|
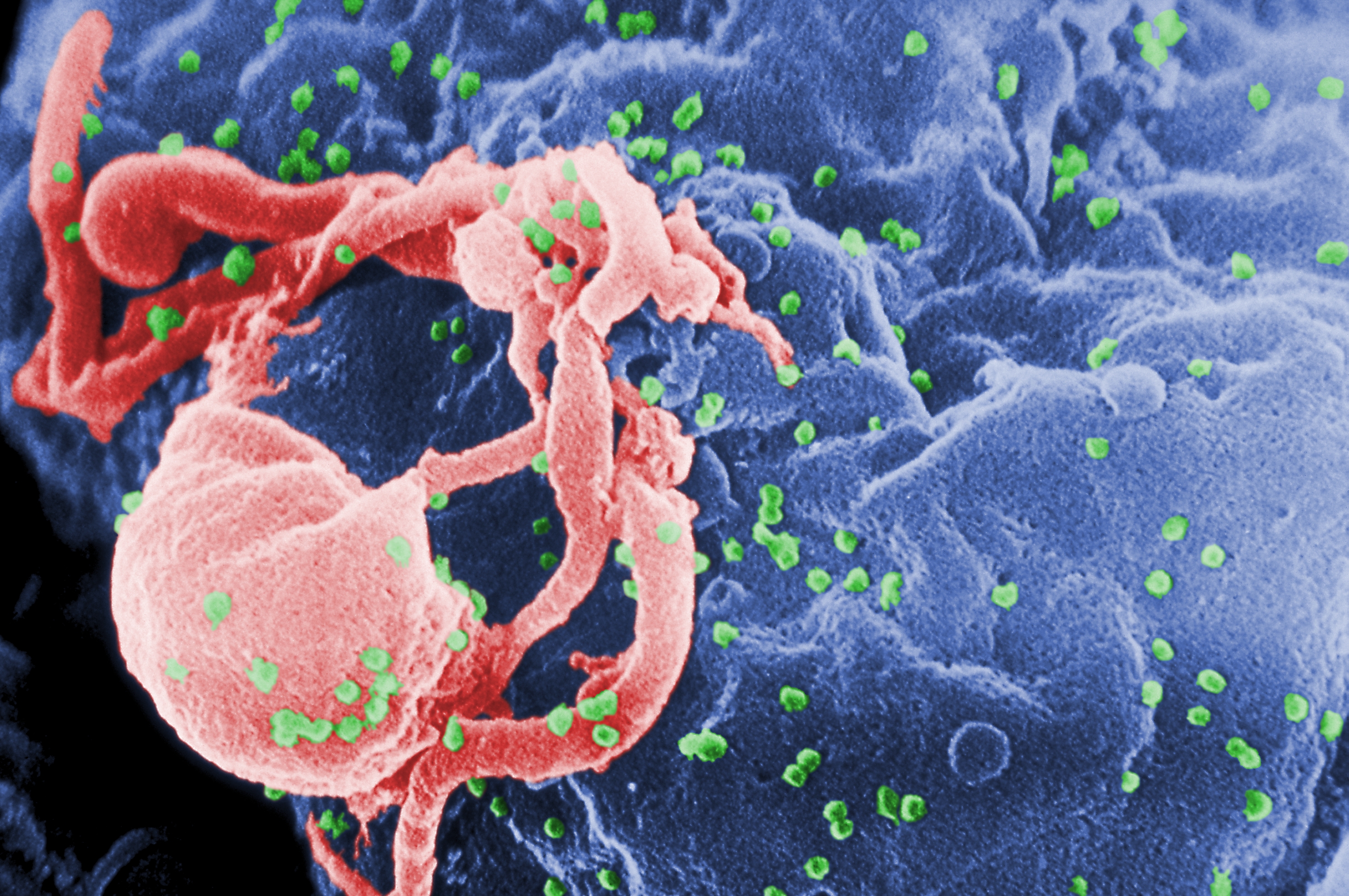
Economic Impact Of AIDS
HIV/AIDS affects economic growth by reducing the availability of human capital. Without proper Prevention of HIV/AIDS, prevention, nutrition, health care and medicine that is available in Developing country, developing countries, large numbers of people are developing AIDS. People living with HIV/AIDS will not only be unable to work, but will also require significant medical care. The forecast is that this will probably cause a collapse of babies and societies in countries with a significant AIDS population. In some heavily infected areas, the epidemic has left behind many orphans, who are cared for by elderly grandparents. The increased mortality in this region will result in a population decline, smaller skilled population and labor force. This smaller labor force will be predominantly young people, with reduced knowledge and work experience leading to reduced productivity. An increase in workers' time off to look after sick family members or for sick leave will also lower pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Life Expectancy In Select Southern African Countries 1960-2012
Life, also known as biota, refers to matter that has biological processes, such as Cell signaling, signaling and self-sustaining processes. It is defined descriptively by the capacity for homeostasis, Structure#Biological, organisation, metabolism, Cell growth, growth, adaptation, response to stimulus (physiology), stimuli, and reproduction. All life over time eventually reaches a state of death, and none is Immortality, immortal. Many philosophical definitions of living systems have been proposed, such as self-organizing systems. Viruses in particular make definition difficult as they replicate only in Host (biology), host cells. Life exists all over the Earth in air, water, and soil, with many ecosystems forming the biosphere. Some of these are harsh environments occupied only by extremophiles. Life has been studied since ancient times, with theories such as Empedocles's materialism asserting that it was composed of Classical element, four eternal elements, and Aristotle's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United Nations Development Programme
The United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) is a United Nations agency tasked with helping countries eliminate poverty and achieve sustainable economic growth and human development. The UNDP emphasizes on developing local capacity towards long-term self-sufficiency and prosperity. Based at the headquarters of the United Nations in New York City, it is the largest UN development aid agency, with offices in 177 countries. The UNDP is funded entirely by voluntary contributions from UN member states. Founding The UNDP was founded on 22 November 1965 through the merger of the Expanded Programme of Technical Assistance (EPTA) and the Special Fund in 1958. The rationale was to "avoid duplication of heiractivities". The EPTA was set up in 1949 to support the economic and political aspects of underdeveloped countries while the Special Fund was to enlarge the scope of UN technical assistance. The Special Fund arose from the idea of a Special United Nations Fund for Economic D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Economic Impact Analysis
An economic impact analysis (EIA) examines the effect of an event on the economy in a specified area, ranging from a single neighborhood to the entire globe. It usually measures changes in business revenue, business profits, personal wages, and/or jobs. The economic event analyzed can include implementation of a new policy or project, or may simply be the presence of a business or organization. An economic impact analysis is commonly conducted when there is public concern about the potential impacts of a proposed project or policy. An economic impact analysis typically measures or estimates the change in economic activity between two scenarios, one assuming the economic event ''occurs'', and one assuming it ''does not occur'' (which is referred to as the counterfactual case). This can be accomplished either before or after the event (''ex ante'' or ''ex post''). An economic impact analysis attempts to measure or estimate the change in economic activity in a specified region ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Welfare Economics
Welfare economics is a field of economics that applies microeconomic techniques to evaluate the overall well-being (welfare) of a society. The principles of welfare economics are often used to inform public economics, which focuses on the ways in which government intervention can improve social welfare. Additionally, welfare economics serves as the theoretical foundation for several instruments of public economics, such as cost–benefit analysis. The intersection of welfare economics and behavioral economics has given rise to the subfield of behavioral welfare economics. Two fundamental theorems are associated with welfare economics. The first states that competitive markets, under certain assumptions, lead to Pareto efficient outcomes. This idea is sometimes referred to as Adam Smith's invisible hand. The second theorem states that with further restrictions, any Pareto efficient outcome can be achieved through a competitive market equilibrium, provided that a social ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copenhagen Consensus
Copenhagen Consensus is a project that seeks to establish priorities for advancing global welfare using methodologies based on the theory of welfare economics, using cost–benefit analysis. It was conceived and organized around 2004 by Bjørn Lomborg, the author of '' The Skeptical Environmentalist'' and the then director of the Danish government's Environmental Assessment Institute. The project is run by the Copenhagen Consensus Center, which is directed by Lomborg and was part of the Copenhagen Business School, but it is now an independent 501(c)(3) non-profit organisation registered in the USA. The project considers possible solutions to a wide range of problems, presented by experts in each field. These are evaluated and ranked by a panel of economists. The emphasis is on rational prioritization by economic analysis. The panel is given an arbitrary budget constraint and instructed to use cost–benefit analysis to focus on a bottom line approach in solving/ranking pres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the Southern Africa, southernmost country in Africa. Its Provinces of South Africa, nine provinces are bounded to the south by of coastline that stretches along the Atlantic Ocean, South Atlantic and Indian Ocean; to the north by the neighbouring countries of Namibia, Botswana, and Zimbabwe; to the east and northeast by Mozambique and Eswatini; and it encloses Lesotho. Covering an area of , the country has Demographics of South Africa, a population of over 64 million people. Pretoria is the administrative capital, while Cape Town, as the seat of Parliament of South Africa, Parliament, is the legislative capital, and Bloemfontein is regarded as the judicial capital. The largest, most populous city is Johannesburg, followed by Cape Town and Durban. Cradle of Humankind, Archaeological findings suggest that various hominid species existed in South Africa about 2.5 million years ago, and modern humans inhabited the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a list of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations which coordinates responses to international public health issues and emergencies. It is headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland, and has 6 regional offices and 150 field offices worldwide. Only sovereign states are eligible to join, and it is the largest intergovernmental health organization at the international level. The WHO's purpose is to achieve the highest possible level of health for all the world's people, defining health as "a state of complete physical, mental and social well-being and not merely the absence of disease or infirmity." The main functions of the World Health Organization include promoting the control of epidemic and endemic diseases; providing and improving the teaching and training in public health, the medical treatment of disease, and related matters; and promoting the establishment of international standards for biologic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Red Cross And Red Crescent Movement
The organized International Red Cross and Red Crescent Movement is a Humanitarianism, humanitarian movement with approximately 16million volunteering, volunteers, members, and staff worldwide. It was founded to protect human life and health, to ensure respect for all human beings, and to prevent and alleviate human suffering. History Foundation Until the middle of the nineteenth century, there were no organized or well-established army nursing systems for casualties, nor safe or protected institutions, to accommodate and treat those who were wounded on the battlefield. A devout Calvinism, Calvinist, the Swiss businessman Jean-Henri Dunant traveled to Italy to meet then-French emperor Napoleon III in June 1859 with the intention of discussing difficulties in conducting business in French Algeria, Algeria, which at that time was occupied by France. He arrived in the small town of Solferino on the evening of 24 June after the Battle of Solferino, an engagement in the Second Itali ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zimbabwe
file:Zimbabwe, relief map.jpg, upright=1.22, Zimbabwe, relief map Zimbabwe, officially the Republic of Zimbabwe, is a landlocked country in Southeast Africa, between the Zambezi and Limpopo Rivers, bordered by South Africa to the south, Botswana to the southwest, Zambia to the north, and Mozambique to the east. The capital and largest city is Harare, and the second largest is Bulawayo. A country of roughly 16.6 million people as per 2024 census, Zimbabwe's largest ethnic group are the Shona people, Shona, who make up 80% of the population, followed by the Northern Ndebele people, Northern Ndebele and other #Demographics, smaller minorities. Zimbabwe has 16 official languages, with English, Shona language, Shona, and Northern Ndebele language, Ndebele the most common. Zimbabwe is a member of the United Nations, the Southern African Development Community, the African Union, and the Common Market for Eastern and Southern Africa. The region was long inhabited by the San people, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supply Chain
A supply chain is a complex logistics system that consists of facilities that convert raw materials into finished products and distribute them to end consumers or end customers, while supply chain management deals with the flow of goods in distribution channels within the supply chain in the most efficient manner. In sophisticated supply chain systems, used products may re-enter the supply chain at any point where residual value is recyclable. Supply chains link value chains. Suppliers in a supply chain are often ranked by "tier", with first-tier suppliers supplying directly to the client, second-tier suppliers supplying to the first tier, and so on. The phrase "supply chain" may have been first published in a 1905 article in ''The Independent (New York City), The Independent'' which briefly mentions the difficulty of "keeping a supply chain with India unbroken" during the British expedition to Tibet. Overview A typical supply chain can be divided into two stages namely, produ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Overseas Development Institute
ODI Global (formerly Overseas Development Institute) is a global affairs think tank, founded in 1960. Its mission is "to inspire people to act on injustice and inequality through collaborative research and ideas that matter for people and the planet." It does this through "research, convening and influencing, to lead new thinking and future agendas to deliver transformational change." Its chair is Suma Chakrabarti. History In 1960 ODI began in small premises in Regent's Park of Central London. At the time, ODI operated a library devoted to international development issues and also performed consultancy work and contracts with the Department for International Development of the UK government. Since then, the organization has moved several times and is headquartered on Blackfriars Road. In 2007 the ODI was named 'Think Tank of the Year' by ''Public Affairs News'' magazine. It was named 'Think-tank to Watch' in the '' Prospect'' 'Think-tank of the Year' awards in 2005 and is c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Per Capita
''Per capita'' is a Latin phrase literally meaning "by heads" or "for each head", and idiomatically used to mean "per person". Social statistics The term is used in a wide variety of social science, social sciences and statistical research contexts, including government statistics, economic indicators, and built environment studies. It is commonly used in the academic discipline, field of statistics in place of saying "per person" (although ''per caput'' is the Latin for "per head"). It is also used in will and testament, wills to indicate that each of the named beneficiary, beneficiaries should receive, by devise or bequest and devise, bequest, equal shares of the estate. This is in contrast to a ''per stirpes'' division, in which each branch (Latin: ''stirps'', : ''stirpes'') of the inheritance, inheriting family inherits an equal share of the estate (law), estate. This is often used with the '2-0 rule', a statistical principle that determines which group is larger ''per capit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |