|
Dyserythropoiesis
Dyserythropoiesis refers to the defective development of red blood cells, also called erythrocytes. This problem can be congenital, acquired, or inherited. Some red blood cells may be destroyed within the bone marrow during the maturation process, whereas others can enter the circulation with abnormalities. These abnormalities can be functional and/or morphological, which can lead to anemia since there may be increased turnover of red blood cells. There are a number of diseases that cause dyserythropoiesis. Congenital/inherited causes include congenital dyserythropoietic anemia, thalassemia, pyruvate kinase deficiency, hereditary pyropoikilocytosis, and abetalipoproteinemia. Acquired causes include nutrient deficiency/malnutrition (e.g. cobalamine, folate, and iron), myelodysplasia, HIV infection, and certain medications (e.g. zidovudine). See also * Erythropoiesis * Erythrocyte * Congenital dyserythropoietic anemia Congenital dyserythropoietic anemia (CDA) is a rare blood di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myelodysplasia
A myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) is one of a group of cancers in which blood cells in the bone marrow do not mature, and as a result, do not develop into healthy blood cells. Early on, no symptoms typically are seen. Later, symptoms may include fatigue, shortness of breath, bleeding disorders, anemia, or frequent infections. Some types may develop into acute myeloid leukemia. Risk factors include previous chemotherapy or radiation therapy, exposure to certain chemicals such as tobacco smoke, pesticides, and benzene, and exposure to heavy metals such as mercury or lead. Problems with blood cell formation result in some combination of low red blood cell, platelet, and white blood cell counts. Some types of MDS cause an increase in the production of immature blood cells (called blasts), in the bone marrow or blood. The different types of MDS are identified based on the specific characteristics of the changes in the blood cells and bone marrow. Treatments may include supportiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Red Blood Cells
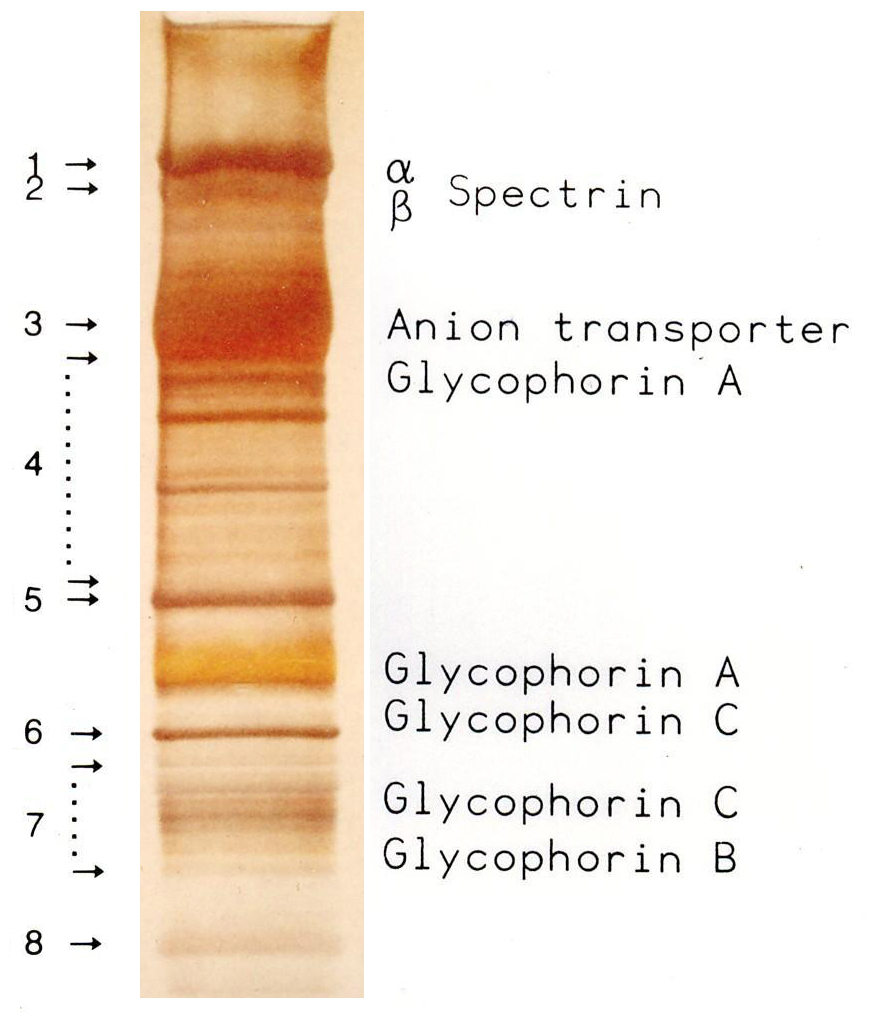
Red blood cells (RBCs), referred to as erythrocytes (, with -''cyte'' translated as 'cell' in modern usage) in academia and medical publishing, also known as red cells, erythroid cells, and rarely haematids, are the most common type of blood cell and the vertebrate's principal means of delivering oxygen () to the body tissue (biology), tissues—via blood flow through the circulatory system. Erythrocytes take up oxygen in the lungs, or in fish the gills, and release it into tissues while squeezing through the body's capillary, capillaries. The cytoplasm of a red blood cell is rich in hemoglobin (Hb), an iron-containing biomolecule that can bind oxygen and is responsible for the red color of the cells and the blood. Each human red blood cell contains approximately 270 million hemoglobin molecules. The cell membrane is composed of proteins and lipids, and this structure provides properties essential for physiological Cell (biology), cell function such as erythrocyte deformabil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Folate Deficiency
Folate deficiency, also known as vitamin B9 deficiency, is a low level of folate and derivatives in the body. This may result in megaloblastic anemia in which red blood cells become abnormally large, and folate deficiency anemia is the term given for this medical condition. Signs of folate deficiency are often subtle. Symptoms may include fatigue, heart palpitations, shortness of breath, feeling faint, open sores on the tongue, loss of appetite, changes in the color of the skin or hair, irritability, and behavioral changes. Temporary reversible infertility may occur. Folate deficiency anemia during pregnancy may give rise to the birth of low weight birth premature infants and infants with neural tube defects. Not consuming enough folate can lead to folate deficiency within a few months. Otherwise, causes may include increased needs as with pregnancy, and in those with shortened red blood cell lifespan. Folate deficiency can be secondary to vitamin B12 deficiency or a defect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erythrocyte
Red blood cells (RBCs), referred to as erythrocytes (, with -''cyte'' translated as 'cell' in modern usage) in academia and medical publishing, also known as red cells, erythroid cells, and rarely haematids, are the most common type of blood cell and the vertebrate's principal means of delivering oxygen () to the body tissues—via blood flow through the circulatory system. Erythrocytes take up oxygen in the lungs, or in fish the gills, and release it into tissues while squeezing through the body's capillaries. The cytoplasm of a red blood cell is rich in hemoglobin (Hb), an iron-containing biomolecule that can bind oxygen and is responsible for the red color of the cells and the blood. Each human red blood cell contains approximately 270 million hemoglobin molecules. The cell membrane is composed of proteins and lipids, and this structure provides properties essential for physiological cell function such as deformability and stability of the blood cell while traversing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erythropoiesis
Erythropoiesis (from Greek ''erythro'', meaning ''red'' and ''poiesis'', meaning ''to make'') is the process which produces red blood cells (erythrocytes), which is the development from erythropoietic stem cell to mature red blood cell. It is stimulated by decreased O2 in circulation, which is detected by the kidneys, which then secrete the hormone erythropoietin.Sherwood, L, Klansman, H, Yancey, P: ''Animal Physiology'', Brooks/Cole, Cengage Learning, 2005. This hormone stimulates proliferation and differentiation of red cell precursors, which activates increased erythropoiesis in the hemopoietic tissues, ultimately producing red blood cells (erythrocytes). In postnatal birds and mammals (including humans), this usually occurs within the red bone marrow. In the early fetus, erythropoiesis takes place in the mesodermal cells of the yolk sac. By the third or fourth month, erythropoiesis moves to the liver. After seven months, erythropoiesis occurs in the bone marrow. Increased ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zidovudine
Zidovudine (ZDV), also known as azidothymidine (AZT), was the first antiretroviral medication used to prevent and treat HIV/AIDS. It is generally recommended for use in combination with other antiretrovirals. It may be used to prevent mother-to-child spread during birth or after a needlestick injury or other potential exposure. It is sold both by itself and together as lamivudine/zidovudine and abacavir/lamivudine/zidovudine. It can be used by mouth or by slow injection into a vein. Common side effects include headaches, fever, and nausea. Serious side effects include liver problems, muscle damage, and high blood lactate levels. It is commonly used in pregnancy and appears to be safe for the fetus. ZDV is of the nucleoside analog reverse-transcriptase inhibitor (NRTI) class. It works by inhibiting the enzyme reverse transcriptase that HIV uses to make DNA and therefore decreases replication of the virus. Zidovudine was first described in 1964. It was resynthesize ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HIV/AIDS
The HIV, human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is a retrovirus that attacks the immune system. Without treatment, it can lead to a spectrum of conditions including acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). It is a Preventive healthcare, preventable disease. It can be managed with treatment and become a manageable chronic health condition. While there is no cure or vaccine for HIV, Management of HIV/AIDS, antiretroviral treatment can slow the course of the disease, and if used before significant disease progression, can extend the life expectancy of someone living with HIV to a nearly standard level. An HIV-positive person on treatment can expect to live a normal life, and die with the virus, not of it. Effective #Treatment, treatment for HIV-positive people (people living with HIV) involves a life-long regimen of medicine to suppress the virus, making the viral load undetectable. Treatment is recommended as soon as the diagnosis is made. An HIV-positive person who has an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iron Deficiency
Iron deficiency, or sideropenia, is the state in which a body lacks enough iron to supply its needs. Iron is present in all cells in the human body and has several vital functions, such as carrying oxygen to the tissues from the lungs as a key component of the hemoglobin protein, acting as a transport medium for electrons within the cells in the form of cytochromes, and facilitating oxygen enzyme reactions in various tissues. Too little iron can interfere with these vital functions and lead to morbidity and death. Total body iron averages approximately 3.8 g in men and 2.3 g in women. In blood plasma, iron is carried tightly bound to the protein transferrin. Several mechanisms control iron metabolism and safeguard against iron deficiency. The main regulatory mechanism is situated in the gastrointestinal tract. Most iron absorption occurs in the duodenum, the first section of the small intestine. Several dietary factors may affect iron absorption. Iron deficiency develops when ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vitamin B12 Deficiency
Vitamin B12 deficiency, also known as cobalamin deficiency, is the medical condition in which the blood and tissue have a lower than normal level of Vitamin B12, vitamin B12. Symptoms can vary from none to severe. Mild deficiency may have few or absent symptoms. In moderate deficiency, Fatigue, feeling tired, Headache, headaches, glossitis, soreness of the tongue, Aphthous stomatitis, mouth ulcers, breathlessness, Presyncope, feeling faint, Tachycardia, rapid heartbeat, low blood pressure, pallor, hair loss, decreased ability to think and severe arthralgia, joint pain and the beginning of neurological symptoms, including Paresthesia, abnormal sensations such as ''pins and needles'', numbness and tinnitus may occur. Severe deficiency may include symptoms of cardiomyopathy, reduced heart function as well as more severe neurological symptoms, including changes in reflexes, poor muscle function, memory problems, blurred vision, irritability, ataxia, decreased Anosmia, smell and Hy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bone Marrow
Bone marrow is a semi-solid biological tissue, tissue found within the Spongy bone, spongy (also known as cancellous) portions of bones. In birds and mammals, bone marrow is the primary site of new blood cell production (or haematopoiesis). It is composed of Blood cell, hematopoietic cells, marrow adipose tissue, and supportive stromal cells. In adult humans, bone marrow is primarily located in the Rib cage, ribs, vertebrae, sternum, and Pelvis, bones of the pelvis. Bone marrow comprises approximately 5% of total body mass in healthy adult humans, such that a person weighing 73 kg (161 lbs) will have around 3.7 kg (8 lbs) of bone marrow. Human marrow produces approximately 500 billion blood cells per day, which join the Circulatory system, systemic circulation via permeable vasculature sinusoids within the medullary cavity. All types of Hematopoietic cell, hematopoietic cells, including both Myeloid tissue, myeloid and Lymphocyte, lymphoid lineages, are create ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abetalipoproteinemia
Abetalipoproteinemia (also known as: Bassen–Kornzweig syndrome, microsomal triglyceride transfer protein deficiency disease, MTP deficiency, and betalipoprotein deficiency syndrome) is a disorder characterized by abnormal absorption of fat and fat-soluble vitamins from food. It is caused by a mutation in microsomal triglyceride transfer protein resulting in deficiencies in the apolipoproteins B-48 and B-100, which are used in the synthesis and exportation of chylomicrons and VLDL respectively. It is not to be confused with familial dysbetalipoproteinemia. It is a rare autosomal recessive disorder. Presentation Symptoms Initial symptoms usually appear in infancy, including: * Failure to thrive (i.e. failure to grow in infancy) * Steatorrhea (i.e. fatty, pale stools) * Frothy stools * Foul smelling stools * Protruding abdomen The rate of occurrence of additional symptoms later in life varies and increases with age. These may include: * Intellectual disability/developmenta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hereditary Pyropoikilocytosis
Hereditary pyropoikilocytosis (HPP) is an autosomal recessive form of hemolytic anemia characterized by an abnormal sensitivity of red blood cells to heat and erythrocyte morphology similar to that seen in thermal burns or from prolonged exposure of a healthy patient's blood sample to high ambient temperatures. Patients with HPP tend to experience severe hemolysis and anemia in infancy that gradually improves, evolving toward typical elliptocytosis later in life. However, the hemolysis can lead to rapid sequestration and destruction of red cells. Splenectomy is curative when this occurs. HPP has been associated with a defect of the erythrocyte membrane protein spectrin and with spectrin deficiency. It was characterized in 1975. It is considered a severe form of hereditary elliptocytosis. Signs and symptoms Causes Mutations of the alphaspectrin gene causes this disease. HPP can be considered as a subset of hereditary elliptocytosis. Diagnosis Genetic testing for the presence o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |