|
E2v
Teledyne e2v (previously known as e2v) is a manufacturer with its headquarters in England, that designs, develops and manufactures systems and components in healthcare, life sciences, space, transportation, defence and security and industrial markets. The company was previously known as English Electric Valve Company and for a short time Marconi Applied Technologies. e2v was acquired by US company Teledyne Technologies in March 2017. Company history The company began in the early 1940s as a part of the Marconi group, manufacturing magnetrons for defence radar systems. The company was first registered as a separate company in Chelmsford, Essex in 1947 under Simeon Aisenstein. Its initial name was the Phoenix Dynamo Co Ltd, though it immediately changed its name to English Electric Valve Company Ltd. In 1959, Bob Coulson established travelling-wave tube and microwave tube sections, and they were producing ceramic hydrogen thyratrons as well. By this time EEV was the largest hi-tec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chelmsford, Essex
Chelmsford () is a City status in the United Kingdom, city in the City of Chelmsford district in the county of Essex, England. It is the county town of Essex and one of three cities in the county, along with Colchester and Southend-on-Sea. It is located north-east of London at Charing Cross and south-west of Colchester. The population of the urban area was 110,625 in the 2021 Census, while the wider district has 181,763. The main conurbation of Chelmsford incorporates all or part of the former parishes of Broomfield, Essex, Broomfield, Newland Spring, Great Leighs, Great Waltham, Little Waltham, Great Baddow, Little Baddow, Galleywood, Howe Green, Chelmsford, Howe Green, Margaretting, Pleshey, Stock, Essex, Stock, Roxwell, Danbury, Essex, Danbury, Bicknacre, Writtle, Moulsham, Rettendon, The Hanningfields, The Chignals, Widford, Essex, Widford and Springfield, Essex, Springfield, including Springfield Barnes, now known as Chelmer Village. The communities of Chelmsford, Mass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chelmsford
Chelmsford () is a city in the City of Chelmsford district in the county of Essex, England. It is the county town of Essex and one of three cities in the county, along with Colchester and Southend-on-Sea. It is located north-east of London at Charing Cross and south-west of Colchester. The population of the urban area was 110,625 in the 2021 Census, while the wider district has 181,763. The main conurbation of Chelmsford incorporates all or part of the former parishes of Broomfield, Newland Spring, Great Leighs, Great Waltham, Little Waltham, Great Baddow, Little Baddow, Galleywood, Howe Green, Margaretting, Pleshey, Stock, Roxwell, Danbury, Bicknacre, Writtle, Moulsham, Rettendon, The Hanningfields, The Chignals, Widford and Springfield, including Springfield Barnes, now known as Chelmer Village. The communities of Chelmsford, Massachusetts; Chelmsford, Ontario; and Chelmsford, New Brunswick, are named after the city. The demonym for a Chelmsford r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
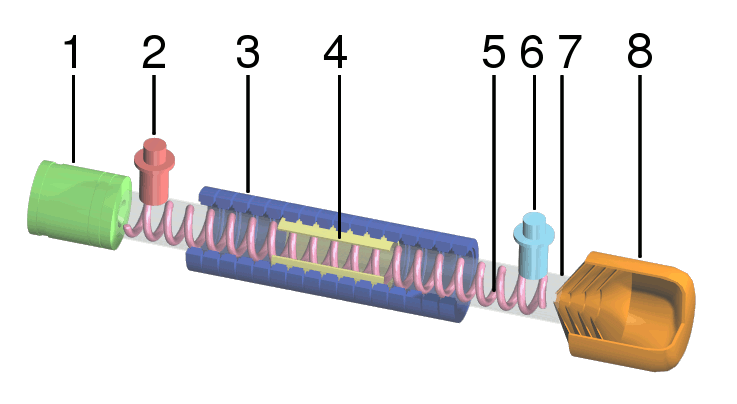
Travelling-wave Tube
A traveling-wave tube (TWT, pronounced "twit") or traveling-wave tube amplifier (TWTA, pronounced "tweeta") is a specialized vacuum tube that is used in electronics to amplify radio frequency (RF) signals in the microwave range. It was invented by Andrei Haeff around 1933 as a graduate student at Caltech, and its present form was invented by Rudolf Kompfner in 1942–43. The TWT belongs to a category of "linear beam" tubes, such as the klystron, in which the radio wave is amplified by absorbing power from a beam of electrons as it passes down the tube. Although there are various types of TWT, two major categories are: *''Helix TWT'' - in which the radio waves interact with the electron beam while traveling down a wire helix which surrounds the beam. These have wide bandwidth, but output power is limited to a few hundred watts. *''Coupled cavity TWT'' - in which the radio wave interacts with the beam in a series of cavity resonators through which the beam passes. These function ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simeon Aisenstein
Simeon Aisenstein (25 January 1884, Kyiv, Kiyv, Ukraine, Russian Empire, Imperial Russia – 3 September 1962, Chelmsford, Essex, United Kingdom; born Семёна Моисеевича Айзенштейна, Semyon Moise'evich Aisenstein) was a scientist, entrepreneur and educator in the field of radio communications whose achievements spanned from the birth of wireless into the age of television and satellite communication. He was put in charge of national radio communication in Imperial Russia in 1906 and quickly built a network connecting the vast country, which led to his name and reputation becoming known worldwide. In 1916, he was the first to achieve communication to a submerged submarine using Very low frequency, very low frequencies and during the First World War constructed a secure communication system between the governments of Russia, Britain and France (who awarded him the Legion of Honour, Légion d'honneur). He was a professor at Bauman Moscow State Technical U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teledyne Technologies
Teledyne Technologies Incorporated is an American industrial conglomerate. It was founded in 1960, as Teledyne, Inc. by Henry Singleton and George Kozmetsky. From August 1996 to November 1999, Teledyne existed as part of the conglomerate Allegheny Teledyne Incorporated – a combination of the former Teledyne, Inc. and the former Allegheny Ludlum Corporation. On November 29, 1999, three separate entities, Teledyne Technologies, Allegheny Technologies, and Water Pik Technologies, were spun off as free-standing public companies. Allegheny Technologies retained several companies of the former Teledyne, Inc. that fit with Allegheny's core business of steel and exotic metals production. At various times, Teledyne, Inc. owned more than 150 companies with interests as varied as insurance, dental appliances, specialty metals, and aerospace electronics, but many of these had been divested prior to the merger with Allegheny. The new Teledyne Technologies was initially composed of 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sir Arthur Clarke Award
The Sir Arthur Clarke Award is a British award given annually since 2005 in recognition of notable contributions to Outer space, space exploration, particularly British achievements. The awards are presented by the Arthur C. Clarke Foundation, although the selection is delegated to the British Interplanetary Society, with the exception of the International award, whose recipient is voted on by the Foundation Nominations for the awards are made by members of the public, with shortlists drawn up by a panel of judges, who also choose the winner. Sir Arthur C Clarke, Sir Arthur C. Clarke chose a special award independently of the public nominations. History Founded in 2005, the idea for the awards was proposed by Dave Wright to Jerry Stone, who then suggested they be named after Arthur C. Clarke, Sir Arthur Clarke. Once permission was granted, Jerry Stone decided what the awards should look like, what categories should be included, and how they should be nominated and judged. Hav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charge-coupled Devices
A charge-coupled device (CCD) is an integrated circuit containing an array of linked, or coupled, capacitors. Under the control of an external circuit, each capacitor can transfer its electric charge to a neighboring capacitor. CCD sensors are a major technology used in digital imaging. Overview In a CCD image sensor, pixels are represented by p-doped metal–oxide–semiconductor (MOS) capacitors. These MOS capacitors, the basic building blocks of a CCD, are biased above the threshold for inversion when image acquisition begins, allowing the conversion of incoming photons into electron charges at the semiconductor-oxide interface; the CCD is then used to read out these charges. Although CCDs are not the only technology to allow for light detection, CCD image sensors are widely used in professional, medical, and scientific applications where high-quality image data are required. In applications with less exacting quality demands, such as consumer and professional digital came ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semiconductors
A semiconductor is a material with electrical conductivity between that of a conductor and an insulator. Its conductivity can be modified by adding impurities (" doping") to its crystal structure. When two regions with different doping levels are present in the same crystal, they form a semiconductor junction. The behavior of charge carriers, which include electrons, ions, and electron holes, at these junctions is the basis of diodes, transistors, and most modern electronics. Some examples of semiconductors are silicon, germanium, gallium arsenide, and elements near the so-called "metalloid staircase" on the periodic table. After silicon, gallium arsenide is the second-most common semiconductor and is used in laser diodes, solar cells, microwave-frequency integrated circuits, and others. Silicon is a critical element for fabricating most electronic circuits. Semiconductor devices can display a range of different useful properties, such as passing current more easily in one ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Oatley
Sir Charles William Oatley (14 February 1904 – 11 March 1996) was Professor of Electrical Engineering, University of Cambridge, 1960–1971, and developer of one of the first commercial scanning electron microscopes. He was also a founder member of the Royal Academy of Engineering. Biography He was born in Frome on Valentine's Day, 14 February 1904. A plaque has been placed on the house at the junction of Badcox Parade and Catherine Hill. He was educated at Bedford Modern School and St. John's College, Cambridge. He lectured at King's College London for 12 years, until the war. He was a director of the English Electric Valve Company from 1966 to 1985. In 1969, he was elected to the Royal Society. Oatley also received an Honorary degree, Honorary Doctorate from Heriot-Watt University in 1974. In that same year, he was knighted. He received an Honorary Degree (Doctor of Science) from the University of Bath in 1977. He retired from the English Electric Valve Company in 1985. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seville
Seville ( ; , ) is the capital and largest city of the Spain, Spanish autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community of Andalusia and the province of Seville. It is situated on the lower reaches of the Guadalquivir, River Guadalquivir, in the southwest of the Iberian Peninsula. Seville has a municipal population of about 701,000 , and a Seville metropolitan area, metropolitan population of about 1.5 million, making it the largest city in Andalusia and the List of metropolitan areas in Spain, fourth-largest city in Spain. Its old town, with an area of , contains a UNESCO World Heritage Site comprising three buildings: the Alcázar of Seville, Alcázar palace complex, the Seville Cathedral, Cathedral and the General Archive of the Indies. The Seville harbour, located about from the Atlantic Ocean, is the only river port in Spain. The capital of Andalusia features hot temperatures in the summer, with daily maximums routinely above in July and August. Seville was founded ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microwave
Microwave is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths shorter than other radio waves but longer than infrared waves. Its wavelength ranges from about one meter to one millimeter, corresponding to frequency, frequencies between 300 MHz and 300 GHz, broadly construed. A more common definition in radio-frequency engineering is the range between 1 and 100 GHz (wavelengths between 30 cm and 3 mm), or between 1 and 3000 GHz (30 cm and 0.1 mm). In all cases, microwaves include the entire super high frequency, super high frequency (SHF) band (3 to 30 GHz, or 10 to 1 cm) at minimum. The boundaries between far infrared, terahertz radiation, microwaves, and ultra-high-frequency (UHF) are fairly arbitrary and differ between different fields of study. The prefix ' in ''microwave'' indicates that microwaves are small (having shorter wavelengths), compared to the radio waves used in prior radio technology. Frequencies in the micr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |