|
Drive Mapping
Drive mapping is how MS-DOS and Microsoft Windows associate a local drive letter (A-Z) with a shared storage area to another computer (often referred as a File Server) over a network. After a drive has been mapped, a software application on a client's computer can read and write files from the shared storage area by accessing that drive, just as if that drive represented a local physical hard disk drive. Drive mapping Mapped drives are hard drives (even if located on a virtual or cloud computing system, or network drives) that are always represented by names, letter(s), or number(s) and they are often followed by additional strings of data, directory tree branches, or alternate level(s) separated by a "\" symbol. Drive mapping is used to locate directories, files or objects, and programs or apps, and is needed by end users, administrators, and various other operators or groups. Mapped drives are usually assigned a letter of the alphabet after the first few taken, such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MS-DOS
MS-DOS ( ; acronym for Microsoft Disk Operating System, also known as Microsoft DOS) is an operating system for x86-based personal computers mostly developed by Microsoft. Collectively, MS-DOS, its rebranding as IBM PC DOS, and a few operating systems attempting to be compatible with MS-DOS, are sometimes referred to as "DOS" (which is also the generic acronym for disk operating system). MS-DOS was the main operating system for IBM PC compatibles during the 1980s, from which point it was gradually superseded by operating systems offering a graphical user interface (GUI), in various generations of the graphical Microsoft Windows operating system. IBM licensed and re-released it in 1981 as PC DOS 1.0 for use in its PCs. Although MS-DOS and PC DOS were initially developed in parallel by Microsoft and IBM, the two products diverged after twelve years, in 1993, with recognizable differences in compatibility, syntax and capabilities. Beginning in 1988 with DR-DOS, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Local Area Network
A local area network (LAN) is a computer network that interconnects computers within a limited area such as a residence, campus, or building, and has its network equipment and interconnects locally managed. LANs facilitate the distribution of data and sharing network devices, such as printers. The LAN contrasts the wide area network (WAN), which not only covers a larger geographic distance, but also generally involves Leased line, leased telecommunication circuits or Internet links. An even greater contrast is the Internet, which is a system of globally connected business and personal computers. Ethernet and Wi-Fi are the two most common technologies used for local area networks; historical network technologies include ARCNET, Token Ring, and LocalTalk. Cabling Most wired network infrastructures utilize Category 5 cable, Category 5 or Category 6 cable, Category 6 twisted pair cabling with RJ45 (telecommunications), RJ45 compatible terminations. This medium provides physical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Windows Architecture
Windows is a Product lining, product line of Proprietary software, proprietary graphical user interface, graphical operating systems developed and marketed by Microsoft. It is grouped into families and subfamilies that cater to particular sectors of the computing industry – Windows (unqualified) for a consumer or corporate workstation, Windows Server for a Server (computing), server and Windows IoT for an embedded system. Windows is sold as either a consumer retail product or licensed to Original equipment manufacturer, third-party hardware manufacturers who sell products Software bundles, bundled with Windows. The first version of Windows, Windows 1.0, was released on November 20, 1985, as a graphical operating system shell for MS-DOS in response to the growing interest in graphical user interfaces (GUIs). The name "Windows" is a reference to the windowing system in GUIs. The 1990 release of Windows 3.0 catapulted its market success and led to various other product families ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Disk Formatting
Disk formatting is the process of preparing a data storage device such as a hard disk drive, solid-state drive, floppy disk, memory card or USB flash drive for initial use. In some cases, the formatting operation may also create one or more new file systems. The first part of the formatting process that performs basic medium preparation is often referred to as "low-level formatting". Partitioning is the common term for the second part of the process, dividing the device into several sub-devices and, in some cases, writing information to the device allowing an operating system to be booted from it. The third part of the process, usually termed "high-level formatting" most often refers to the process of generating a new file system. In some operating systems all or parts of these three processes can be combined or repeated at different levels and the term "format" is understood to mean an operation in which a new disk medium is fully prepared to store files. Some formatting utilit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SUBST
In computing, SUBST is a command on the DOS, IBM OS/2, Microsoft Windows and ReactOS operating systems used for substituting paths on physical and logical drives as virtual drives. Overview In MS-DOS, the SUBST command was added with the release of MS-DOS 3.1. The command is similar to floating drives, a more general concept in operating systems of Digital Research origin, including CP/M-86 2.x, Personal CP/M-86 2.x, Concurrent DOS, Multiuser DOS, System Manager 7, REAL/32, as well as DOS Plus and DR DOS (up to 6.0). DR DOS 6.0 includes an implementation of the command. The command is also available in FreeDOS and PTS-DOS. The Windows SUBST command is available in supported versions of the command line interpreter cmd.exe. In Windows NT, SUBST uses to create the disk mappings. The JOIN command is the "opposite" of SUBST, because JOIN will take a drive letter and make it appear as a directory. Some versions of MS-DOS COMMAND.COM support the undocumented internal TRUENAM ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drive Letter Assignment
In computer data storage, drive letter assignment is the process of assigning alphabetical identifiers to volumes. Unlike the concept of UNIX mount points, where volumes are named and located arbitrarily in a single hierarchical namespace, drive letter assignment allows multiple highest-level namespaces. Drive letter assignment is thus a process of using letters to name the roots of the "forest" representing the file system; each volume holds an independent "tree" (or, for non-hierarchical file systems, an independent list of files). Origin The concept of drive letters, as used today, presumably owes its origins to IBM's VM family of operating systems, dating back to CP/CMS in 1967 (and its research predecessor CP-40), by way of Digital Research's (DRI) CP/M. The concept evolved through several steps: * CP/CMS uses drive letters to identify '' minidisks'' attached to a user session. A full file reference (''pathname'' in today's parlance) consists of a ''filename'', a ''file ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount (computing)
Mounting is a process by which a computer's operating system makes Computer file, files and Directory (computing), directories on a Computer data storage, storage device (such as Hard disk drive, hard drive, CD-ROM, or network share) available for users to access via the computer's file system. In general, the process of mounting comprises the operating system acquiring access to the storage medium; recognizing, reading, and processing file system structure and metadata on it before registering them to the virtual file system (VFS) component. The location in the VFS to which the newly mounted medium was registered is called a "mount point"; when the mounting process is completed, the user can access files and directories on the medium from there. An opposite process of mounting is called unmounting, in which the operating system cuts off all user access to files and directories on the mount point, writes the remaining queue of user data to the storage device, refreshes file sys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
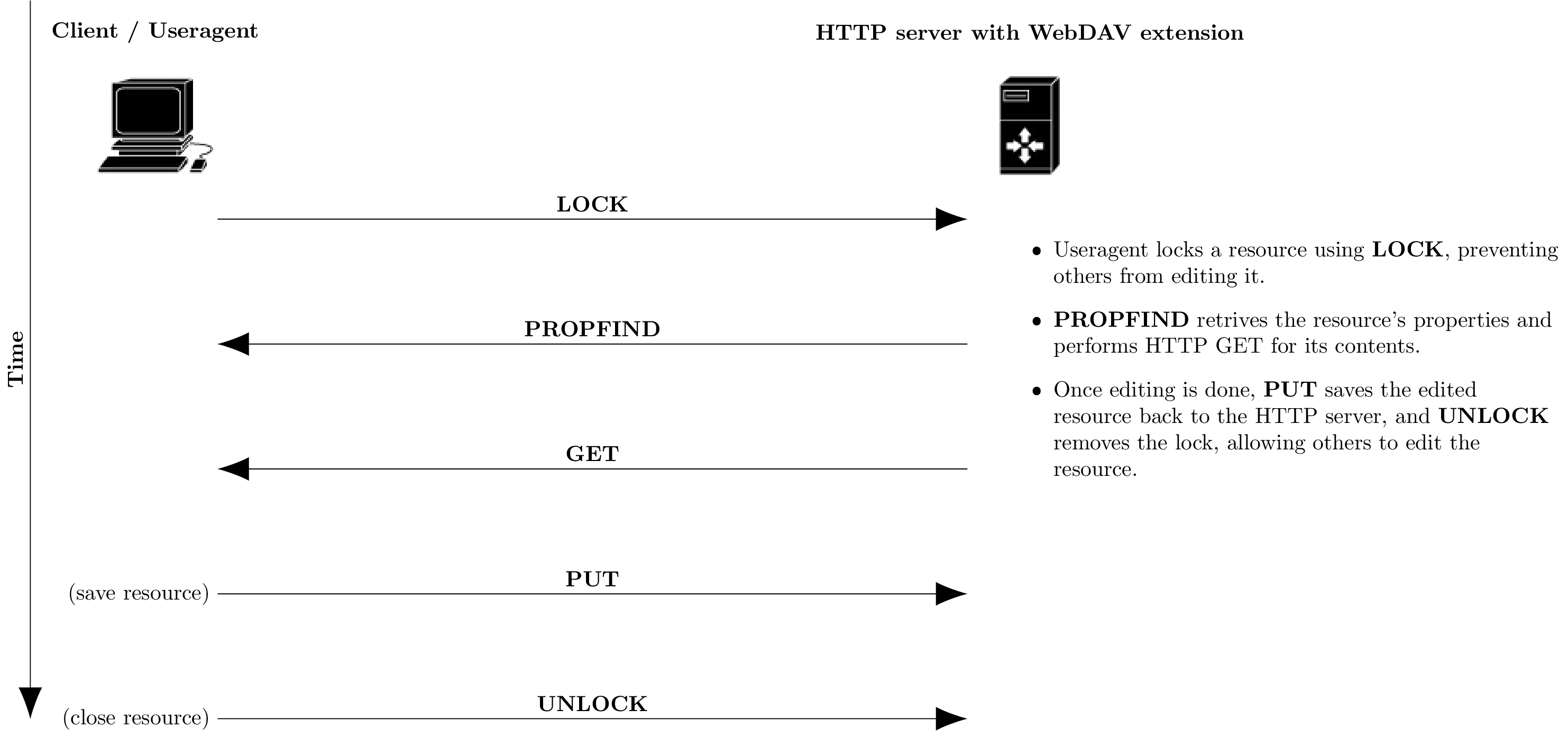
WebDAV
WebDAV (Web Distributed Authoring and Versioning) is a set of extensions to the Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP), which allows user agents to collaboratively author contents ''directly'' in an HTTP web server by providing facilities for concurrency control and namespace operations, thus allowing the Web to be viewed as a ''writeable, collaborative medium'' and not just a read-only medium. WebDAV is defined in by a working group of the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF). The WebDAV protocol provides a framework for users to create, change and move documents on a server. The most important features include the maintenance of properties about an author or modification date, namespace management, collections, and overwrite protection. Maintenance of properties includes such things as the creation, removal, and querying of file information. Namespace management deals with the ability to copy and move web pages within a server's namespace. Collections deal with the creation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linux
Linux ( ) is a family of open source Unix-like operating systems based on the Linux kernel, an kernel (operating system), operating system kernel first released on September 17, 1991, by Linus Torvalds. Linux is typically package manager, packaged as a Linux distribution (distro), which includes the kernel and supporting system software and library (computing), libraries—most of which are provided by third parties—to create a complete operating system, designed as a clone of Unix and released under the copyleft GPL license. List of Linux distributions, Thousands of Linux distributions exist, many based directly or indirectly on other distributions; popular Linux distributions include Debian, Fedora Linux, Linux Mint, Arch Linux, and Ubuntu, while commercial distributions include Red Hat Enterprise Linux, SUSE Linux Enterprise, and ChromeOS. Linux distributions are frequently used in server platforms. Many Linux distributions use the word "Linux" in their name, but the Free ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UNIX
Unix (, ; trademarked as UNIX) is a family of multitasking, multi-user computer operating systems that derive from the original AT&T Unix, whose development started in 1969 at the Bell Labs research center by Ken Thompson, Dennis Ritchie, and others. Initially intended for use inside the Bell System, AT&T licensed Unix to outside parties in the late 1970s, leading to a variety of both academic and commercial Unix variants from vendors including University of California, Berkeley ( BSD), Microsoft (Xenix), Sun Microsystems ( SunOS/ Solaris), HP/ HPE ( HP-UX), and IBM ( AIX). The early versions of Unix—which are retrospectively referred to as " Research Unix"—ran on computers such as the PDP-11 and VAX; Unix was commonly used on minicomputers and mainframes from the 1970s onwards. It distinguished itself from its predecessors as the first portable operating system: almost the entire operating system is written in the C programming language (in 1973), which allows U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Network File System
Network File System (NFS) is a distributed file system protocol originally developed by Sun Microsystems (Sun) in 1984, allowing a user on a client computer to access files over a computer network much like local storage is accessed. NFS, like many other protocols, builds on the Open Network Computing Remote Procedure Call (ONC RPC) system. NFS is an open IETF standard defined in a Request for Comments (RFC), allowing anyone to implement the protocol. Versions and variations Sun used version 1 only for in-house experimental purposes. When the development team added substantial changes to NFS version 1 and released it outside of Sun, they decided to release the new version as v2, so that version interoperation and RPC version fallback could be tested. NFSv2 Version 2 of the protocol (defined in , March 1989) originally operated only over User Datagram Protocol (UDP). Its designers meant to keep the server side stateless, with locking (for example) implement ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Server Message Block
Server Message Block (SMB) is a communication protocol used to share files, printers, serial ports, and miscellaneous communications between nodes on a network. On Microsoft Windows, the SMB implementation consists of two vaguely named Windows services: "Server" (ID: LanmanServer) and "Workstation" (ID: LanmanWorkstation). It uses NTLM or Kerberos protocols for user authentication. It also provides an authenticated inter-process communication (IPC) mechanism. SMB was originally developed in 1983 by Barry A. Feigenbaum at IBM to share access to files and printers across a network of systems running IBM's IBM PC DOS. In 1987, Microsoft and 3Com implemented SMB in LAN Manager for OS/2, at which time SMB used the NetBIOS service atop the NetBIOS Frames protocol as its underlying transport. Later, Microsoft implemented SMB in Windows NT 3.1 and has been updating it ever since, adapting it to work with newer underlying transports: TCP/IP and NetBT. SMB over QUIC was introd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |