|
Ducted Fan
In aeronautics, a ducted fan is a thrust-generating mechanical fan or Propeller (aeronautics), propeller mounted within a cylindrical wiktionary:duct, duct or shroud. Other terms include ducted propeller or shrouded propeller. When used in vertical takeoff and landing (VTOL) applications it is also known as a shrouded rotor.Kotwani, Kailash;Ducted Fan or Shrouded Rotor Aerodynamics and its Application in Miniature VTOL Aerial Vehicles, 2009. (retrieved 22 March 2022). Ducted fans are used for propulsion or direct lift in many types of vehicle including Airplane, airplanes, airships, hovercraft, and powered lift VTOL aircraft. The high-bypass turbofan engines used on many modern airliners is an example of a very successful and popular use of ducted fan design. The duct increases thrust (physics), thrust, in comparison to a similar-sized propeller in free air. Ducted fans are quieter, and offer good opportunities for thrust vectoring. The shroud offers good protection to ground per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turbofan
A turbofan or fanjet is a type of airbreathing jet engine that is widely used in aircraft engine, aircraft propulsion. The word "turbofan" is a combination of references to the preceding generation engine technology of the turbojet and the additional fan stage. It consists of a gas turbine engine which achieves mechanical energy from combustion, and a ducted fan that uses the mechanical energy from the gas turbine to force air rearwards. Thus, whereas all the air taken in by a turbojet passes through the combustion chamber and turbines, in a turbofan some of that air bypasses these components. A turbofan thus can be thought of as a turbojet being used to drive a ducted fan, with both of these contributing to the thrust. The ratio of the mass-flow of air bypassing the engine core to the mass-flow of air passing through the core is referred to as the bypass ratio. The engine produces thrust through a combination of these two portions working together. Engines that use more Propel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Maryland
The University of Maryland, College Park (University of Maryland, UMD, or simply Maryland) is a public land-grant research university in College Park, Maryland, United States. Founded in 1856, UMD is the flagship institution of the University System of Maryland. It is known as the biggest university in the state of Maryland. UMD is the largest university in Maryland and the Washington metropolitan area. Its eleven schools and colleges offer over 200 degree-granting programs, including 113 undergraduate majors, 107 master's programs, and 83 doctoral programs. UMD's athletic teams are known as the Maryland Terrapins and compete in NCAA Division I as a member of the Big Ten Conference. A member of the Association of American Universities, The University of Maryland's proximity to Washington, D.C. has resulted in many research partnerships with the federal government; faculty receive research funding and institutional support from many agencies, such as the National In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lockheed Martin F-35 Lightning II
The Lockheed Martin F-35 Lightning II is an American family of single-seat, single-engine, supersonic Stealth aircraft, stealth strike fighters. A multirole combat aircraft designed for both Air superiority fighter, air superiority and attack aircraft, strike missions, it also has electronic warfare and intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance capabilities. Lockheed Martin is the prime F-35 contractor with principal partners Northrop Grumman and BAE Systems. The aircraft has three main variants: the CTOL, conventional takeoff and landing (CTOL) F-35A, the STOVL, short take-off and vertical-landing (STOVL) F-35B, and the carrier-based, carrier variant (CV) Catapult Assisted Take-Off But Arrested Recovery, catapult-assisted take-off but arrested recovery (CATOBAR) F-35C. The aircraft descends from the Lockheed Martin X-35, which in 2001 beat the Boeing X-32 to win the Joint Strike Fighter program, Joint Strike Fighter (JSF) program intended to replace the General Dynami ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
US Navy 060817-N-1467R-042 A Sailor Assigned To Assault Craft Unit Four (ACU 4) Stationed At Little Creek Amphibious Base, Va
US or Us most often refers to: * ''Us'' (pronoun), the objective case of the English first-person plural pronoun ''we'' * US, an abbreviation for the United States US, U.S., Us, us, or u.s. may also refer to: Arts and entertainment Albums * ''Us'' (Brother Ali album) or the title song, 2009 * ''Us'' (Empress Of album), 2018 * ''Us'' (Mull Historical Society album), 2003 * ''Us'' (Peter Gabriel album), 1992 * ''Us'' (EP), by Moon Jong-up, 2021 * ''Us'', by Maceo Parker, 1974 * ''Us'', mini-album by Peakboy, 2019 Songs * "Us" (James Bay song), 2018 * "Us" (Jennifer Lopez song), 2018 * "Us" (Regina Spektor song), 2004 * "Us" (Gracie Abrams song), 2024 * "Us", by Azealia Banks from '' Fantasea'', 2012 * "Us", by Celine Dion from ''Let's Talk About Love'', 1997 * "Us", by Gucci Mane from '' Delusions of Grandeur'', 2019 * "Us", by Spoon from '' Hot Thoughts'', 2017 Other media * US Festival, two 1980s California music festivals organized by Steve Wozniak * ''Us'' (1991 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avian 2-180 Gyroplane
Avian may refer to: *Anything related to birds (animals of the class ''Aves'') Aviation *Avro Avian, a series of light aircraft made by Avro in the 1920s and 1930s *Avian Limited, a hang glider manufacturer founded in 1989 Places *Avian, Iran, a village in Razavi Khorasan Province, Iran *, Friulian name of Aviano, a town and ''comune'' in northern Italy *Avian Island, Antarctica *Avian Tower, a high-rise building in Surabaya, Indonesia People *Avian (band), an American heavy metal band *Avian (given name), Russian male first name *Bob Avian (1937–2021), American choreographer and theater director See also * *Avian influenza, a virus adapted to birds *Evian, a brand of mineral water *Évian-les-Bains Évian-les-Bains (), or simply Évian (, , or ), is a Communes of France, commune in Eastern France, by the border with Switzerland. It is located in the northern part of the Haute-Savoie department in the Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes region. A high-m ..., a commune in eastern Fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helicopters
A helicopter is a type of rotorcraft in which lift and thrust are supplied by horizontally spinning rotors. This allows the helicopter to take off and land vertically, to hover, and to fly forward, backward and laterally. These attributes allow helicopters to be used in congested or isolated areas where fixed-wing aircraft and many forms of short take-off and landing (STOL) or short take-off and vertical landing ( STOVL) aircraft cannot perform without a runway. The Focke-Wulf Fw 61 was the first successful, practical, and fully controllable helicopter in 1936, while in 1942, the Sikorsky R-4 became the first helicopter to reach full-scale production. Starting in 1939 and through 1943, Igor Sikorsky worked on the development of the VS-300, which over four iterations, became the basis for modern helicopters with a single main rotor and a single tail rotor. Although most earlier designs used more than one main rotor, the configuration of a single main rotor accompan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
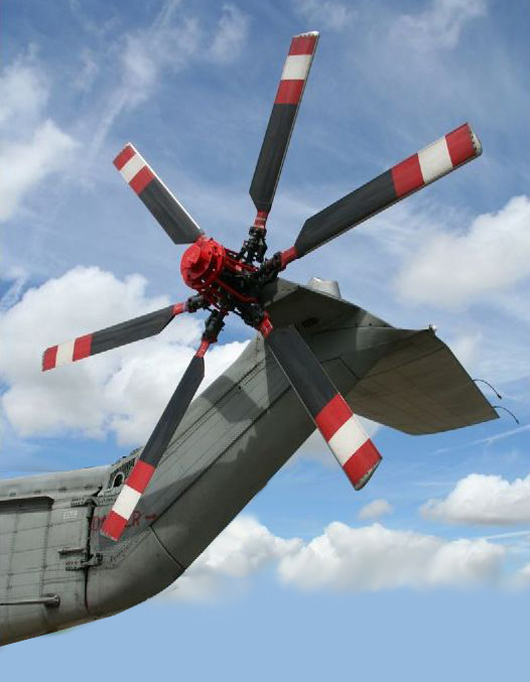
Tail Rotor
The tail rotor is a smaller rotor mounted vertically or near-vertically at the tail of a traditional single-rotor helicopter, where it rotates to generate a propeller-like horizontal thrust in the same direction as the main rotor's rotation. The tail rotor's position and distance from the helicopter's center of mass allow it to develop enough thrust leverage to counter the reactional torque exerted on the fuselage by the spinning of the main rotor. Without the tail rotor or other anti-torque mechanisms (e.g. NOTAR), the helicopter would be constantly spinning in the opposite direction of the main rotor when flying. Tail rotors are simpler than main rotors since they require only collective changes in pitch to vary thrust. The pitch of the tail rotor blades is adjustable by the pilot via the anti-torque pedals, which also provide directional control by allowing the pilot to rotate the helicopter around its vertical axis. Its drive system consists of a shaft powered from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fenestron
A Fenestron (sometimes alternatively referred to as a fantail or a "fan-in-fin" arrangementLeishman 2006, p. 321.) is an enclosed helicopter tail rotor that operates like a ducted fan. The term ''Fenestron'' is a trademark of multinational helicopter manufacturing consortium Airbus Helicopters (formerly known as Eurocopter). The word itself comes from the Occitan term for a ''small window'', and is ultimately derived from the Latin word ''fenestra'' for ''window''.Prouty, Ray. ''Helicopter Aerodynamics'', Helobooks, 1985, 2004. p. 266. Like the conventional tail rotor it replaces, a Fenestron counteracts the torque generated by the main rotor. However, it differs from a conventional open tail rotor by being integrally housed within the tail boom. While conventional tail rotors typically have between two and six blades, Fenestrons have between seven and eighteen blades; these may have variable angular spacing so that the noise is distributed over different frequencies. By placing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electric Motor
An electric motor is a machine that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. Most electric motors operate through the interaction between the motor's magnetic field and electric current in a electromagnetic coil, wire winding to generate Laplace force in the form of torque applied on the motor's shaft. An electric generator is mechanically identical to an electric motor, but operates in reverse, converting mechanical energy into electrical energy. Electric motors can be powered by direct current (DC) sources, such as from batteries or rectifiers, or by alternating current (AC) sources, such as a power grid, Inverter (electrical), inverters or electrical generators. Electric motors may also be classified by considerations such as power source type, construction, application and type of motion output. They can be brushed motor, brushed or brushless motor, brushless, single-phase electric power, single-phase, two-phase electric power, two-phase, or three-phase electric p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
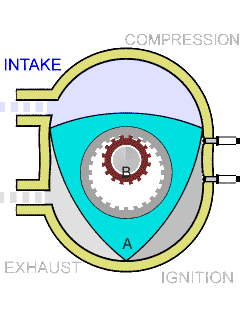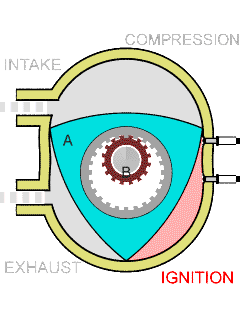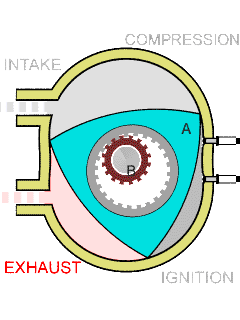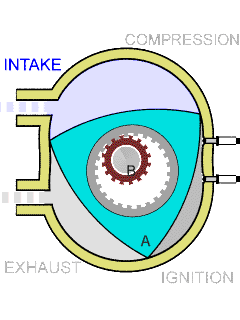
Wankel Engine
The Wankel engine (, ) is a type of internal combustion engine using an eccentric (mechanism), eccentric Pistonless rotary engine, rotary design to convert pressure into rotating motion. The concept was proven by German engineer Felix Wankel, followed by a commercially feasible engine designed by German engineer Hanns-Dieter Paschke. The Wankel engine's rotor is similar in shape to a Reuleaux triangle, with the sides having less curvature. The rotor spins inside a figure-eight-like epitrochoidal housing around a fixed gear. The midpoint of the rotor moves in a circle around the output shaft, rotating the shaft via a Cam (mechanism), cam. In its basic gasoline-fuelled form, the Wankel engine has lower thermal efficiency and higher exhaust emissions relative to the Four-stroke engine, four-stroke reciprocating engine. This thermal inefficiency has restricted the Wankel engine to limited use since its introduction in the 1960s. However, many disadvantages have mainly been overcome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reciprocating Engine
A reciprocating engine, more often known as a piston engine, is a heat engine that uses one or more reciprocating pistons to convert high temperature and high pressure into a rotating motion. This article describes the common features of all types. The main types are: the internal combustion engine, used extensively in motor vehicles; the steam engine, the mainstay of the Industrial Revolution; and the Stirling engine for niche applications. Internal combustion engines are further classified in two ways: either a spark-ignition (SI) engine, where the spark plug initiates the combustion; or a compression-ignition (CI) engine, where the air within the cylinder is compressed, thus heating it, so that the heated air ignites fuel that is injected then or earlier.''Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach'' by Yunus A. Cengal and Michael A. Boles Common features in all types There may be one or more pistons. Each piston is inside a cylinder, into which a gas is introduced, e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |