|
Duct (anatomy)
In anatomy and physiology, a duct is a circumscribed channel leading from an exocrine gland or organ. Types of ducts Examples include: Duct system As ducts travel from the acinus which generates the fluid to the target, the ducts become larger and the epithelium becomes thicker. The parts of the system are classified as follows: Some sources consider "lobar" ducts to be the same as "interlobar ducts", while others consider lobar ducts to be larger and more distal from the acinus. For sources that make the distinction, the interlobar ducts are more likely to classified with simple columnar epithelium (or pseudostratified epithelium), reserving the stratified columnar for the lobar ducts. File:Gray1025.png, Section of submaxillary gland of kitten. Duct semidiagrammatic. X 200. File:Gray1173.png, Section of portion of mamma. Intercalated duct The intercalated duct, also called intercalary duct (ducts of Boll), is the portion of an exocrine gland leading directly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
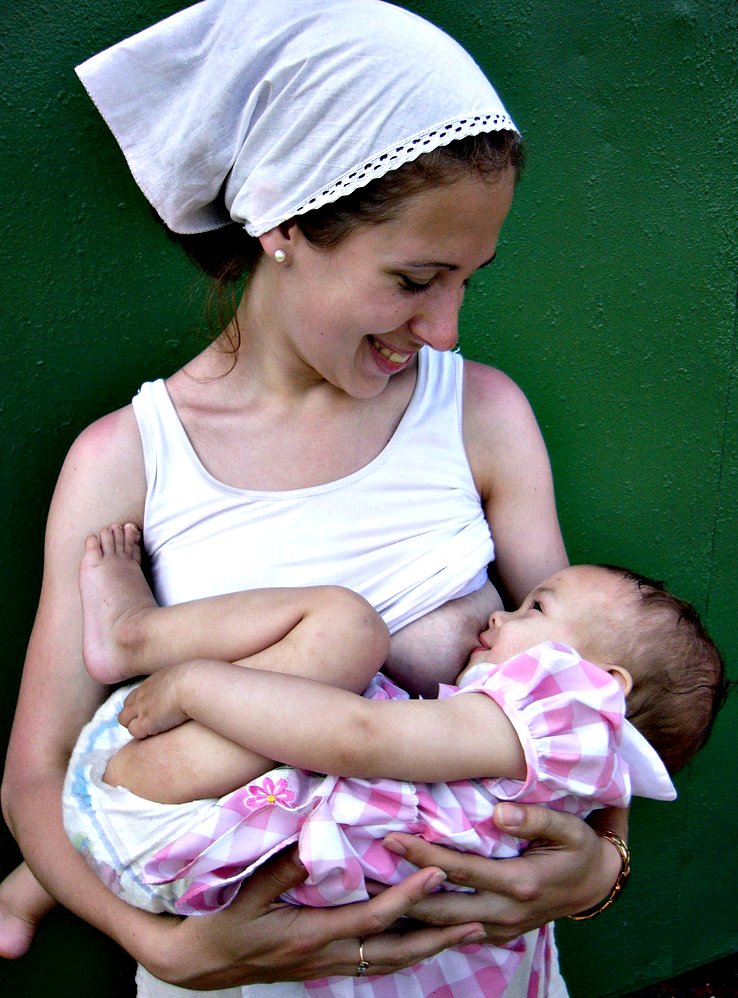
Lactiferous Duct
Lactiferous ducts are ducts that converge and form a Morphogenesis#Branching morphogenesis, branched system connecting the nipple to the lobules of the mammary gland. When lactogenesis occurs, under the influence of hormones, the breast milk, milk is moved to the nipple by the action of smooth muscle contractions along the ductal system to the tip of the nipple. They are also referred to as ''galactophores'', ''galactophorous ducts'', ''mammary ducts'', ''mamillary ducts'' or ''milk ducts''. Structure Lactiferous ducts are lined by a columnar epithelium supported by myoepithelial cells. Prior to 2005, it was thought within the areola the lactiferous duct would dilate to form the lactiferous sinus in which milk accumulates between breastfeeding sessions. However past studies have shown that the lactiferous sinus does not exist. Function The columnar epithelium plays a key role in balancing milk production, milk stasis and reabsorption. The cells of the columnar epithelium form tig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exocrine Gland
Exocrine glands are glands that secrete substances onto an epithelial surface by way of a duct. Examples of exocrine glands include sweat, salivary, mammary, ceruminous, lacrimal, sebaceous, prostate and mucous. Exocrine glands are one of two types of glands in the human body, the other being endocrine glands, which secrete their products directly into the bloodstream. The liver and pancreas are both exocrine and endocrine glands; they are exocrine glands because they secrete products—bile and pancreatic juice—into the gastrointestinal tract through a series of ducts, and endocrine because they secrete other substances directly into the bloodstream. Exocrine sweat glands are part of the integumentary system; they have eccrine and apocrine types. Classification Structure Exocrine glands contain a glandular portion and a duct portion, the structures of which can be used to classify the gland. * The duct portion may be branched (called compound) or unbranched (called sim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cystic Duct
The cystic duct is the duct that (typically) joins the gallbladder and the common hepatic duct; the union of the cystic duct and common hepatic duct forms the bile duct (formerly known as the common bile duct). Its length varies. Anatomy The cystic duct typically measures (sources differ) 2–4 cm/2–3 cm in length (though its length has been known to range from 0.5 cm to 9 cm), and 2–3 mm in diameter. It is often tortuous. It is the distal continuation of the neck of the gallbladder, from where it is directed inferoposteriorly and to the left/medially (this occurs in half of individuals). It typically terminates by uniting with the common hepatic duct to form the bile duct (usually anterior to the right hepatic artery). It usually joins the common bile duct from the right lateral side (forming an oblique angle between the two), and at such a distance that the bile duct is twice as long as the common hepatic duct. It often fuses with the common ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Common Hepatic Duct
The common hepatic duct is the first part of the biliary tract. It joins the cystic duct coming from the gallbladder to form the common bile duct. Structure The common hepatic duct is the first part of the biliary tract. It is formed by the union of the right hepatic duct (which drains bile from the right functional lobe of the liver) and the left hepatic duct (which drains bile from the left functional lobe of the liver). The duct is about 3 cm long. The common hepatic duct is about 6 mm in diameter in adults, with some variation.Gray's Anatomy, 39th ed, p. 1228 Termination The common hepatic duct typically unites with the cystic duct some 1–2 cm superior to the duodenum and anterior to the right hepatic artery, with the cystic duct approaching the common hepatic duct from the right. Relations The right branch of the hepatic artery proper usually passes posterior to the duct, but may rarely pass anterior to it instead. Histology The inner surface ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Common Bile Duct
The common bile duct (also bile duct) is a part of the biliary tract. It is formed by the union of the common hepatic duct and cystic duct. It ends by uniting with the pancreatic duct to form the ampulla of Vater (hepatopancreatic ampulla). Its sphincter the sphincter of Oddi, enables the regulation of bile flow. Anatomy The bile duct is some 6–8 cm long, and normally up to 8 mm in diameter. Its proximal supraduodenal part is situated within the free edge of the lesser omentum. Its middle retroduodenal part is oriented inferiorly and right-ward, and is situated posterior to the first part of the duodenum, and anterior to the inferior vena cava. Its distal paraduodenal part is oriented still more right-ward, is accommodated by a groove upon (sometimes a channel within) the posterior aspect of the head of the pancreas, and is situated anterior to the right renal vein. The bile duct terminates by uniting with the pancreatic duct (at an angle of about 60°) t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liver
The liver is a major metabolic organ (anatomy), organ exclusively found in vertebrates, which performs many essential biological Function (biology), functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the Protein biosynthesis, synthesis of various proteins and various other Biochemistry, biochemicals necessary for digestion and growth. In humans, it is located in the quadrants and regions of abdomen, right upper quadrant of the abdomen, below the thoracic diaphragm, diaphragm and mostly shielded by the lower right rib cage. Its other metabolic roles include carbohydrate metabolism, the production of a number of hormones, conversion and storage of nutrients such as glucose and glycogen, and the decomposition of red blood cells. Anatomical and medical terminology often use the prefix List of medical roots, suffixes and prefixes#H, ''hepat-'' from ἡπατο-, from the Greek language, Greek word for liver, such as hepatology, and hepatitis The liver is also an accessory digestive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Common Hepatic Duct
The common hepatic duct is the first part of the biliary tract. It joins the cystic duct coming from the gallbladder to form the common bile duct. Structure The common hepatic duct is the first part of the biliary tract. It is formed by the union of the right hepatic duct (which drains bile from the right functional lobe of the liver) and the left hepatic duct (which drains bile from the left functional lobe of the liver). The duct is about 3 cm long. The common hepatic duct is about 6 mm in diameter in adults, with some variation.Gray's Anatomy, 39th ed, p. 1228 Termination The common hepatic duct typically unites with the cystic duct some 1–2 cm superior to the duodenum and anterior to the right hepatic artery, with the cystic duct approaching the common hepatic duct from the right. Relations The right branch of the hepatic artery proper usually passes posterior to the duct, but may rarely pass anterior to it instead. Histology The inner surface ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bile
Bile (from Latin ''bilis''), also known as gall, is a yellow-green/misty green fluid produced by the liver of most vertebrates that aids the digestion of lipids in the small intestine. In humans, bile is primarily composed of water, is produced continuously by the liver, and is stored and concentrated in the gallbladder. After a human eats, this stored bile is discharged into the first section of the small intestine, known as the duodenum. Composition In the human liver, bile is composed of 97–98% water, 0.7% bile salts, 0.2% bilirubin, 0.51% fats ( cholesterol, fatty acids, and lecithin), and 200 meq/L inorganic salts. The two main pigments of bile are bilirubin, which is orange-yellow, and its oxidised form biliverdin, which is green. When mixed, they are responsible for the brown color of feces. About of bile is produced per day in adult human beings. Function Bile or gall acts to some extent as a surfactant, helping to emulsify the lipids in food. B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Common Bile Duct
The common bile duct (also bile duct) is a part of the biliary tract. It is formed by the union of the common hepatic duct and cystic duct. It ends by uniting with the pancreatic duct to form the ampulla of Vater (hepatopancreatic ampulla). Its sphincter the sphincter of Oddi, enables the regulation of bile flow. Anatomy The bile duct is some 6–8 cm long, and normally up to 8 mm in diameter. Its proximal supraduodenal part is situated within the free edge of the lesser omentum. Its middle retroduodenal part is oriented inferiorly and right-ward, and is situated posterior to the first part of the duodenum, and anterior to the inferior vena cava. Its distal paraduodenal part is oriented still more right-ward, is accommodated by a groove upon (sometimes a channel within) the posterior aspect of the head of the pancreas, and is situated anterior to the right renal vein. The bile duct terminates by uniting with the pancreatic duct (at an angle of about 60°) t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gallbladder
In vertebrates, the gallbladder, also known as the cholecyst, is a small hollow Organ (anatomy), organ where bile is stored and concentrated before it is released into the small intestine. In humans, the pear-shaped gallbladder lies beneath the liver, although the structure and position of the gallbladder can vary significantly among animal species. It receives bile, produced by the liver, via the common hepatic duct, and stores it. The bile is then released via the common bile duct into the duodenum, where the bile helps in the digestion of fats. The gallbladder can be affected by gallstones, formed by material that cannot be dissolved – usually cholesterol or bilirubin, a product of hemoglobin breakdown. These may cause significant pain, particularly in the upper-right corner of the abdomen, and are often treated with removal of the gallbladder (called a cholecystectomy). Cholecystitis, inflammation of the gallbladder, has a wide range of causes, including result from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cystic Duct
The cystic duct is the duct that (typically) joins the gallbladder and the common hepatic duct; the union of the cystic duct and common hepatic duct forms the bile duct (formerly known as the common bile duct). Its length varies. Anatomy The cystic duct typically measures (sources differ) 2–4 cm/2–3 cm in length (though its length has been known to range from 0.5 cm to 9 cm), and 2–3 mm in diameter. It is often tortuous. It is the distal continuation of the neck of the gallbladder, from where it is directed inferoposteriorly and to the left/medially (this occurs in half of individuals). It typically terminates by uniting with the common hepatic duct to form the bile duct (usually anterior to the right hepatic artery). It usually joins the common bile duct from the right lateral side (forming an oblique angle between the two), and at such a distance that the bile duct is twice as long as the common hepatic duct. It often fuses with the common ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Milk
Milk is a white liquid food produced by the mammary glands of lactating mammals. It is the primary source of nutrition for young mammals (including breastfeeding, breastfed human infants) before they are able to digestion, digest solid food. Milk contains many nutrients, including calcium and protein, as well as lactose and saturated fat; the enzyme lactase is needed to break down lactose. Immune factors and immune-modulating components in milk contribute to milk immunity. The first milk, which is called colostrum, contains antibody, antibodies and immune-modulating components that milk immunity, strengthen the immune system against many diseases. As an agricultural product, Milking, milk is collected from farm animals, mostly cattle, on a dairy. It is used by humans as a drink and as the base ingredient for dairy products. The US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, CDC recommends that children over the age of 12 months (the minimum age to stop giving breast milk or Ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |