|
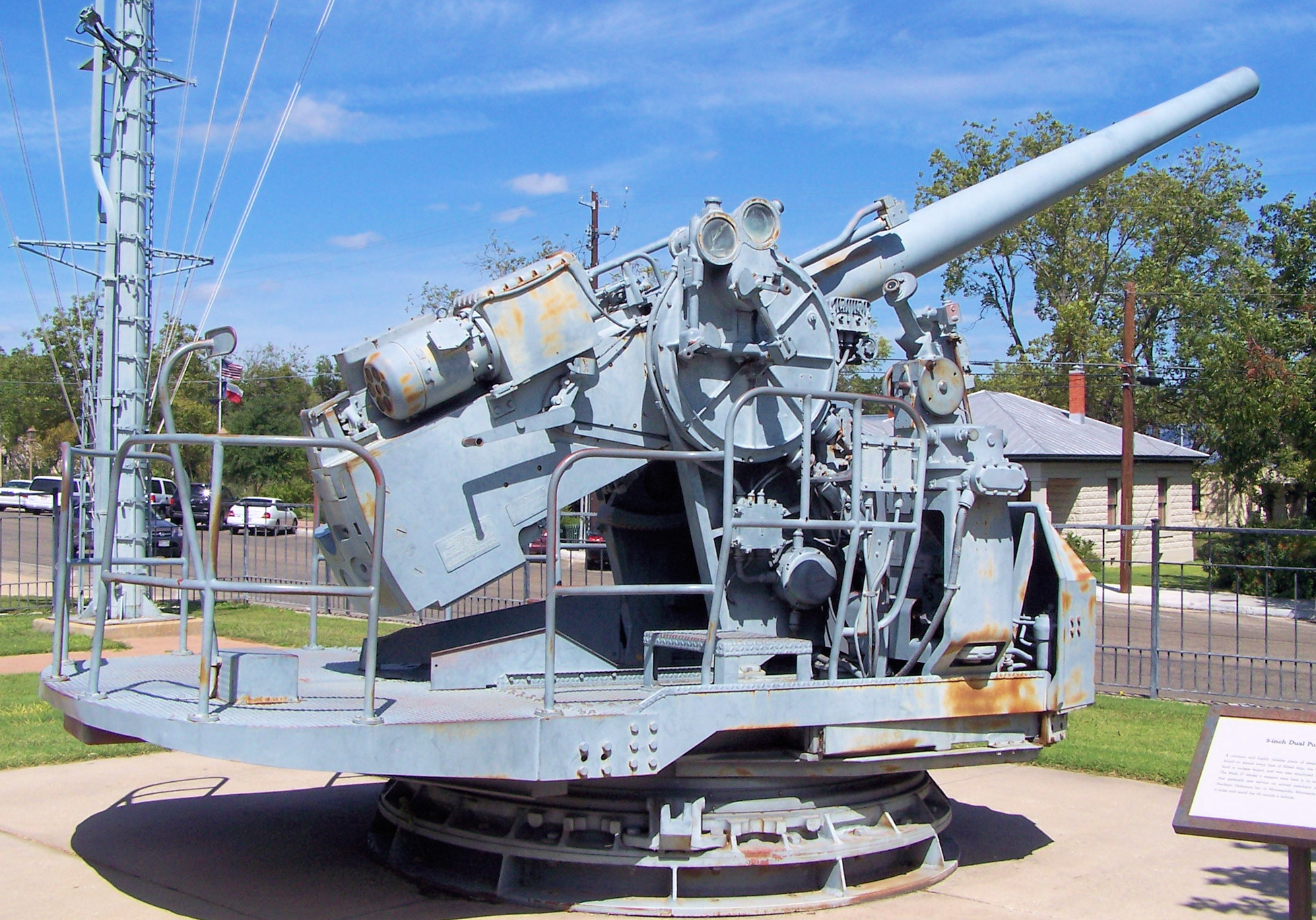
Dual-purpose Gun
A dual-purpose gun is a naval artillery mounting designed to engage both surface and air targets. Description Second World War-era capital ships had four classes of artillery: the heavy main battery, intended to engage opposing battleships and cruisers of 305 mm to 457 mm (12 inch to 18 inch); a secondary battery for use against enemy destroyers of 152 mm to 203 mm (6 inch to 8 inch); heavy anti-aircraft guns of 76 mm to 127 mm (3 inch to 5 inch), which could create barrages to knock out airplanes at a distance; finally, light rapid-fire anti-aircraft batteries (A/A) to track and bring down aircraft at close range. The light A/A was dispersed throughout the ship and included both automatic cannons of 20 mm to 40 mm (.787 inch to 1.57 inch) and heavy machine guns of 12.7 mm to 14.5 mm (.50 inch to .58 inch). During World War II, the US Navy, Royal Navy, the French Navy, and the Imperial Japanese Navy combined the secondary bat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
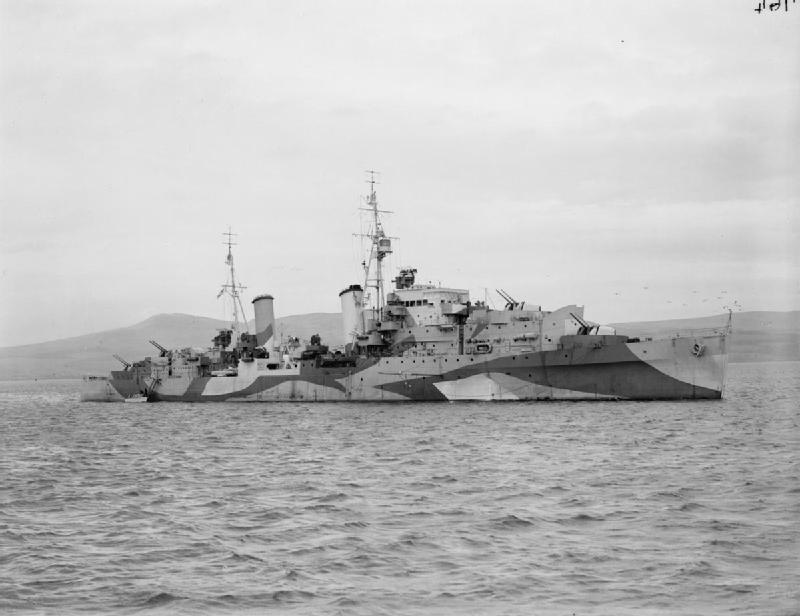
Tribal-class Destroyer (1936)
The Tribal class, or ''Afridi'' class, was a ship class, class of destroyers built for the Royal Navy, Royal Canadian Navy and Royal Australian Navy that saw service in World War II. Originally conceived during design studies for a light fleet cruiser, the Tribals evolved into fast, powerful destroyers, with greater emphasis on guns over torpedoes than previous destroyers, in response to new designs by Japan, Italy, and Germany. The Tribals were well admired by their crews and the public when they were in service due to their power, often becoming symbols of prestige while in service. As some of the Royal Navy's most modern and powerful escort ships, the Tribal class served with distinction in nearly all theatres of World War II. Only a handful of Royal Navy Tribals survived the war, all of which were subsequently scrapped from hard use, while Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth Tribals continued to serve into the Cold War, serving with distinction in the Korean War. Only one ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
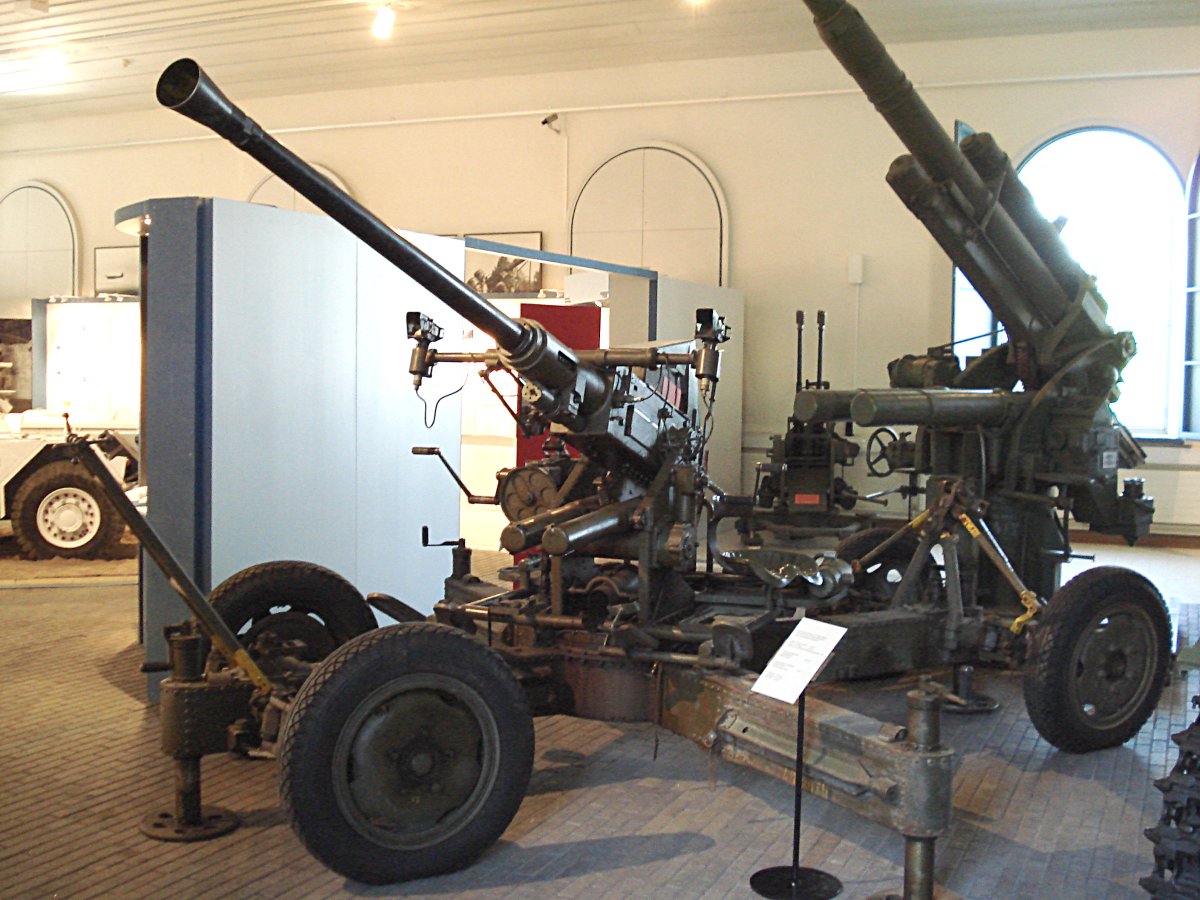
Bofors 40 Mm L/60 Gun
The Bofors 40 mm Automatic Gun L/60 (often referred to simply as the "Bofors 40 mm gun", the "Bofors gun" and the like, see name) is an anti-aircraft autocannon, designed in the 1930s by the Swedish arms manufacturer AB Bofors. The gun was designed as an intermediate anti-aircraft gun, filling the gap between fast firing close-range small calibre anti-aircraft guns and slower firing long-range high calibre anti-aircraft guns. For its time, the Bofors 40 mm L/60 was perfectly suited for this role and outperformed competing designs in the years leading up to World War II in both effectiveness and reliability. It entered the export market around 1932 and was in service with 18 countries by 1939. Throughout World War II it became one of the most popular and widespread medium-weight anti-aircraft guns. It was used by the majority of the western Allies and some Axis powers such as Nazi Germany and Hungary. In the post-war era, the Bofors 40 mm L/60 design was not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
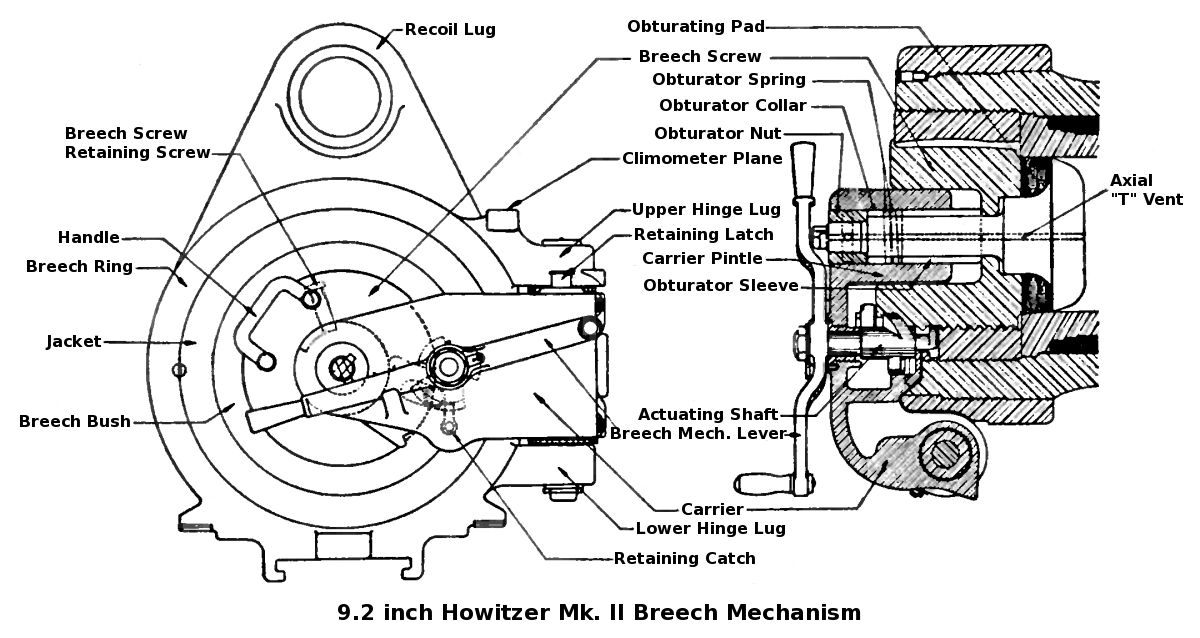
British Ordnance Terms
This article explains terms used for the British Armed Forces' Materiel, ordnance (weapons) and ammunition. The terms may have different meanings depending on their usage in another country's military. BD Between decks: applies to a naval gun mounting in which part of the rotating mass is below the deck, and part of it is above the deck. This allows for a lower profile for a gun turret, turret, meaning that the turrets need not be superfiring (i.e. they can be mounted on the same deck and not obstruct each other at high angles of elevation). BL The term BL, in its general sense, stood for breech loading, and contrasted with muzzle loading. The shell was loaded via the breech (i.e. the gunner's end of the barrel, which opened) followed by the propellant charge, and the breech mechanism was closed to seal the chamber. Breech loading, in its formal British ordnance sense, served to identify the gun as the type of Rifled breech-loader, rifled breechloading gun for which the powder c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
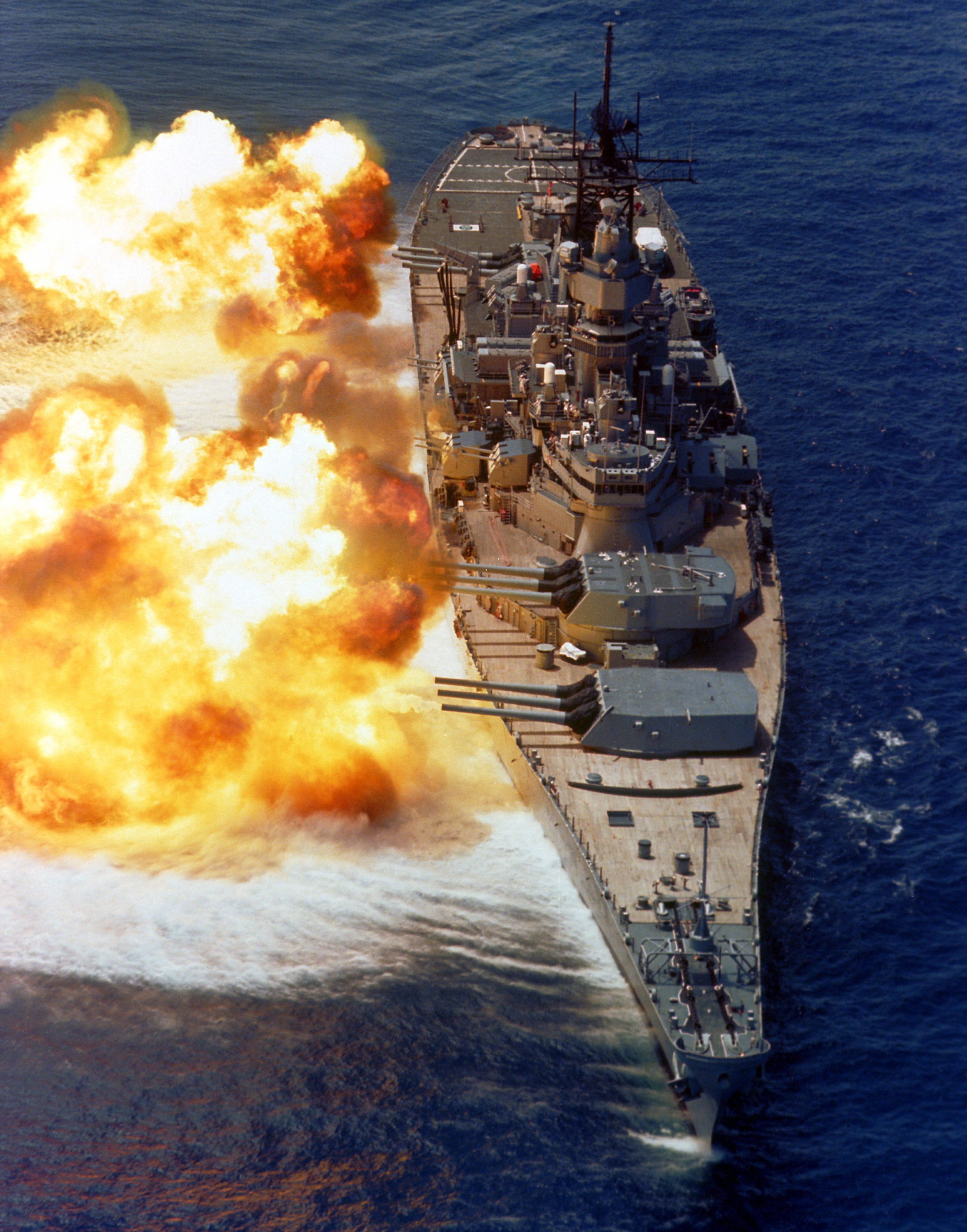
Battleship
A battleship is a large, heavily naval armour, armored warship with a main battery consisting of large naval gun, guns, designed to serve as a capital ship. From their advent in the late 1880s, battleships were among the largest and most formidable weapon systems ever built, until they were surpassed by aircraft carriers beginning in the 1940s. The modern battleship traces its origin to the sailing ship of the line, which was developed into the steam ship of the line and soon thereafter the ironclad warship. After a period of extensive experimentation in the 1870s and 1880s, ironclad design was largely standardized by the British , which are usually referred to as the first "pre-dreadnought battleships". These ships carried an armament that usually included four large guns and several medium-caliber guns that were to be used against enemy battleships, and numerous small guns for self-defense. Naval powers around the world built dozens of pre-dreadnoughts in the 1890s and early ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Cruiser
A cruiser is a type of warship. Modern cruisers are generally the largest ships in a fleet after aircraft carriers and amphibious assault ships, and can usually perform several operational roles from search-and-destroy to ocean escort to sea denial. The term "cruiser", which has been in use for several hundred years, has changed its meaning over time. During the Age of Sail, the term ''cruising'' referred to certain kinds of missions—independent scouting, commerce protection, or raiding—usually fulfilled by frigates or sloop-of-war, sloops-of-war, which functioned as the ''cruising warships'' of a fleet. In the middle of the 19th century, ''cruiser'' came to be a classification of the ships intended for cruising distant waters, for commerce raiding, and for scouting for the battle fleet. Cruisers came in a wide variety of sizes, from the medium-sized protected cruiser to large armored cruisers that were nearly as big (although not as powerful or as well-armored) as a pre- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Junkers Ju 88
The Junkers Ju 88 is a twin-engined multirole combat aircraft designed and produced by the German aircraft manufacturer Junkers Aircraft and Motor Works. It was used extensively during the Second World War by the ''Luftwaffe'' and became one of the most versatile combat aircraft of the conflict. The Ju 88 originated from a ''Reichsluftfahrtministerium'' (RLM) requirement issued in 1934 for a new multipurpose aircraft. Junkers was one of several firms to respond, producing two separate design studies that produced both the Ju 85 and Ju 88. The design work was headed by Junkers' chief designer Ernst Zindel. The Ju 88 was envisioned to function as a so-called '' Schnellbomber'' ("fast bomber") that would evade interception by enemy fighters of its era by flying at high speed. On 21 December 1936, the first prototype performed its maiden flight. The performance of the third prototype was highly favourable, resulting in the competing Henschel Hs 127 and Messerschmitt Bf 162 bein ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Romsdalsfjord
or is the ninth-longest fjord in Norway. The long fjord is located in the Romsdal district of Møre og Romsdal county. It flows through the municipalities of Molde, Haram, Vestnes, and Rauma. The deepest point in the fjord is just southwest of the town of Molde, where it is deep. The fjord is a threshold-fjord, as it is separated from the ocean by a deep shallower areas at the mouth. Several islands and skerries also shelter the wide central fjord from the Atlantic. The western inlet of the fjord is generally considered to be between the island of Dryna (in Molde Municipality) and the village of Brattvåg (in Haram Municipality). A second inlet is to the north, through the Julsundet strait, bound by the island of Otrøya to the west and Molde Municipality to the east. The fjord branches off to the minor Tresfjorden and Tomrefjorden to the south, while the main body continues an east-west bound direction. The fjord then forks into three main branches: Moldefjorden ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Sir Philip Vian
Admiral of the Fleet Sir Philip Louis Vian, & Two Bars (15 June 1894 – 27 May 1968) was a Royal Navy officer who served in both World Wars. Vian specialised in naval gunnery from the end of the First World War and received several appointments as gunnery officer. In the early 1930s, he was given command of a destroyer, , and, later, various destroyer flotillas. During this phase of his career, in early 1940, he commanded a force that forcibly released captured British merchant sailors from the German supply ship in Jøssingfjord in then-neutral Norway and, later, his flotilla took an active role in the final action of the . Much of Vian's Second World War service was in the Mediterranean, where he commanded a cruiser squadron, defended several critical convoys and led naval support at the Allied invasions of Sicily and Italy. His wartime service was completed in command of the air component of the British Pacific Fleet, with successful actions against the Japanese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
HACS
High Angle Control System (HACS) was a British anti-aircraft fire-control system employed by the Royal Navy from 1931 and used widely during World War II. HACS calculated the necessary deflection required to place an explosive shell in the location of a target flying at a known height, bearing and speed. Early history The HACS was first proposed in the 1920s and began to appear on Royal Navy (RN) ships in January 1930, when HACS I went to sea in . HACS I did not have any stabilisation or power assist for director training. HACS III which appeared in 1935, had provision for stabilisation, was hydraulically driven, featured much improved data transmission and it introduced the HACS III Table. The HACS III table (computer) had numerous improvements including raising maximum target speed to , continuous automatic fuze prediction, improved geometry in the deflection Screen, and provisions for gyro inputs to provide stabilisation of data received from the director. The HACS was a ''co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |