|
Dysbiosis
Dysbiosis (also called dysbacteriosis) is characterized by a disruption to the microbiome resulting in an imbalance in the microbiota, changes in their functional composition and metabolic activities, or a shift in their local distribution. For example, a part of the human microbiota such as the skin flora, gut flora, or vaginal flora, can become deranged (unbalanced), when normally dominating species become underrepresented and species that normally are outcompeted or contained increase to fill the void. Similar to the human gut microbiome, diverse microbes colonize the plant rhizosphere, and dysbiosis in the rhizosphere, can negatively impact plant health. Dysbiosis is most commonly reported as a condition in the gastrointestinal tract or plant rhizosphere. Typical microbial colonies found on or in the body are benign or beneficial. These appropriately sized microbial colonies carry out a series of helpful and necessary functions, such as aiding in digestion. They also hel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microbiome
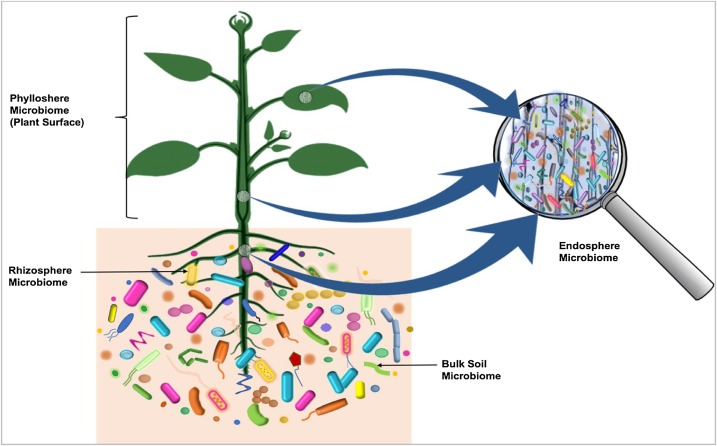
A microbiome () is the community of microorganisms that can usually be found living together in any given habitat. It was defined more precisely in 1988 by Whipps ''et al.'' as "a characteristic microbial community occupying a reasonably well-defined habitat which has distinct physio-chemical properties. The term thus not only refers to the microorganisms involved but also encompasses their theatre of activity". In 2020, an international panel of experts published the outcome of their discussions on the definition of the microbiome. They proposed a definition of the microbiome based on a revival of the "compact, clear, and comprehensive description of the term" as originally provided by Whipps ''et al.'', but supplemented with two explanatory paragraphs, the #First explanatory paragraph, first pronouncing the dynamic character of the microbiome, and the #Second explanatory paragraph, second clearly separating the term ''microbiota'' from the term ''microbiome''. Modified text ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gut Flora
Gut microbiota, gut microbiome, or gut flora are the microorganisms, including bacteria, archaea, fungi, and viruses, that live in the digestive tracts of animals. The gastrointestinal metagenome is the aggregate of all the genomes of the gut microbiota. The gut is the main location of the human microbiome. The gut microbiota has broad impacts, including effects on colonization, resistance to pathogens, maintaining the intestinal epithelium, metabolizing dietary and pharmaceutical compounds, controlling immune function, and even behavior through the gut–brain axis. The microbial composition of the gut microbiota varies across regions of the digestive tract. The colon contains the highest microbial density of any human-associated microbial community studied so far, representing between 300 and 1000 different species. Bacteria are the largest and to date, best studied component and 99% of gut bacteria come from about 30 or 40 species. About 55% of the dry mass of feces ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microbiota
Microbiota are the range of microorganisms that may be commensal, mutualistic, or pathogenic found in and on all multicellular organisms, including plants. Microbiota include bacteria, archaea, protists, fungi, and viruses, and have been found to be crucial for immunologic, hormonal, and metabolic homeostasis of their host. The term ''microbiome'' describes either the collective genomes of the microbes that reside in an ecological niche or else the microbes themselves. The microbiome and host emerged during evolution as a synergistic unit from epigenetics and genetic characteristics, sometimes collectively referred to as a holobiont. The presence of microbiota in human and other metazoan guts has been critical for understanding the co-evolution between metazoans and bacteria. Microbiota play key roles in the intestinal immune and metabolic responses via their fermentation product ( short-chain fatty acid), acetate. Introduction All plants and animals, from simple life fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is a group of inflammatory conditions of the colon and small intestine, with Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis (UC) being the principal types. Crohn's disease affects the small intestine and large intestine, as well as the mouth, esophagus, stomach and the anus, whereas UC primarily affects the colon and the rectum. Signs and symptoms In spite of Crohn's and UC being very different diseases, both may present with any of the following symptoms: abdominal pain, diarrhea, rectal bleeding, severe internal cramps/muscle spasms in the region of the pelvis and weight loss. Anemia is the most prevalent extraintestinal complication of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Associated complaints or diseases include arthritis, pyoderma gangrenosum, primary sclerosing cholangitis, and non-thyroidal illness syndrome (NTIS). Associations with deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia (BOOP) have also been reported. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atopic Dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis (AD), also known as atopic eczema, is a long-term type of inflammation of the skin. Atopic dermatitis is also often called simply eczema but the same term is also used to refer to dermatitis, the larger group of skin conditions. Atopic dermatitis results in puritis, itchy, red, swollen, and cracked skin. Clear fluid may come from the affected areas, which can thicken over time. Atopic dermatitis affects about 20% of people at some point in their lives. It is more common in younger children. Females are affected slightly more often than males. Many people outgrow the condition. While the condition may occur at any age, it typically starts in childhood, with changing severity over the years. In children under one year of age, the face and limbs and much of the body may be affected. As children get older, the areas on the insides of the knees and folds of the elbows and around the neck are most commonly affected. In adults, the hands and feet are commonly affec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Microbiota
Human microbiota are microorganisms (bacteria, viruses, fungi and archaea) found in a specific environment. They can be found in the stomach, intestines, skin, genitals and other parts of the body. Various body parts have diverse microorganisms. Some microbes are specific to certain body parts and others are associated with many microbiomes. This article lists some of the species recognized as belonging to the human microbiome and focuses on the oral, vaginal, ovarian follicle, uterus and the male reproductive tract microbiota. Categories of bacteria The "reference" 70 kg human body is estimated to have around 39 trillion bacteria with a mass of about 0.2 kg. These can be separated into about 10,000 microbial species, about 180 of the most studied is listed below here. However, these can broadly be put into three categories: Spheres or ball-shaped (cocci bacteria) Cocci are usually round or spherical in shape. They can form clusters and are non-motile. Examples incl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gastrointestinal Tract
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the Digestion, digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The tract is the largest of the body's systems, after the cardiovascular system. The GI tract contains all the major organ (biology), organs of the digestive system, in humans and other animals, including the esophagus, stomach, and intestines. Food taken in through the mouth is digestion, digested to extract nutrients and absorb energy, and the waste expelled at the anus as feces. ''Gastrointestinal'' is an adjective meaning of or pertaining to the stomach and intestines. Nephrozoa, Most animals have a "through-gut" or complete digestive tract. Exceptions are more primitive ones: sponges have small pores (ostium (sponges), ostia) throughout their body for digestion and a larger dorsal pore (osculum) for excretion, comb jellies have both a ventral mouth and dorsal anal pores, while cnidarians and acoels have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fecal Microbiota Transplant
Fecal microbiota transplant (FMT), also known as a stool transplant, is the process of transferring fecal bacteria and other microbes from a healthy individual into another individual. FMT is an effective treatment for Clostridioides difficile infection, ''Clostridioides difficile'' infection (CDI). For recurrent CDI, FMT is more effective than vancomycin alone, and may improve the outcome after the first index infection. Side effects include a risk of infections; therefore, donors should be Screening (medicine), screened for pathogens. With CDI becoming more common, FMT is gaining prominence. Some experts call for it to become the first-line therapy for CDI. FMT has been used experimentally to treat other gastrointestinal diseases, including colitis, constipation, irritable bowel syndrome, and Neurology, neurological conditions, such as multiple sclerosis and Parkinson's. In the United States, human feces have been regulated as an experimental drug since 2013. In the Unite ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Parasite
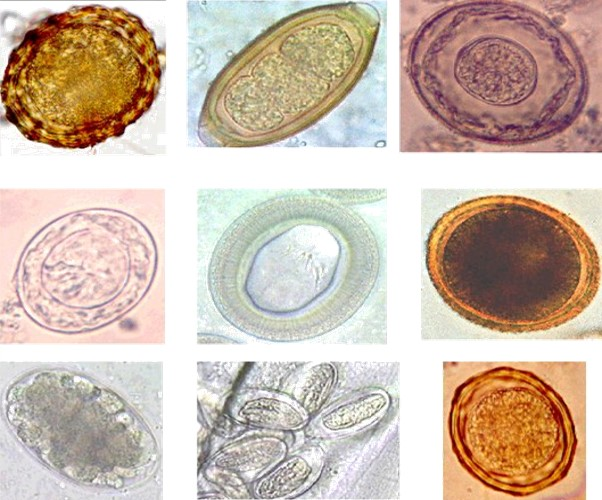
Human parasites are divided into endoparasites, which cause infection inside the body, and ectoparasites, which cause infection superficially within the skin. Parasites in general are hosts-dependent organisms that obtain nutrients while potentially harming their host in the process. Parasitic infections cause global health concerns because they impact billions of people throughout the world at different disease severity. These infections split into the three main categories of protozoa and helminths (parasitic worms) alongside ectoparasites. Over 30% of global human population is affected by the roundworm "Ascaris lumbricoides". The incidence of certain parasitic diseases including malaria and schistosomiasis continue to rise year after year. The AIDS epidemic has worsened the situation by causing elevated rates of parasitic opportunistic infections to affect mainly weak-immune people through conditions such as cryptosporidiosis, Pneumocystis pneumonia and strongyloidiasis. Refuge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antiviral Drug
Antiviral drugs are a class of medication used for treating viral infections. Most antivirals target specific viruses, while a broad-spectrum antiviral is effective against a wide range of viruses. Antiviral drugs are a class of antimicrobials, a larger group which also includes antibiotic (also termed antibacterial), antifungal and antiparasitic drugs, or antiviral drugs based on monoclonal antibodies. Most antivirals are considered relatively harmless to the host, and therefore can be used to pharmacotherapy, treat infections. They should be distinguished from virucides, which are not medication but deactivate or destroy virus particles, either inside or outside the body. Natural virucides are produced by some plants such as eucalyptus and Australian tea trees. Medical uses Most of the antiviral drugs now available are designed to help deal with HIV, Herpesviridae, herpes viruses, the hepatitis B and Hepatitis C, C viruses, and Influenzavirus A, influenza A and Influenzavirus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hormone Therapy
Hormone therapy or hormonal therapy is the use of hormones in medical treatment. Treatment with hormone antagonists may also be referred to as hormonal therapy or antihormone therapy. The most general classes of hormone therapy are hormonal therapy (oncology), oncologic hormone therapy, hormone replacement therapy (for menopause), androgen replacement therapy (ART), oral contraceptive pills, and Gender-affirming hormone therapy. __TOC__ Types * Hormone replacement therapy (HRT), also known as menopausal hormone therapy (MHT), is for women with menopause, menopausal symptoms. It is based on the idea that the treatment may prevent discomfort caused by diminished circulating estrogen and progesterone hormones, or in the case of the surgically or prematurely menopausal, that it may prolong life and may reduce incidence of dementia. It involves the use of one or more of a group of medications designed to artificially boost hormone levels. The main types of hormones involved are estrogen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helminths
Parasitic worms, also known as helminths, are a polyphyletic group of large macroparasites; adults can generally be seen with the naked eye. Many are intestinal worms that are soil-transmitted and infect the gastrointestinal tract. Other parasitic worms such as schistosomes reside in blood vessels. Some parasitic worms, including leeches and monogeneans, are ectoparasites thus, they are not classified as helminths, which are endoparasites. Parasitic worms live in and feed in living hosts. They receive nourishment and protection while disrupting their hosts' ability to absorb nutrients. This can cause weakness and disease in the host, and poses a global health and economic problem. Parasitic worms cannot reproduce entirely within their host's body; they have a life cycle that includes some stages that need to take place outside of the host. Helminths are able to survive in their mammalian hosts for many years due to their ability to manipulate the host's immune respons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |