|
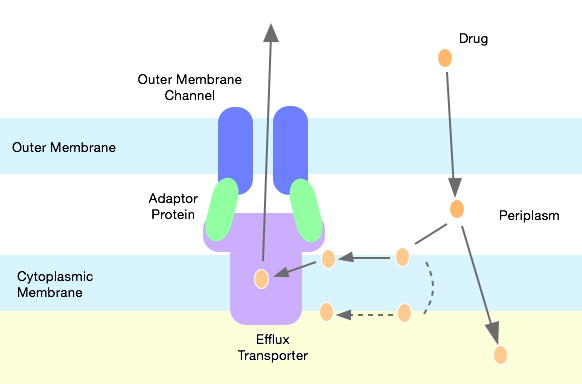
Drug Efflux
An efflux pump is an active transporter in cells that moves out unwanted material. Efflux pumps are an important component in bacteria, particularly in their ability to remove antibiotics. The efflux process can also involve the movement of heavy metals, organic pollutants, plant-produced compounds, quorum sensing signals, bacterial metabolites, and neurotransmitters. All microorganisms, with a few exceptions, have highly conserved DNA sequences in their genome that encode efflux pumps. Efflux pumps actively move substances out of a microorganism, in a process known as active efflux, which is a vital part of xenobiotic metabolism. This active efflux mechanism is responsible for various types of resistance to bacterial pathogens within bacterial species, the most concerning being antibiotic resistance, as microorganisms can have adapted efflux pumps to divert toxins out of the cytoplasm and into extracellular media. Efflux systems function via an energy-dependent mechanism (activ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amino Acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although over 500 amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the 22 α-amino acids incorporated into proteins. Only these 22 appear in the genetic code of life. Amino acids can be classified according to the locations of the core structural functional groups ( alpha- , beta- , gamma- amino acids, etc.); other categories relate to polarity, ionization, and side-chain group type ( aliphatic, acyclic, aromatic, polar, etc.). In the form of proteins, amino-acid '' residues'' form the second-largest component (water being the largest) of human muscles and other tissues. Beyond their role as residues in proteins, amino acids participate in a number of processes such as neurotransmitter transport and biosynthesis. It is thought that they played a key role in enabling life on Earth and its emergence. Amino acids are formally named by the IUPAC- IUBMB Joint Commi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Streptomyces
''Streptomyces'', from στρεπτός (''streptós''), meaning "twisted", and μύκης (''múkés''), meaning "fungus", is the largest genus of Actinomycetota, and the type genus of the family Streptomycetaceae. Over 700 species of ''Streptomyces'' bacteria have been described. As with the other Actinomycetota, streptomycetes are gram-positive, and have very large genomes with high GC content. Found predominantly in soil and decaying vegetation, most streptomycetes produce spores, and are noted for their distinct "earthy" odor that results from production of a volatile metabolite, geosmin. Different strains of the same species may colonize very diverse environments. Streptomycetes are characterised by a complex secondary metabolism. Between 5-23% (average: 12%) of the protein-coding genes of each ''Streptomyces'' species are implicated in secondary metabolism. Streptomycetes produce over two-thirds of the clinically useful antibiotics of natural origin (e.g., neomy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Escherichia Coli
''Escherichia coli'' ( )Wells, J. C. (2000) Longman Pronunciation Dictionary. Harlow ngland Pearson Education Ltd. is a gram-negative, facultative anaerobic, rod-shaped, coliform bacterium of the genus '' Escherichia'' that is commonly found in the lower intestine of warm-blooded organisms. Most ''E. coli'' strains are part of the normal microbiota of the gut, where they constitute about 0.1%, along with other facultative anaerobes. These bacteria are mostly harmless or even beneficial to humans. For example, some strains of ''E. coli'' benefit their hosts by producing vitamin K2 or by preventing the colonization of the intestine by harmful pathogenic bacteria. These mutually beneficial relationships between ''E. coli'' and humans are a type of mutualistic biological relationship—where both the humans and the ''E. coli'' are benefitting each other. ''E. coli'' is expelled into the environment within fecal matter. The bacterium grows massi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
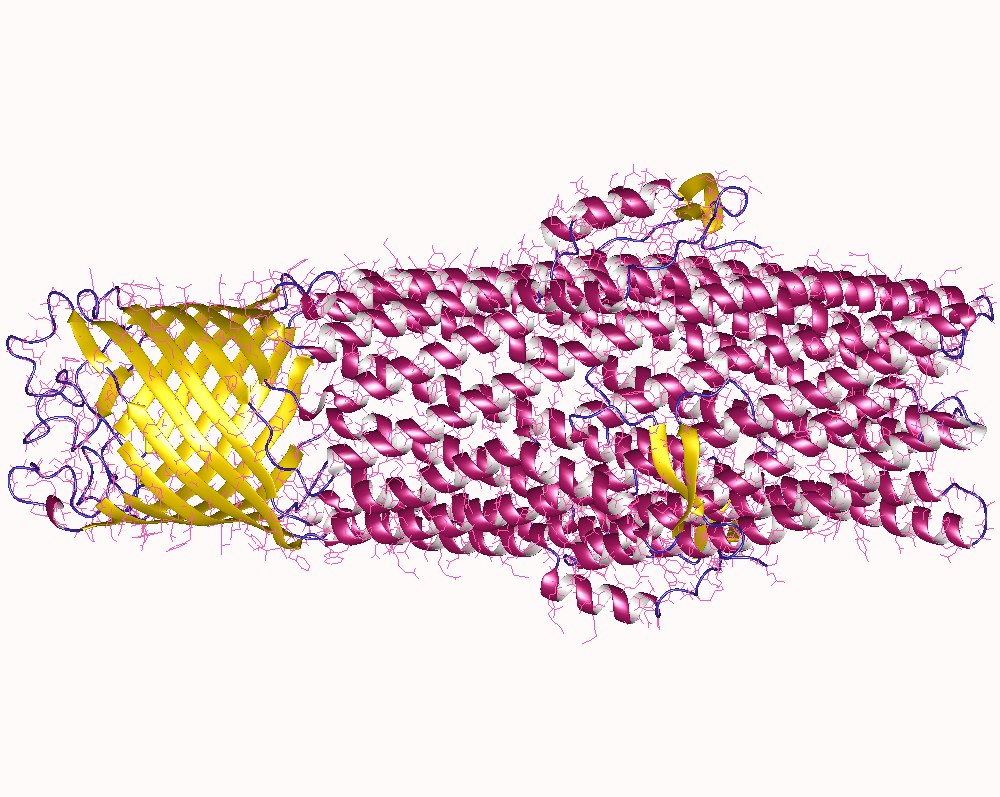
Outer Membrane Efflux Protein
The outer membrane efflux protein is a protein family member that forms trimeric (three-piece) channels allowing the export of a variety of substrates in gram-negative bacteria. Each efflux protein is composed of two repeats. The trimeric channel is composed of a 12-stranded beta-barrel that spans the outer membrane, and a long tail helical barrel that spans the periplasm. Examples include the ''Escherichia coli'' TolC outer membrane protein, which is required for proper expression of outer membrane protein genes; the Rhizobium nodulation protein; and the Pseudomonas FusA protein, which is involved in resistance to fusaric acid Fusaric acid is a picolinic acid derivative and an antibiotic (wilting agent) first isolated from the fungus '' Fusarium heterosporium''. It is typically isolated from various Fusarium species, and has been proposed for a various therapeutic appl .... References * Protein domains Protein families Outer membrane proteins {{membrane-protein ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom (taxonomy)
In biology, a kingdom is the second highest taxonomic rank, just below domain. Kingdoms are divided into smaller groups called phyla (singular phylum). Traditionally, textbooks from Canada and the United States have used a system of six kingdoms (Animalia, Plantae, Fungi, Protista, Archaea/Archaebacteria, and Bacteria or Eubacteria), while textbooks in other parts of the world, such as Bangladesh, Brazil, Greece, India, Pakistan, Spain, and the United Kingdom have used five kingdoms (Animalia, Plantae, Fungi, Protista and Monera). Some recent classifications based on modern cladistics have explicitly abandoned the term ''kingdom'', noting that some traditional kingdoms are not monophyletic, meaning that they do not consist of all the descendants of a common ancestor. The terms ''flora'' (for plants), ''fauna'' (for animals), and, in the 21st century, '' funga'' (for fungi) are also used for life present in a particular region or time. Definition and associated terms When ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gram Positive Bacteria
In bacteriology, gram-positive bacteria are bacteria that give a positive result in the Gram stain test, which is traditionally used to quickly classify bacteria into two broad categories according to their type of cell wall. The Gram stain is used by microbiologists to place bacteria into two main categories, gram-positive (+) and gram-negative (−). Gram-positive bacteria have a thick layer of peptidoglycan within the cell wall, and gram-negative bacteria have a thin layer of peptidoglycan. Gram-positive bacteria retain the crystal violet stain used in the test, resulting in a purple color when observed through an optical microscope. The thick layer of peptidoglycan in the bacterial cell wall retains the stain after it has been fixed in place by iodine. During the decolorization step, the decolorizer removes crystal violet from all other cells. Conversely, gram-negative bacteria cannot retain the violet stain after the decolorization step; alcohol used in this stage degrades ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ion Gradient
An electrochemical gradient is a gradient of electrochemical potential, usually for an ion that can move across a membrane. The gradient consists of two parts: * The chemical gradient, or difference in solute concentration across a membrane. * The electrical gradient, or difference in charge across a membrane. If there are unequal concentrations of an ion across a permeable membrane, the ion will move across the membrane from the area of higher concentration to the area of lower concentration through simple diffusion. Ions also carry an electric charge that forms an electric potential across a membrane. If there is an unequal distribution of charges across the membrane, then the difference in electric potential generates a force that drives ion diffusion until the charges are balanced on both sides of the membrane. Electrochemical gradients are essential to the operation of batteries and other electrochemical cells, photosynthesis and cellular respiration, and certain othe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proton
A proton is a stable subatomic particle, symbol , Hydron (chemistry), H+, or 1H+ with a positive electric charge of +1 ''e'' (elementary charge). Its mass is slightly less than the mass of a neutron and approximately times the mass of an electron (the proton-to-electron mass ratio). Protons and neutrons, each with a mass of approximately one Dalton (unit), dalton, are jointly referred to as ''nucleons'' (particles present in atomic nuclei). One or more protons are present in the Atomic nucleus, nucleus of every atom. They provide the attractive electrostatic central force which binds the atomic electrons. The number of protons in the nucleus is the defining property of an element, and is referred to as the atomic number (represented by the symbol ''Z''). Since each chemical element, element is identified by the number of protons in its nucleus, each element has its own atomic number, which determines the number of atomic electrons and consequently the chemical characteristi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Secondary Transporters
In cellular biology, active transport is the movement of molecules or ions across a cell membrane from a region of lower concentration to a region of higher concentration—against the concentration gradient. Active transport requires cellular energy to achieve this movement. There are two types of active transport: primary active transport that uses adenosine triphosphate (ATP), and secondary active transport that uses an electrochemical gradient. This process is in contrast to passive transport, which allows molecules or ions to move down their concentration gradient, from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration, with energy. Active transport is essential for various physiological processes, such as nutrient uptake, hormone secretion, and nig impulse transmission. For example, the sodium-potassium pump uses ATP to pump sodium ions out of the cell and potassium ions into the cell, maintaining a concentration gradient essential for cellular function. Active ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multi Antimicrobial Extrusion Protein
Multi-antimicrobial extrusion protein (MATE) also known as multidrug and toxin extrusion or multidrug and toxic compound extrusion is a family of proteins which function as drug/sodium or proton antiporters. Function The MATE proteins in bacteria, archaea and eukaryotes function as fundamental transporters of metabolic and xenobiotic organic cations. Structure These proteins are predicted to have 12 alpha helix, alpha-helical transmembrane protein, transmembrane regions, some of the animal proteins may have an additional C-terminus, C-terminal helix. The X-ray structure of the NorM was determined to 3.65 Å, revealing an outward-facing conformation with two portals open to the outer leaflet of the membrane and a unique topology of the predicted 12 transmembrane helices distinct from any other known multidrug resistance transporter. Discovery The multidrug efflux (microbiology), efflux Membrane transport protein, transporter NorM from ''Vibrio parahaemolyticus, V. para ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Resistance-Nodulation-Cell Division Superfamily (RND)
Resistance-nodulation-division (RND) family transporters are a category of bacterial efflux pumps, especially identified in Gram-negative bacteria and located in the cytoplasmic membrane, that actively transport substrates. The RND superfamily includes seven families: the heavy metal efflux (HME), the hydrophobe/amphiphile efflux-1 (gram-negative bacteria), the nodulation factor exporter family (NFE), the SecDF protein-secretion accessory protein family, the hydrophobe/amphiphile efflux-2 family, the eukaryotic sterol homeostasis family, and the hydrophobe/amphiphile efflux-3 family. These RND systems are involved in maintaining homeostasis of the cell, removal of toxic compounds, and export of virulence determinants. They have a broad substrate spectrum and can lead to the diminished activity of unrelated drug classes if over-expressed. The first reports of drug resistant bacterial infections were reported in the 1940s after the first mass production of antibiotics. Most of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |