|
Dynamic Angiothermography
Dynamic angiothermography (DATG) is a technique for the diagnosis of breast cancer. This technique, though springing from the previous conception of thermography, is based on a completely different principle. DATG records the temperature variations linked to the vascular changes in the breast due to angiogenesis. The presence, change, and growth of tumors and lesions in breast tissue change the vascular network in the breast. Consequently, through measuring the vascular structure over time, DATG effectively monitors the change in breast tissue due to tumors and lesions. It is currently used in combination with other techniques for diagnosis of breast cancer. This diagnostic method is a low-cost one compared with other techniques. Angiothermography is not a test that substitutes for other tests, but stands in relation to them as a technique that gives additional information to clarify the clinical picture and improve the quality of diagnosis. History In the early 1970s, studies of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breast Cancer
Breast cancer is a cancer that develops from breast tissue. Signs of breast cancer may include a Breast lump, lump in the breast, a change in breast shape, dimpling of the skin, Milk-rejection sign, milk rejection, fluid coming from the nipple, a newly inverted nipple, or a red or scaly patch of skin. In those with Metastatic breast cancer, distant spread of the disease, there may be bone pain, swollen lymph nodes, shortness of breath, or yellow skin. Risk factors for developing breast cancer include obesity, a Sedentary lifestyle, lack of physical exercise, alcohol consumption, hormone replacement therapy during menopause, ionizing radiation, an early age at Menarche, first menstruation, having children late in life (or not at all), older age, having a prior history of breast cancer, and a family history of breast cancer. About five to ten percent of cases are the result of an inherited genetic predisposition, including BRCA mutation, ''BRCA'' mutations among others. Breast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breast Ultrasound
Breast ultrasound is a medical imaging technique that uses medical ultrasonography to perform imaging of the breast. It can be performed for either diagnostic or screening purposes and can be used with or without a mammogram. In particular, breast ultrasound may be useful for younger women who have denser fibrous breast tissue that may make mammograms more challenging to interpret. Automated whole-breast ultrasound (AWBU) is a technique that produces volumetric images of the breast and is largely independent of operator skill. It utilizes high-frequency ultrasound to help perform a diagnostic evaluation of the lactiferous ducts (duct sonography) and make dilated ducts and intraductal masses visible. Galactography is another technique that can be used to visualize the system of lactiferous ducts and allows a wider area to be visualized. Elastography is a type of ultrasound examination that measures tissue stiffness and can be used to detect tumours. Breast ultrasound is als ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breast Cancer
Breast cancer is a cancer that develops from breast tissue. Signs of breast cancer may include a Breast lump, lump in the breast, a change in breast shape, dimpling of the skin, Milk-rejection sign, milk rejection, fluid coming from the nipple, a newly inverted nipple, or a red or scaly patch of skin. In those with Metastatic breast cancer, distant spread of the disease, there may be bone pain, swollen lymph nodes, shortness of breath, or yellow skin. Risk factors for developing breast cancer include obesity, a Sedentary lifestyle, lack of physical exercise, alcohol consumption, hormone replacement therapy during menopause, ionizing radiation, an early age at Menarche, first menstruation, having children late in life (or not at all), older age, having a prior history of breast cancer, and a family history of breast cancer. About five to ten percent of cases are the result of an inherited genetic predisposition, including BRCA mutation, ''BRCA'' mutations among others. Breast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
In-vitro Fertilization
In vitro fertilisation (IVF) is a process of fertilisation in which an egg is combined with sperm in vitro ("in glass"). The process involves monitoring and stimulating the ovulatory process, then removing an ovum or ova (egg or eggs) from the ovaries and enabling sperm to fertilise them in a culture medium in a laboratory. After a fertilised egg (zygote) undergoes embryo culture for 2–6 days, it is transferred by catheter into the uterus, with the intention of establishing a successful pregnancy. IVF is a type of assisted reproductive technology used to treat infertility, enable gestational surrogacy, and, in combination with pre-implantation genetic testing, avoid the transmission of abnormal genetic conditions. When a fertilised egg from egg and sperm donors implants in the uterus of a genetically unrelated surrogate, the resulting child is also genetically unrelated to the surrogate. Some countries have banned or otherwise regulated the availability of IVF treatment, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hormone Replacement Therapy
Hormone replacement therapy (HRT), also known as menopausal hormone therapy or postmenopausal hormone therapy, is a form of hormone therapy used to treat symptoms associated with female menopause. Effects of menopause can include symptoms such as hot flashes, accelerated skin aging, vaginal dryness, decreased muscle mass, and complications such as osteoporosis (bone loss), sexual dysfunction, and vaginal atrophy. They are mostly caused by low levels of female sex hormones (e.g. estrogens) that occur during menopause. Estrogens and progestogens are the main hormone drugs used in HRT. Progesterone is the main female sex hormone that occurs naturally and is also manufactured into a drug that is used in menopausal hormone therapy. Although both classes of hormones can have symptomatic benefit, progestogen is specifically added to estrogen regimens, unless the uterus has been removed, to avoid the increased risk of endometrial cancer. Unopposed estrogen therapy promotes end ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Risk Factors For Breast Cancer
Risk factors for breast cancer may be divided into preventable and non-preventable. Their study belongs in the field of epidemiology. Breast cancer, like other forms of cancer, can result from multiple environmental and hereditary risk factors. The term ''environmental'', as used by cancer researchers, means any risk factor that is not genetically inherited. For breast cancer, the list of environmental risk factors includes the individual person's development, exposure to microbes, "medical interventions, dietary exposures to nutrients, energy and toxicants, ionizing radiation, and chemicals from industrial and agricultural processes and from consumer products...reproductive choices, energy balance, adult weight gain, body fatness, voluntary and involuntary physical activity, medical care, exposure to tobacco smoke and alcohol, and occupational exposures, including shift work" as well as "metabolic and physiologic processes that modify the body's internal environment." Some of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Invasive Lobular Carcinoma
Invasive lobular carcinoma (ILC) is breast cancer arising from the lobules of the mammary glands. It accounts for 5–10% of invasive breast cancer. Rare cases of this carcinoma have been diagnosed in men (see male breast cancer). Types The histologic patterns include:Fletcher's diagnostic histopathology of tumors. 3rd Ed. p. 931-932. File:Histopathology of invasive lobular carcinoma, next to lobular carcinoma in situ, annotated.jpg, Histopathology of invasive lobular carcinoma (ILC), next to lobular carcinoma in situ (LCIS) File:Breast invasive lobular carcinoma (2).jpg, Invasive lobular carcinoma demonstrating a predominantly lobular growth pattern File:LobularBreastCancer.jpg, Lobular breast cancer. Single file cells and cell nests. File:Histopathology of subtle invasive lobular carcinoma, annotated.png, ILC may be subtle on low magnification (left). Higher magnification (right) shows invasive growth pattern and vesicular nuclei with prominent nucleoli. Prognosis Overall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
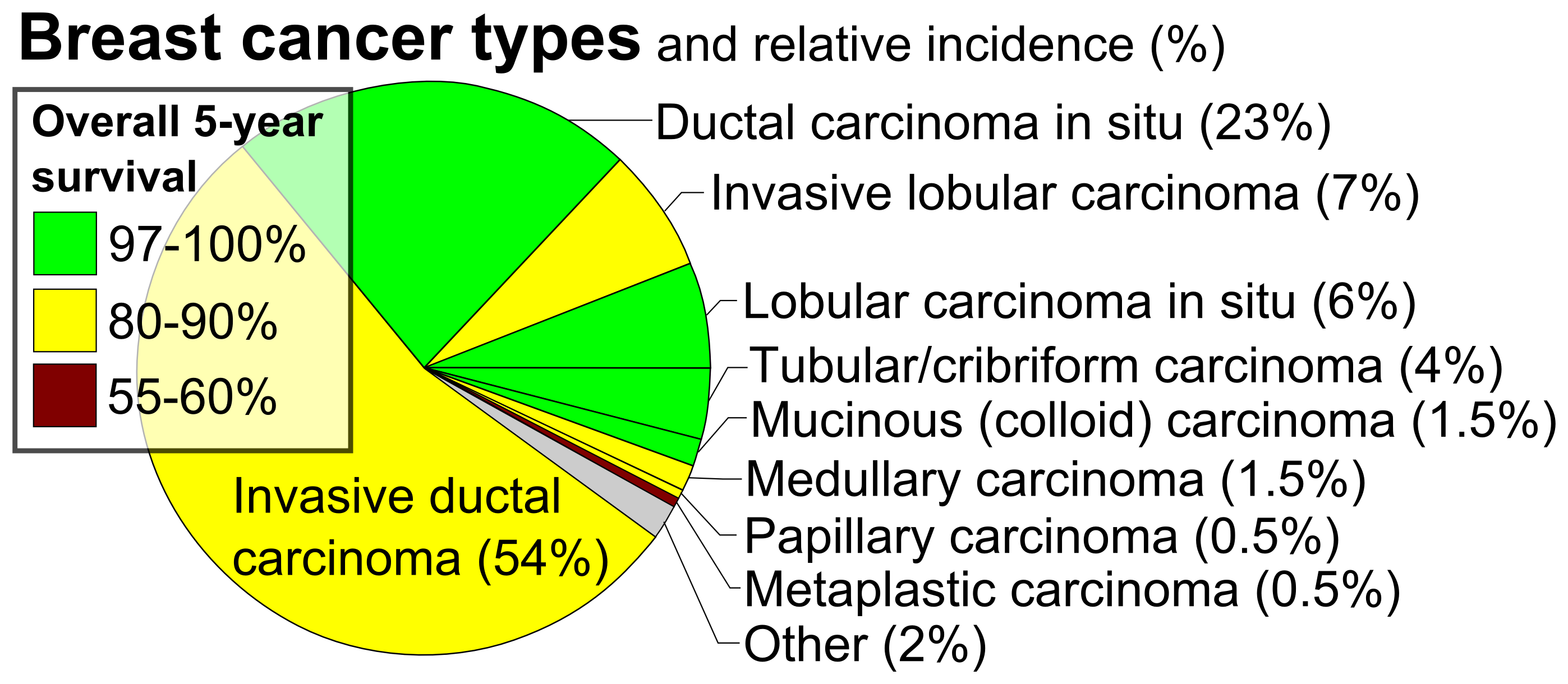
Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
Invasive carcinoma of no special type (invasive carcinoma NST), invasive breast carcinoma of no special type (IBC-NST), invasive ductal carcinoma (IDC), infiltrating ductal carcinoma (IDC) or invasive ductal carcinoma, not otherwise specified (NOS) is a disease. For international audiences this article will use "invasive carcinoma NST" because it is the preferred term of the World Health Organization (WHO). Invasive carcinoma NST accounts for half of all breast cancer diagnoses in women and is the most common type of invasive breast cancer. It is also the most commonly diagnosed form of male breast cancer. Invasive carcinoma NST is classified by its microscopic, molecular, and genetic features. Microscopically it is a breast carcinoma of the adenocarcinoma type, originating from the breast ducts. It shows invasive features but lacks the "specific differentiating features" of other types of invasive breast cancers. Invasive carcinoma NST is a diagnosis of exclusion, which means that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Screening (medicine)
In medicine, screening is a strategy used to look for as-yet-unrecognised conditions or risk markers. This testing can be applied to individuals or to a whole population without symptoms or signs of the disease being screened. Screening Public health intervention, interventions are designed to identify conditions which could at some future point turn into disease, thus enabling earlier intervention and management in the hope to reduce mortality and suffering from a disease. Although screening may lead to an earlier diagnosis, not all screening tests have been shown to benefit the person being screened; overdiagnosis, misdiagnosis, and creating a false sense of security are some potential Adverse effect (medicine), adverse effects of screening. Additionally, some screening tests can be inappropriately overused. For these reasons, a test used in a screening program, especially for a disease with low Incidence (epidemiology), incidence, must have good Sensitivity (tests), sensitivity ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ionizing Radiation
Ionizing (ionising) radiation, including Radioactive decay, nuclear radiation, consists of subatomic particles or electromagnetic waves that have enough energy per individual photon or particle to ionization, ionize atoms or molecules by detaching electrons from them. Some particles can travel up to 99% of the speed of light, and the electromagnetic waves are on the high-energy portion of the electromagnetic spectrum. Gamma rays, X-rays, and the higher energy vacuum ultraviolet, ultraviolet part of the electromagnetic spectrum are ionizing radiation; whereas the lower energy ultraviolet, visible light, infrared, microwaves, and radio waves are non-ionizing radiation. Nearly all types of laser light are non-ionizing radiation. The boundary between ionizing and non-ionizing radiation in the ultraviolet area cannot be sharply defined, as different molecules and atoms ionize at Ionization energies of the elements (data page), different energies. The energy of ionizing radiation starts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CT Scanning
A computed tomography scan (CT scan), formerly called computed axial tomography scan (CAT scan), is a medical imaging technique used to obtain detailed internal images of the body. The personnel that perform CT scans are called radiographers or radiology technologists. CT scanners use a rotating X-ray tube and a row of detectors placed in a gantry to measure X-ray attenuations by different tissues inside the body. The multiple X-ray measurements taken from different angles are then processed on a computer using tomographic reconstruction algorithms to produce tomographic (cross-sectional) images (virtual "slices") of a body. CT scans can be used in patients with metallic implants or pacemakers, for whom magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is contraindicated. Since its development in the 1970s, CT scanning has proven to be a versatile imaging technique. While CT is most prominently used in medical diagnosis, it can also be used to form images of non-living objects. The 1979 Nobel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Contrast Agent
A contrast agent (or contrast medium) is a substance used to increase the contrast of structures or fluids within the body in medical imaging. Contrast agents absorb or alter external electromagnetism or ultrasound, which is different from radiopharmaceuticals, which emit radiation themselves. In X-ray imaging, contrast agents enhance the radiodensity in a target tissue or structure. In magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), contrast agents shorten (or in some instances increase) the relaxation times of nuclei within body tissues in order to alter the contrast in the image. Contrast agents are commonly used to improve the visibility of blood vessels and the gastrointestinal tract. The types of contrast agent are classified according to their intended imaging modalities. Radiocontrast media For radiography, which is based on X-rays, iodine and barium are the most common types of contrast agent. Various sorts of iodinated contrast agents exist, with variations occurring between the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |