|
Dual-use Technology
In politics, diplomacy and export control, dual-use items refer to goods, software and technology that can be used for both civilian and military applications.''Exporting dual-use goods.'' European Commission (accessed Aug 2022) More generally speaking, dual-use can also refer to any goods or technology which can satisfy more than one goal at any given time. Thus, expensive technologies originally benefitting only military purposes would in the future also be used to serve civilian commercial interests if they were not otherwise engaged, such as the Global Positioning System developed by the U.S. Department of Defense. The "dual-use dilemma" was first noted with the discovery of the process for synthesizing and mass-producing ammonia which revolutionized agriculture wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
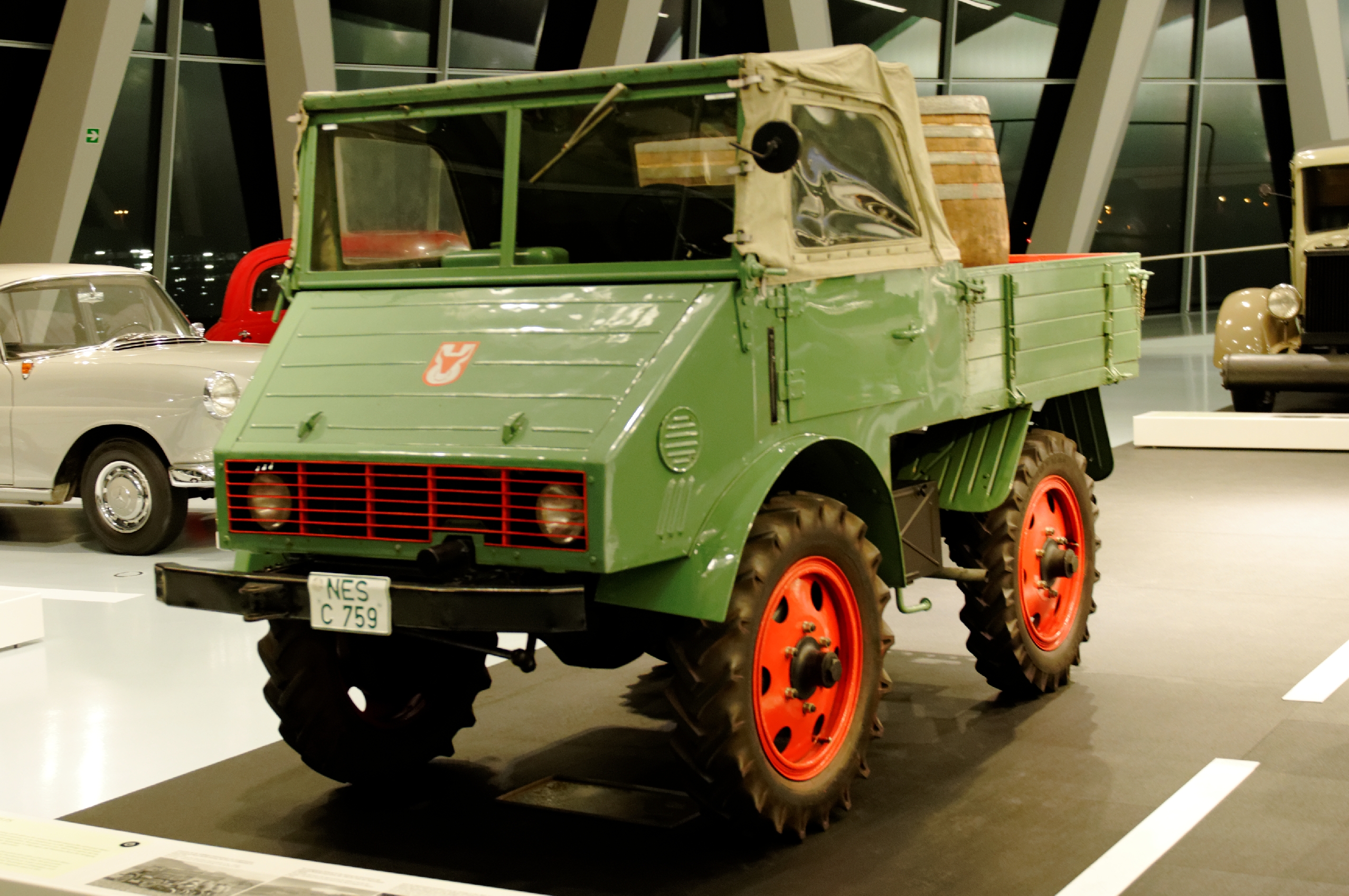
Unimog
The Unimog (pronunciation in American English: ''YOU-nuh-mog''; British English: ''YOU-knee-mog''; German: , ) is a Daimler Truck line of multi-purpose, highly offroad capable AWD vehicles produced since 1948. Utilizing engine-driven power take-offs (PTO) Unimogs have operated in the roles of tractors, light trucks and lorries, for snow plowing, in agriculture, forestry, rural firefighting, in the military, even in rallying and as recreational vehicles. The frame is designed to be a flexible part of the suspension, not to carry heavy loads. Overview Conceived in 1944 in response to the Morgenthau Plan, former Daimler-Benz airplane engine engineers developed prototypes under occupation. The small universally-applicable motorised 25hp workhorse was designed to be able to fit over two rows of potatoes to work on fields like a slow agricultural tractor, but with four equal size wheels on portal axles, coil spring suspension, and many gears allowing it to run on roads like a truck. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Cold War
The Cold War was a period of global Geopolitics, geopolitical rivalry between the United States (US) and the Soviet Union (USSR) and their respective allies, the capitalist Western Bloc and communist Eastern Bloc, which lasted from 1947 until the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991. The term ''Cold war (term), cold war'' is used because there was no direct fighting between the two superpowers, though each supported opposing sides in regional conflicts known as proxy wars. In addition to the struggle for ideological and economic influence and an arms race in both conventional and Nuclear arms race, nuclear weapons, the Cold War was expressed through technological rivalries such as the Space Race, espionage, propaganda campaigns, Economic sanctions, embargoes, and sports diplomacy. After the end of World War II in 1945, during which the US and USSR had been allies, the USSR installed satellite state, satellite governments in its occupied territories in Eastern Europe and N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Nuclear Proliferation
Nuclear proliferation is the spread of nuclear weapons to additional countries, particularly those not recognized as List of states with nuclear weapons, nuclear-weapon states by the Treaty on the Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons, commonly known as the ''Non-Proliferation Treaty'' or ''NPT''. Nuclear proliferation occurs through the spread of fissile material, and the technology and capabilities needed to produce it and to Nuclear weapon design, design and manufacture nuclear weapons. In a modern context, it also includes the spread of nuclear weapons to non-state actors. Proliferation has been opposed by many nations with and without nuclear weapons, as governments fear that more countries with nuclear weapons will increase the possibility of nuclear warfare (including the so-called countervalue targeting of civilians), de-stabilize international relations, or infringe upon the principle of Sovereign state, state sovereignty. Conversely, supporters of deterrence theory arg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Nuclear Program Of Iran
The nuclear program of Iran is one of the most scrutinized nuclear programs in the world. The military capabilities of the program are possible through its mass enrichment activities in facilities such as Natanz and Arak. In June 2025, the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) found Iran non-compliant with its nuclear obligations for the first time in 20 years. Iran retaliated by launching a new enrichment site and installing advanced centrifuges. Iran's nuclear program began in the 1950s under the Pahlavi dynasty with US support. It expanded in the 1970s with plans for power reactors, paused after the 1979 Iranian Revolution, and resumed secretly during the 1980s Iran–Iraq War. In the 1990s, Iran pursued a full nuclear fuel cycle and acquired centrifuge technology through illicit networks, including ties with Pakistan and North Korea. Undeclared enrichment sites at Natanz and Arak were exposed in 2002, and Fordow, an underground fuel enrichment site, was reveale ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Atomic Bomb
A nuclear weapon is an explosive device that derives its destructive force from nuclear reactions, either fission (fission or atomic bomb) or a combination of fission and fusion reactions (thermonuclear weapon), producing a nuclear explosion. Both bomb types release large quantities of energy from relatively small amounts of matter. Nuclear bombs have had yields between 10 tons (the W54) and 50 megatons for the Tsar Bomba (see TNT equivalent). Yields in the low kilotons can devastate cities. A thermonuclear weapon weighing as little as can release energy equal to more than 1.2 megatons of TNT (5.0 PJ). Apart from the blast, effects of nuclear weapons include firestorms, extreme heat and ionizing radiation, radioactive nuclear fallout, an electromagnetic pulse, and a radar blackout. The first nuclear weapons were developed by the Allied Manhattan Project during World War II. Their production continues to require a large scientific and industrial complex, primari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Nuclear Weapons
A nuclear weapon is an explosive device that derives its destructive force from nuclear reactions, either nuclear fission, fission (fission or atomic bomb) or a combination of fission and nuclear fusion, fusion reactions (thermonuclear weapon), producing a nuclear explosion. Both bomb types release large quantities of energy from relatively small amounts of matter. Nuclear bombs have had Nuclear weapon yield, yields between 10 tons (the W54) and 50 megatons for the Tsar Bomba (see TNT equivalent). Yields in the low kilotons can devastate cities. A thermonuclear weapon weighing as little as can release energy equal to more than 1.2 megatons of TNT (5.0 Petajoule, PJ). Apart from the blast, Effects of nuclear explosions, effects of nuclear weapons include Firestorm, firestorms, extreme Thermal radiation, heat and ionizing radiation, radioactive nuclear fallout, an Nuclear electromagnetic pulse, electromagnetic pulse, and a radar blackout. The first nuclear weapons were deve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Nuclear Fuel Cycle
The nuclear fuel cycle, also known as the nuclear fuel chain, describes the series of stages that nuclear fuel undergoes during its production, use, and recycling or disposal. It consists of steps in the ''front end'', which are the preparation of the fuel, steps in the ''service period'' in which the fuel is used during reactor operation, and steps in the ''back end'', which are necessary to safely manage, contain, and either reprocess or dispose of spent nuclear fuel. If spent fuel is not reprocessed, the fuel cycle is referred to as an ''open fuel cycle'' (or a ''once-through fuel cycle''); if the spent fuel is reprocessed, it is referred to as a ''closed fuel cycle''. Basic concepts Nuclear power relies on fissionable material that can sustain a chain reaction with neutrons. Examples of such materials include uranium and plutonium. Most nuclear reactors use a moderator to lower the kinetic energy of the neutrons and increase the probability that fission will occur. This ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Nuclear Power
Nuclear power is the use of nuclear reactions to produce electricity. Nuclear power can be obtained from nuclear fission, nuclear decay and nuclear fusion reactions. Presently, the vast majority of electricity from nuclear power is produced by nuclear ''fission'' of uranium and plutonium in nuclear power plants. Nuclear ''decay'' processes are used in niche applications such as radioisotope thermoelectric generators in some space probes such as ''Voyager 2''. Reactors producing controlled fusion power, ''fusion'' power have been operated since 1958 but have yet to generate net power and are not expected to be commercially available in the near future. The first nuclear power plant was built in the 1950s. The global installed nuclear capacity grew to 100GW in the late 1970s, and then expanded during the 1980s, reaching 300GW by 1990. The 1979 Three Mile Island accident in the United States and the 1986 Chernobyl disaster in the Soviet Union resulted in increased regulation and p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Multiple Independently Targetable Reentry Vehicle
A multiple independently targetable reentry vehicle (MIRV) is an exoatmospheric ballistic missile payload containing several warheads, each capable of being aimed to hit a different target. The concept is almost invariably associated with intercontinental ballistic missiles carrying thermonuclear warheads, even if not strictly being limited to them. An intermediate case is the multiple reentry vehicle (MRV) missile which carries several warheads which are dispersed but not individually aimed. All nuclear-weapon states except Pakistan and North Korea are currently confirmed to have deployed MIRV missile systems. The first true MIRV design was the Minuteman III, first successfully tested in 1968 and introduced into actual use in 1970. The Minuteman III held three smaller W62 warheads, with yields of about each in place of the single W56 used on the Minuteman II. From 1970 to 1975, the United States would remove approximately 550 earlier versions of the Minuteman ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Atmospheric Entry
Atmospheric entry (sometimes listed as Vimpact or Ventry) is the movement of an object from outer space into and through the gases of an atmosphere of a planet, dwarf planet, or natural satellite. Atmospheric entry may be ''uncontrolled entry,'' as in the entry of astronomical objects, space debris, or bolides. It may be ''controlled entry'' (or ''reentry'') of a spacecraft that can be navigated or follow a predetermined course. Methods for controlled atmospheric ''entry, descent, and landing'' of spacecraft are collectively termed as ''EDL''. Objects entering an atmosphere experience atmospheric drag, which puts mechanical stress on the object, and aerodynamic heating—caused mostly by compression of the air in front of the object, but also by drag. These forces can cause loss of mass ( ablation) or even complete disintegration of smaller objects, and objects with lower compressive strength can explode. Objects have reentered with speeds ranging from 7.8 km/s for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
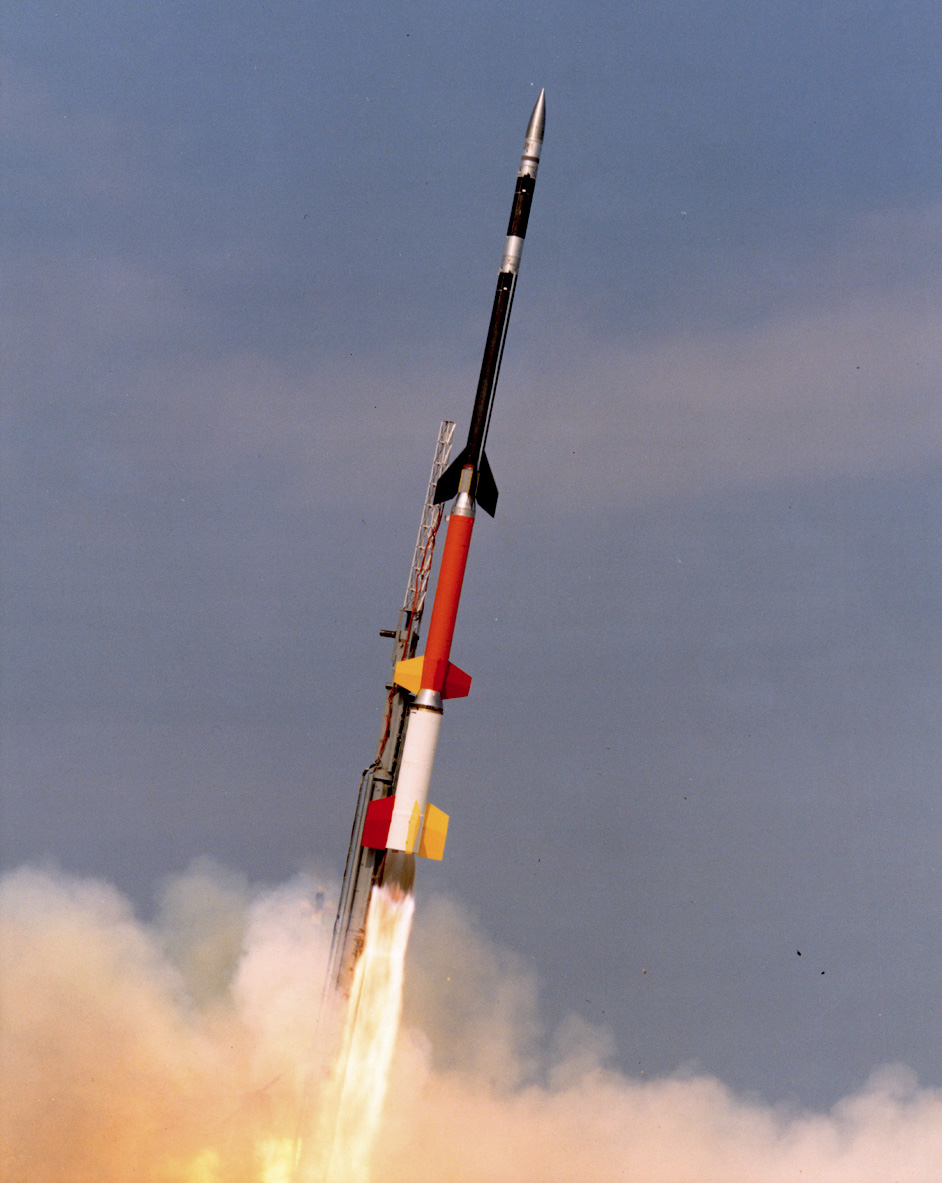
Sounding Rocket
A sounding rocket or rocketsonde, sometimes called a research rocket or a suborbital rocket, is an instrument-carrying rocket designed to take measurements and perform scientific experiments during its sub-orbital flight. The rockets are often used to launch instruments from above the surface of the Earth, the altitude generally between weather balloons and satellites; the maximum altitude for balloons is about and the minimum for satellites is approximately . Due to their suborbital flight profile, sounding rockets are often much simpler than their counterparts built for orbital flight. Certain sounding rockets have an apogee between , such as the Black Brant X and XII, which is the maximum apogee of their class. For certain purposes, sounding rockets may be flown to altitudes as high as to allow observing times of around 40 minutes to provide geophysical observations of the magnetosphere, ionosphere, thermosphere, and mesosphere. Etymology The origin of the term comes fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Intercontinental Ballistic Missile
An intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) is a ballistic missile with a range (aeronautics), range greater than , primarily designed for nuclear weapons delivery (delivering one or more Thermonuclear weapon, thermonuclear warheads). Conventional weapon, Conventional, Chemical weapon, chemical, and Biological agent, biological weapons can also be delivered with varying effectiveness, but have never been deployed on ICBMs. Most modern designs support multiple independently targetable reentry vehicle (MIRVs), allowing a single missile to carry several warheads, each of which can strike a different target. The Nuclear weapons of the United States, United States, Russia and weapons of mass destruction, Russia, China and weapons of mass destruction, China, France and weapons of mass destruction, France, India and weapons of mass destruction, India, the United Kingdom and weapons of mass destruction, United Kingdom, Nuclear weapons and Israel, Israel, and North Korea and weapons of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |