Redistribution
A tax is a mandatory financial charge or levy imposed on an individual or legal entity by a governmental organization to support government spending and public expenditures collectively or to regulate and reduce negative externalities. Tax compliance refers to policy actions and individual behavior aimed at ensuring that taxpayers are paying the right amount of tax at the right time and securing the correct tax allowances and tax relief. The first known taxation occurred in Ancient Egypt around 3000–2800 BC. Taxes consist of direct or indirect taxes and may be paid in money or as labor equivalent. All countries have a tax system in place to pay for public, common societal, or agreed national needs and for the functions of government. Some countries levy a flat percentage rate of taxation on personal annual income, but most scale taxes are progressive based on brackets of yearly income amounts. Most countries charge a tax on an individual's income and corporate income. Cou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |