|
Economic Stimulus Payment
Economic stimulus payment or economic impact payment may refer to several tax rebates, tax credits, tax deductions and grants from the federal government of the United States: * Tax rebates as part of the Economic Growth and Tax Relief Reconciliation Act of 2001 * Tax rebates as part of the Economic Stimulus Act of 2008 * First coronavirus stimulus (called "EIP 1" by the IRS), as part of the CARES Act, March 2020 * Second coronavirus stimulus ("EIP 2"), as part of the Consolidated Appropriations Act, 2021 (Dec. 2020) * Third coronavirus stimulus ("EIP 3"), as part of the American Rescue Plan Act of (March) 2021 See also * Stimulus (economics) ** For government spending as stimulus, see fiscal policy ** For an increase in money designed to speed growth, see monetary policy Monetary policy is the policy adopted by the monetary authority of a nation to affect monetary and other financial conditions to accomplish broader objectives like high employment and price stability (norma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Economic Stimulus Act Of 2008
The Economic Stimulus Act of 2008 () was an Act of Congress providing for several kinds of economic stimuli intended to boost the United States economy in 2008 and to avert a recession, or ameliorate economic conditions. The stimulus package was passed by the U.S. House of Representatives on January 29, 2008, and in a slightly different version by the U.S. Senate on February 7, 2008. The Senate version was then approved in the House the same day. It was signed into law on February 13, 2008, by President George W. Bush with the support of both Democratic and Republican lawmakers. The law provides for tax rebates to low- and middle-income U.S. taxpayers, tax incentives to stimulate business investment, and an increase in the limits imposed on mortgages eligible for purchase by government-sponsored enterprises (e.g. Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac). The total cost of this bill was projected at $152 billion for 2008. Tax rebates Tax rebates that were created by the law were paid to i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Economic Growth And Tax Relief Reconciliation Act Of 2001
An economy is an area of the production, distribution and trade, as well as consumption of goods and services. In general, it is defined as a social domain that emphasize the practices, discourses, and material expressions associated with the production, use, and management of resources. A given economy is a set of processes that involves its culture, values, education, technological evolution, history, social organization, political structure, legal systems, and natural resources as main factors. These factors give context, content, and set the conditions and parameters in which an economy functions. In other words, the economic domain is a social domain of interrelated human practices and transactions that does not stand alone. Economic agents can be individuals, businesses, organizations, or governments. Economic transactions occur when two groups or parties agree to the value or price of the transacted good or service, commonly expressed in a certain currency. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CARES Act
The Coronavirus Aid, Relief, and Economic Security Act, also known as the CARES Act, is a $2.2trillion Stimulus (economics), economic stimulus bill passed by the 116th U.S. Congress and signed into law by President Donald Trump on March 27, 2020, in response to the economic fallout of the COVID-19 pandemic in the United States. The spending primarily includes $300billion in one-time cash payments to individual people who submit a tax return in America (with most single adults receiving $1,200 and families with children receiving more), $260billion in increased unemployment benefits, the creation of the Paycheck Protection Program that provides forgivable loans to small businesses with an initial $350billion in funding (later increased to $669billion by subsequent legislation), $500billion in loans for corporations, and $339.8 billion to state and local governments. The original CARES Act proposal included $500billion in direct payments to Americans, $208billion i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Consolidated Appropriations Act, 2021
The Consolidated Appropriations Act, 2021 () is a $2.3trillion spending bill that combines $900 billion in stimulus relief for the COVID-19 pandemic in the United States with a $1.4trillion omnibus spending bill for the 2021 federal fiscal year (combining 12 separate annual appropriations bills) and prevents a government shutdown.Caitlin Emma & Marianne LeVineBreaking down the $900B stimulus package and $1.4T omnibus bill ''Politico'' (December 20, 2020). The bill is one of the largest spending measures ever enacted, surpassing the $2.2trillion CARES Act, enacted in March 2020. The legislation is the first bill to address the pandemic since April 2020. According to the Senate Historical Office, at 5,593 pages, the legislation is the longest bill ever passed by Congress. The bill was passed by both houses of Congress on December 21, 2020, with large bipartisan majorities in support. The bill was the product of weeks of intense negotiations and compromise between Democrats and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Rescue Plan Act Of 2021
The American Rescue Plan Act of 2021, also called the COVID-19 Stimulus Package or American Rescue Plan, is a economic stimulus bill passed by the 117th United States Congress and signed into law by President Joe Biden on March 11, 2021, to speed up the country's recovery from the economic and health effects of the COVID-19 pandemic and recession. First proposed on January 14, 2021, the package builds upon many of the measures in the CARES Act from March 2020 and in the Consolidated Appropriations Act, 2021, from December. On February 8, 2021, the Financial Services and Education and Labor committees released a draft of $1.9 trillion stimulus legislation. A portion of the relief package was approved by the House Ways and Means on February 11, setting it up for a vote in the House. The legislation was also approved by the Transportation and Infrastructure, Small Business, and House Veterans Affairs committees. On February 22, the House Budget Committee voted 19–16 to a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
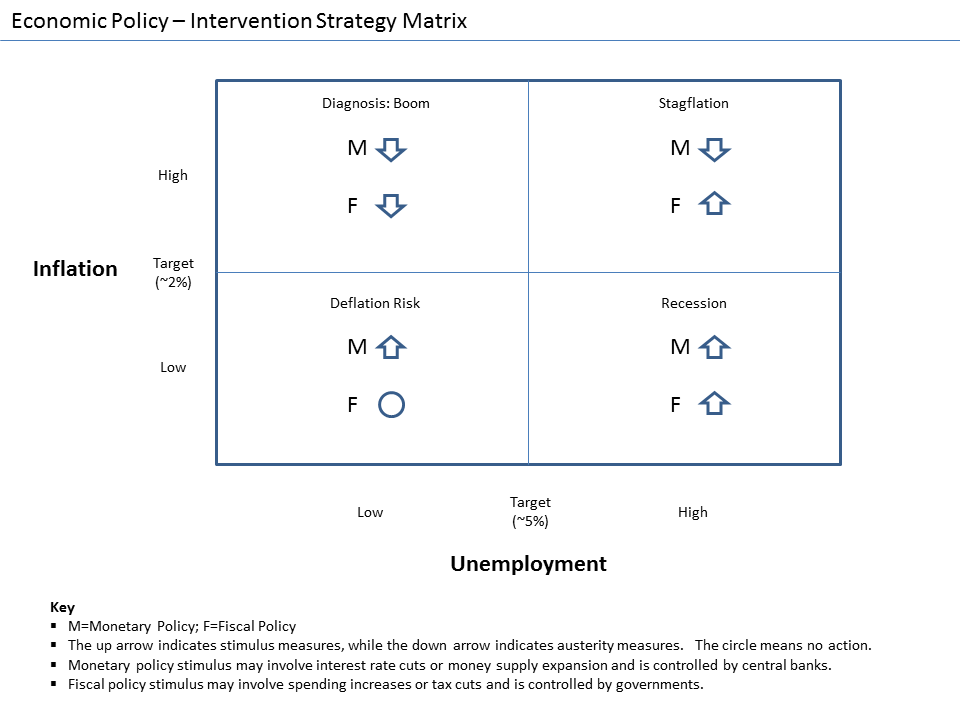
Stimulus (economics)
In economics, stimulus refers to attempts to use monetary policy or fiscal policy (or stabilization policy in general) to stimulate the economy. Stimulus can also refer to monetary policies such as lowering interest rates and quantitative easing. A stimulus is sometimes colloquially referred to as "priming the pump" or "pump priming". Concept During a recession, production and employment are far below their sustainable potential due to lack of demand. It is hoped that increasing demand will stimulate growth and that any adverse side effects from stimulus will be mild. Fiscal stimulus refers to increasing government consumption or transfers or lowering taxes, increasing the rate of growth of public debt. Supporters of Keynesian economics assume the stimulus will cause sufficient economic growth to fill that gap partially or completely via the multiplier effect. Monetary stimulus refers to lowering interest rates, quantitative easing, or other ways of increasing the amou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fiscal Policy
In economics and political science, fiscal policy is the use of government revenue collection ( taxes or tax cuts) and expenditure to influence a country's economy. The use of government revenue expenditures to influence macroeconomic variables developed in reaction to the Great Depression of the 1930s, when the previous laissez-faire approach to economic management became unworkable. Fiscal policy is based on the theories of the British economist John Maynard Keynes, whose Keynesian economics theorised that government changes in the levels of taxation and government spending influence aggregate demand and the level of economic activity. Fiscal and monetary policy are the key strategies used by a country's government and central bank to advance its economic objectives. The combination of these policies enables these authorities to target inflation and to increase employment. In modern economies, inflation is conventionally considered "healthy" in the range of 2%–3%. Add ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |